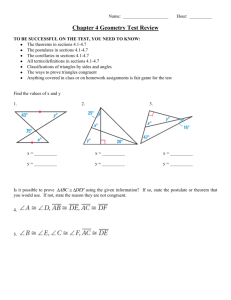
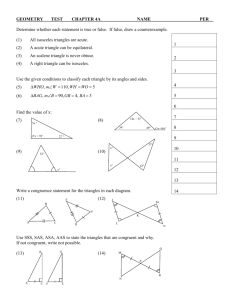
HL Proofs
advertisement

Side Angle Side Theorem By Andrew Moser Summary If two sides and the included angle of a triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. If two pairs of sides of two triangles are equal in length, and the included angles are equal in measurement, then the triangles are congruent. Examples QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Web Links http://www.mathwarehouse.com/trigonomet ry/area/side-angle-side-triangle.html http://hotmath.com/hotmath_help/topics/SA S-postulate.html http://www.jimloy.com/cindy/ass.htm Side Side Side QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Kyle Schroeder Summary You can only find SSS if the three sides in one triangle are congruent. We learned this when using Solving Triangle Proofs Rules, Properties, & Formulas The rule and property for SSS theorem is that you can only determine that you have reached SSS is that the triangle has to be congruent to the other triangle Web Links http://www.cut-theknot.org/pythagoras/SSS.shtml http://www.tutorvista.com/topic/proof-ofsss-theorem http://www.mathwarehouse.com/geometry/c ongruent_triangles/side-side-sidepostulate.php Proofs Involving CPCTC by, Nick Karach Summary: -CPCTC stands for: “Corresponding Parts of Corresponding Triangles are Congruent” This means that once you prove two triangle congruent, you know that corresponding sides and angles are congruent. Rules, Properties & Formulas First of all you must prove the Triangles congruent through a postulate such as ASA, SAS, AAS or HL. Second, once you state the two triangles are congruent, you can state a two sides are congruent. Ex. AB CD Examples Given: # BWO # MNA Statement : Re ason : # BWO # MNA HL NAM ; WOB CPCTC Web Links Main Concept and Some Examples CPCTC WikiPedia Examples Equilateral Triangle By Jake Morra Equilateral Triangles A equilateral triangle is a triangle where all the sides are equal in length. All angles opposite though sides are congruent Finding The Height To find the height add an altitude from vertexes to opposite segment If the added segment is a altitude. angle BPA and APC are 90 degrees QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. If Segment AB, BC, and CA are all 10 then Segment BP and PC are 5 2 2 2 a + 5 = 10 Now that you know all of this can solve the height by the Pythagorean Theorem Other Websites To Help You http://mathcentral.uregina.ca/QQ/database/ QQ.09.02/rosa2.html www.calcenstein.com/calc/1111_help.php www.ehow.com › Education › Math Education › Triangles Angle Bisector and Incenter -What is an angle bisector and an incenter? -Example problems -Web links What is an angle bisector and an incenter? B Incenter An angle bisector is a segment that divided an angle in half. When the three angle bisectors intersect they create a point of concurrency which is called the incenter Ex: 1- Both little angles will be the same measure mBAF = 24.41 ° mCAF = 24.41 ° A H G Incenter mABG = 33.53 ° B mGBC= 33.53 ° mHCA = 32.06 ° F C mBCH= 32.06 ° Ex: 2 Find x Equation: 13x-1= 2(6x+4) 13x-1= 12x+8 -12x 12x x-1= 8 +1 +1 X= 9 Ex:3 Incenter is ALWAYS in the middle Acute Right Obtuse A A Incenter Incenter Incenter C B C B B C Helpful Links http://www.cliffsnotes.com/study_guide/Altitudes-Medians-and-AngleBisectors.topicArticleId-18851,articleId-18787.html http://jwilson.coe.uga.edu/emt725/Prob.2.35.1/Problem.2.35.1.html http://mathworld.wolfram.com/AngleBisector.html Angle Side Angle Theorem By: Daulton Moro AAS Theorem Summary: The AAS theorem is one of the theorems that is used to prove triangles congruent. The AAS theorem is when two angles and one non-included side are congruent. Sample Problems For the first picture you would mark lines BC and CE congruent and angles A and D would be congruent. After mark the vertical angles congruent the you have congruence by AAS. The second picture shows AAS because there are two angles that are congruent and one side that is non-included. The third picture is self explanatory and is proven by using AAS. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Quick Time™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Helpful Websites www.mathwarehouse.com www.library.thinkquest.org www.phschool.com What exactly is an HL proof? By Dylan Sen The hypotenuse leg theorem, or HL, is the congruence theorem used to prove only right triangles congruent. Also The theorem states that any two right triangles that have a congruent hypotenuse and a corresponding, congruent leg are congruent triangles.. The goal of today’s lesson is to prove right triangles congruent using the HL theorem Rules and Formulas As seen in the previous slide, if the hypotenuse and leg of one triangle are congruent to the hypotenuse and leg of the other, the triangles are congruent. The most important formula to remember is: uuuuuuuuur uuuuuuuuuur if BC EF, and AC DF,thenVABC VDEF Given: uuur suur AC ZY Examples QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. ACB ZYX 90 suur suur AB XY ABC VXYZ Prove: Reason uStatement uur suur -Given AC ZY(leg) suur suur (hypotenuse) - Given AB XY ABC and XYZ -They both have a right angle. are right triangles ABC VXYZ - Through the HL theorem. Since the hypotenuse and the leg are congruent, that means the triangles are congruent uuur uuur Given- AB DE uuur uuur BC EF ACB and DFE 90 Prove: ABC VDEF uuur uuur AB DE (leg) uuur uuur BC EF (hypotenuse) ABC and DEF are right triangles QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Given Given They have a right angle ABC VDEFBecause the hypotenuse and corresponding leg are congruent, the triangles are congruent Given: uuuuuuuuur BC EFr uuuuuuuuu AC DF ABC and DEF 90 Prove QuickTime™ and a d eco mpres sor are nee ded to s ee this picture. ABC VDEF Statement uuuuuuuuur Reason BC EF r (leg) Given uuuuuuuuu AC DF (hypotenuse) Given ABC and DEF They have a right angle are right triangles Because the hypotenuse and corresponding leg are congruent, the ABC VDEF triangles are congruent Useful Websites to help you further understand HL: http://delta.classwell.com/ebooks/navigateBook.clg?sectionType=unit&na vigation=1&prevNext=0&curSeq=235&curDispPage=239&xpqData=%2 Fcontent%5B%40id%3D%27mcd_ma_geo_lsn_0395937779_p236.xml% 27%5D - This is the textbook definition. It will show examples and a step by step method of figuring out how to use HL. http://www.mathwarehouse.com/geometry/congruent_triangles/hypotenus e-leg-theorem.php - Much like the textbook, this website shows great examples and will help clarify anything you have trouble with. http://www.onlinemathlearning.com/hypotenuse-leg.html - this example shows more guided examples, which will further help you understand the HL Theorem Medians and Centroids Summary: A median is a segment that connects the vertex of a triangle to the midpoint of the opposite side. The point of concurrency (intersection) of the medians is called the centroid. Goals: The goals of this presentation are to: 1) Review Medians and Centroids 2) Review Sample Problems Medians and Centroids A median is a segment that connects the vertex of a triangle to the midpoint of the opposite side The point of concurrency (intersection) of the medians is called the centroid The distance from the vertex to the centroid is 2/3 of the total distance of the median No matter what type of triangle (right, acute, obtuse), the centroid is ALWAYS inside the triangle Sample Problems 1) Always, Sometimes, Never: The centroid ________________ lies within the triangle. 2) Find x: A B | 2x+5 | D 3x-10 C 3) Fill In The Blank: A triangle has ____________ medians. Helpful Links http://www.mathopenref.com/trianglemedians.html http://mathworld.wolfram.com/TriangleMedian.html http://www.analyzemath.com/Geometry/MediansTriangle/ MediansTriangle.html http://www.cut-the-knot.org/triangle/medians.shtml