Farm Management

Farm Management
Chapter 8
Economic Principles
Choosing Input and Output Combinations
Chapter Outline
• Input Combinations
• Enterprise Combinations farm management chapter 8
2
Chapter Objectives
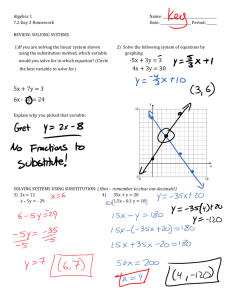
1. To explain the use of substitution in economics and decision making
2. To demonstrate how to compute a substitution ratio and a price ratio for two inputs
3. To use the input substitution and price ratios to find the least-cost combination of two inputs
4. To describe the characteristics of competitive, supplementary, and complementary enterprises
5. To show the use of the output substitution and price ratios to find the profit-maximizing combination of two enterprises farm management chapter 8
3
Input Combinations
Most products require two or more inputs, and the manager may choose the input combination or ratio to use.
The economic question is whether one input can be substituted for another to reduce the cost.
farm management chapter 8
4
Types of Input Substitution
• Constant rate (perfect substitution)
• Decreasing rate
• No substitution farm management chapter 8
5
Figure 8-1
Three possible types of substitution farm management chapter 8
6
Input Substitution Ratio
Input substitution ratio = amount of input replaced amount of input added farm management chapter 8
7
farm management chapter 8
Input Price Ratio
Input price ratio = price of input being added price of input being replaced
8
Decision Rule
input substitution ratio = input price ratio
If they cannot be exactly equal because of the choices available in the table, get as close as possible without letting the price ratio exceed the substitution ratio.
farm management chapter 8
9
Feed ration
D
E
F
G
A
B
C
Table 8-1
Selecting a Least-Cost Feed Ration
Input Input
Grain Hay Substitution Price
(lbs) (lbs) Ratio Ratio
825
900
975
1050
1125
1200
1275
1350
1130
935
770
625
525
445
2.93
2.60
2.20
1.93
1.33
1.07
1.47
1.47
1.47
1.47
1.47
1.47
farm management chapter 8 grain at 4.4
¢ and hay at 3.0¢
10
With Different Types of Substitution
• With a constant rate of substitution, the least-cost combination will be all of one input and none of the other (unless the price ratio is exactly equal to the constant rate of substitution).
• With a decreasing rate of substitution, the least-cost combination will usually include some of each input.
farm management chapter 8
11
Enterprise Combinations
Another decision that must be made is the combination of enterprises to produce to maximize profits. If one or more inputs is limited, there is an upper limit on how much can be produced.
farm management chapter 8
12
Enterprise Relationships
The first step in determining the profit-maximizing combination of enterprises is to determine the physical relationship among the enterprises. farm management chapter 8
13
Types of Relationships
• Competitive : output of one enterprise cannot be increased unless output of the other decreases
• Supplementary : more output from one enterprise can be added without a change in the level of the other enterprise
• Complementary : as output of one enterprise increases, output of the other increases also farm management chapter 8
14
Competitive Enterprises
Competitive enterprises may have constant substitution or increasing substitution. farm management chapter 8
15
farm management chapter 8
Figure 8-2
Production Possibility Curves for Competitive Enterprises
16
Figure 8-3
Supplementary & complementary enterprise relationships farm management chapter 8
17
Output Substitution Ratio
Output Substitution Ratio = quantity of output lost quantity of output gained farm management chapter 8
18
Output Price Ratio
Output Price Ratio = price of output gained price of output lost farm management chapter 8
19
Decision Rule
output substitution ratio = output price ratio
If no available combination makes these exactly equal, get as close as possible without letting the price ratio drop below the substitution ratio.
farm management chapter 8
20
Table 8-2
Profit-Maximizing Enterprise Combination
Output Output
Combination Corn Wheat substitution price number (bu) (bu) ratio ratio
1
4
5
2
3
6
7
0
2,000 5,600
4,000 5,000
6,000 4,100
8,000 3,000
10,000 1,700
12,000
6,000
0
0.20
0.30
0.45
0.55
0.65
0.85
0.70
0.70
0.70
0.70
0.70
0.70
farm management chapter 8 corn at $2.80/bu, wheat at $4.00/bu
21
Summary
This chapter emphasizes the use of substitution principles to decide how and what to produce. To decide how to produce, the manager finds the least-cost combination of inputs.
To decide what to produce, the manager finds the profit-maximizing combination of enterprises.
farm management chapter 8
22