Lecture 5 - International University of Sarajevo
advertisement

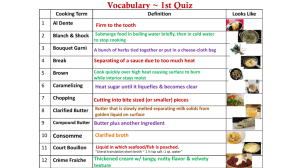
LOGO Lecture 5 : Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Organic Chemistry – FALL 2015 Course lecturer : Jasmin Šutković 11 November 2015 Contents International University of Sarajevo Book chapter 13 13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes 13.2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes 13.3 Cis–Trans Isomers 13.4 Interesting Alkenes in Food and Medicine 13.5 FOCUS ON HEALTH & MEDICINE: Oral Contraceptives 13.6 Reactions of Alkenes 13.7 FOCUS ON HEALTH & MEDICINE: Margarine or Butter? 13.8 Polymers—The Fabric of Modern Society 13.9 Aromatic Compounds 13.10 Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives 13.11 FOCUS ON HEALTH & MEDICINE: Aromatic Drugs, Sunscreens, and Carcinogens 13.12 FOCUS ON HEALTH & MEDICINE: Phenols as Antioxidants Introduction In organic chemistry, a saturated compound is a chemical compound that has a chain of carbon atoms linked together by single bonds and has hydrogen atoms filling all of the other bonding orbitals of the carbon atoms. Alkanes are an example of saturated compounds. An unsaturated compound is a chemical compound that contains carbon-carbon double bonds or triple bonds, such as those found in alkenes or alkynes, respectively. Alkenes Ethylene is a plant hormone, regulating growth and fruit rippening. Common fetures ? CIS – TRANS isomers Chapter 12 covers isomers .... In allkenes and alkynes we face the same fenomena... Stereo- Isomers 2 butane can have two arrangements around the atom ! Naming Interesting alkenes in food and medicine Lycopene – antioxidant – preventing unwanted oxidation reaction to occure Decreses risk of heart disease Found in many food – tomato products Cancer drugs Tamoxifen- a potential anticancer drug – containing double bonds with additional functional groups Requires female hormone – estrogen to react- used for Breast cancer treatment Reaction of Alkenes Addition reaction Hydrogenation Addition of hydrogen grouphydgrogenation Halogenation Addition of halogen elements- halogenation HYDROHALOGENATION ADDITION OF HYDROGEN HALIDES Hydrohalogenation is the addition of HX (X = Cl or Br) to an alkene. Hydration Addition of water (H2O) FOCUS ON HEALTH & MEDICINE MARGARINE OR BUTTER? One addition reaction of alkenes, hydrogenation, is especially important in the food industry. It lies at the heart of the debate over which product, butter or margarine, is better for the consumer. Butter – long C chain – single bonds = solid at room temperature, made from milk- saturated hydrocarbon. Margarine – synthetic- mimics the taste of butter- composed mainly of partially hydrogenated vegetable oils formed by adding hydrogen to the double bonds in the carbon chain derived from unsaturated fatty acids. Facts .... ?????? Soem say that Margarine usually tops butter when it comes to heart health. Margarine is made from vegetable oils, so it contains no cholesterol. Margarine is also higher in "good" fats — polyunsaturated and monounsaturated — than butter is. These types of fats help reduce low-density lipoprotein (LDL), or "bad," cholesterol !!! But...Some Margarines may contain trans fat ...not healthy- supporting the increase of cholesterol in blood!!! Butter, on the other hand, is made from animal fat and so in its structure contains cholesterol and high levels of saturated fat. Why Butter ....? There are a lot of fat soluble vitamins in butter (Vitamin A,E and K) Butter Contains a Lot of Healthy Saturated Fats Butter Lowers Heart Attack Risk Compared to Margarine (Margarine significantly increased the risk of cardiovascular disease, while butter had no effect. - http://wholehealthsource.blogspot.com/2009/10/butter-vsmargarine-showdown.html) Butter is a Good Source of The Fatty Acid Butyrate The 4-carbon fatty acid butyrate is created by bacteria in the colon when they are exposed to dietary fiber.This may be the main reason fiber has health benefits for humans.) Butter is Rich in Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) (This fatty acid has powerful effects on metabolism and is actually sold commercially as a weight loss supplement) Butter is Associated With a Lower Risk of Obesity Butter is Delicious Butter or Margarine ? Which should you choose—butter or margarine—and if it’s margarine, which of the many varieties is best for you? Margarine can be hard or soft. It can be made from olive oil, corn oil, safflower oil, or even yogurt. One fact remains clear to nutritionists. It is best to limit your intake of both butter (high in saturated fat) and margarine (high in trans fat). Important The saturated fatty acids increase the levels of bad cholesterol (LDL) and clog the arteries – heart or brain stroke !!! STOP---It was never really proven that it caused any harm, but dissproven in many recent studies ! http://wholehealthsource.blogspot.com/200 9/10/butter-vs-margarine-showdown.html Unsaturated fatty acids increase the levels of good cholesterol (HDL) by taking the LDL to the liver to be broken down and removed from the body. Too much saturated fat can increase the amount of cholesterol in the blood, which can increase the risk of developing coronary heart disease. POLYMERS—THE FABRIC OF MODERN SOCIETY Polymers are large molecules made up of repeating units of smaller molecules—called monomers—covalently bonded together. Polymers include the naturally occurring proteins that compose hair, tendons, and fingernails. They also include such industrially important plastics as polyethylene, poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC), and polystyrene. Since 1976, the U.S. production of synthetic polymers has exceeded its steel production. Soft drink bottles, plastic bags, food wrap, compact discs, Teflon, and Styrofoam are all made of synthetic polymers. Polymerisation Aromatic compounds Aromatic compounds were originally named because many simple compounds in this family have characteristic smell. Today, the word aromatic refers to compounds that contain a benzene ring, or rings that react in a similar fashion to benzene. Benzene, the simplest and most widely known aromatic compound, contains a six-membered ring and three double bonds. Since each carbon of the ring is also bonded to a hydrogen atom, the molecular formula for benzene is C6H6. Each carbon is surrounded by three groups, making it trigonal planar. Thus, benzene is a planar molecule, and all bond angles are 120°. Nomenclature To name a benzene ring with one substituent, name the substituent and add the word benzene. Carbon substituents are named as alkyl groups. When a halogen is a substituent, name the halogen by changing the -ine ending of the name of the halogen to the suffi x -o; for example, chlorine → chloro. Suncreens Focus on health A wide variety of phenols, compounds that contain a hydroxyl group bonded to a benzene ring, occur in nature. Vanillin from the vanilla bean and eugenol from cloves are both phenols. Curcumin is a yellow pigment isolated from turmeric, a tropical perennial in the ginger family and a principal ingredient in curry powder. Curcumin has long been used as an anti-infl ammatory agent in traditional eastern medicine. Nuts Nuts – rich in antioxidants , like phenols Reminder- Antioxidant! An antioxidant is a molecule that inhibits the oxidation of other molecules. Oxidation reactions can produce free radicals. In turn, these radicals can start chain reactions. When the chain reaction occurs in a cell, it can cause damage or death to the cell. Antioxidance stops these reactions ! Readings Book Chapter 13