Aubry Parker NY 2010 - University of Nebraska Medical Center
advertisement

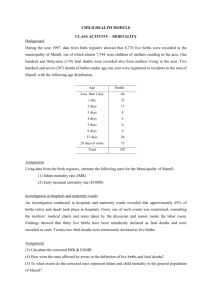
Revealing Disparities in Pregnancy Outcomes Using PPOR and FIMMRR Richard H. Aubry, MD, MPH, Martha Wojtowycz, PhD, Michelle Bode, MD, MPH, Pamela Parker, BA, Kristen Luke-Houseman, RN, BA Center for Maternal and Child Health State University of New York Upstate Medical University Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Supported by a grant from the Community Health Foundation of Western and Central New York. The Community Health Foundation is a non-profit private foundation with a mission to improve the health and health care of the people of Western and Central New York. February 2010 Objective To examine the relationship of poor socioeconomic condition, as reflected by Medicaid status, to poor outcomes of pregnancy. The Central New York Region consists of a 13 county area spanning from St. Lawrence County in the North to Broome and Tioga counties in the South and includes 21 birth hospitals. Statewide Perinatal Data System (SPDS) Population-based birth registry that captures information on all live births in New York State. It consists of the New York State Electronic Birth Certificate (EBC) and additional voluntary questions, e.g., such as the content of prenatal care, intentions of pregnancy, and perinatal depression, that are expected to be used for quality improvement purposes. The SPDS contains data on: maternal demographics; obstetrical history; prenatal care; labor and delivery information; and birth outcomes. SPDS: Pay Source Coding Medicaid – select this choice if the mother’s care was paid for by Medicaid, PCAP, MOMS, Child Health Plus A, Medicaid Managed Care, or Family Health Plus (39.8%) Private Insurance – select this item if the mother’s care was paid for by private insurance including indemnity insurance and/or managed care insurance (51.2%) Self-pay – select this item if the mother had no health insurance (1.1%) Indian Health Service (0.1%) CHAMPUS/TRICARE (Military and dependents) (5.0%) Other government (e.g. Child Health Plus B, Veteran’s Administration) (1.0%) Other (1.8%) Unknown (0.1%) Medicaid group also applies to Medicaid as secondary payor. (5.5%) Fetal-Infant Mortality/Morbidity Review/Registry (FIMMRR) Clinically oriented, community based registry to capture detailed data on mortalities/ morbidities for the 21 birth hospitals in the Central New York Region. By evaluating data from chart reviews of all fetal and infant mortalities (≥ 300 grams) as well as major morbidities, patterns have been identified which have informed recommendations for improvements (both social and medical). FIMMRR: Maternal Risk Factors ____ Major pre-pregnancy medical problems: ________________ ____ Poor OB History: ____ History of infertility ____ 2 Prior losses before 20 weeks ____ Prior loss after 20 weeks ____ History of preterm delivery (<37 Wks) ____ History of previous SGA/IUGR birth ____ Poor nutrition, BMI______ (circle) Obese, underweight ____ Poor Care Seeker (circle) Second Trimester, Third Trimester, No Prenatal Care ____ Poor compliance with prenatal visits (missed >2) ____ Substance abuse (circle) Tobacco, alcohol, marijuana, prescription drugs, other ____ Poor social setting (in present pregnancy): ____ < 12th Grade education completed and no GED ____ Partner uninvolved ____ History of parenting problems ____ Other ____ Transportation problems ____ Occupational problems ____ Family planning problems ____ Economic issues: ____ Unemployed/ partner unemployed ____ Medicaid Insurance ____ Needs public assistance (housing, healthcare, etc.) ____ WIC referral ____ Other ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ Adolescent pregnancy (≤ 16 y.o.) Advanced maternal age (≥ 35 y.o.) Housing problems Mental illness (past or present) Maternal stress: Emotional stress (at work or home) ____ Physical stress (at work or home) ____ Loss of partner (circle) Divorce, Separation, Death, Military Deployment, Other ____ Death of family member ____ Pt or partner incarcerated/Legal problems ____ Other ____ Family violence ____ Cultural problems: ____ Recent immigrant (Non-Western origin) ____ Language barrier (written or verbal) ____ Cultural/Religious belief system limits or prohibits medical interventions ____ Other ____ Less than 6 months since last birth ____ Current pregnancy result of Assisted Reproductive Technology ____ Other FIMMRR: Causes of Fetal Death / Prenatal/Intrapartal Factors Contributing to Infant Death _____ Abruptio Placenta/Placental Infarct _____ Antiphospholipid/SLE Syndrome _____ Blood Factor Sensitization _____ Chorioamnionitis (bacterial) _____ Chronic hypertension/Pre-eclampsia _____ Cocaine Abuse _____ Diabetes: Class ___, Type ___ _____ Fetal Anomaly/Chromosomal Abnormality _____ Feto-Maternal Hemorrhage _____ Perinatal TORCH Infection __________ _____ Intrapartal asphyxia _____ Intrauterine Growth Restriction _____ Maternal Trauma – Type ____________ _____ Non-Immune Hydrops _____ Termination of Pregnancy, Indication__________________ _____ Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome _____ Other ________________ FIMMRR: Causes of Infant Death Circle single dominant cause, check all others noted: _____Congenital Anomaly/Chromosomal Abnormality _____Metabolic Disorder _____Sepsis – Bacterial _____Perinatal Viral Infection _____Perinatal asphyxia _____Hyaline Membrane Disease _____Blood Factor Sensitization _____CNS hemorrhage _____SIDS _____Trauma – accident _____Termination of Pregnancy, Indication _____Overwhelming Immaturity _____Unexplained _____Physical Abuse/Neglect _____Other _____________________ If SIDS, check-off appropriate items: _____Co-sleeping _____ Smoking Household _____ Substance Abuse in Household _____ Use of Any Impairing Substance _____ Unsafe Sleep Environment _____ Exclusive Breastfeeding _____ Any Breastfeeding _____Unsafe Sleep Environment _____Smoking Household _____Substance Abuse in Household _____Prone Sleeping _____Other _______________ FIMMRR: Causes of Death-ICD10 _____Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities _____Disorders related to short gestation, low birth weight, not elsewhere classified _____Sudden infant death syndrome _____Newborn affected by maternal complications of pregnancy _____Newborn affected by complications of placenta, cord and membranes _____Accidents (unintentional injuries) _____Respiratory distress of newborn _____Bacterial sepsis of newborn _____Neonatal hemorrhage _____Intrauterine hypoxia and birth asphyxia _____All other causes Data Notes Statewide Perinatal Data System (SPDS) primary source for population characteristics secondary source for identification of neonatal and post neonatal deaths Fetal Infant Morbidity/Mortality Review/Registry (FIMMRR) only source for detailed data on fetal deaths primary source for detailed data on neonatal and post neonatal deaths Population Characteristics Central New York Region 2006-2007 ≥ 300 grams Total Non-Medicaid Insured Medicaid Insured Live Births + Fetal Deaths 38962 21277 17685 Live Births 38739 21166 17573 Maternal Age (<17 y) 1.2% 0.3% 2.2% < .001 Maternal Race (non-white) 14.7% 9.4% 21.0% < .001 Maternal Education (< 12 y) 16.0% 4.3% 30.2% < .001 Marital Status (not married) 42.5% 17.8% 72.2% <.001 p value Population Characteristics Central New York Region 2006-2007 Non-Medicaid Medicaid p value Insured Insured ≥ 300 grams Total Live Births + Fetal Deaths 38962 21277 17685 Live Births 38739 21166 17573 Early Prenatal Care 75.3% 84.4% 64.3% < .001 Adequate Prenatal Care 82.5% 88.4% 75.4% < .001 Smoking During Pregnancy 21.8% 10.3% 35.6% < .001 Illegal Drug Use 2.1% 0.5% 4.1% < .001 Obese (prepregnancy BMI>30) 27.1% 25.8% 28.7% < .001 Breastfeeding 67.6% 76.8% 56.6% < .001 Birth Outcomes Despite increased risk factors for the Medicaid insured women, most birth outcomes in the Central New York Region are not significantly different between Medicaid and Non-Medicaid insured women. Gestational Age Central New York Region 2006-2007 Non-Medicaid Medicaid Insured Insured ≥ 300 grams Total Live Births + Fetal Deaths 38962 21277 17685 Live Births 38739 21166 17573 Preterm 9.7% 9.8% 9.5% NS <24 weeks 0.2% 0.2% 0.2% NS 24-27 weeks 0.5% 0.4% 0.5% NS 28-31 weeks 1.0% 1.0% 0.9% NS 32-36 weeks 8.0% 8.1% 7.9% NS 37+ weeks 90.3% 90.2% 90.4% NS p value Birthweight/Intrauterine Growth Central New York Region 2006-2007 ≥ 300 grams Total Non-Medicaid Insured Medicaid Insured Live Births + Fetal Deaths 38962 21277 17685 Live Births 38739 21166 17573 LBW (<2500 grams) 7.7% 7.3% 8.2% < .001 VLBW (<1500 grams) 1.4% 1.5% 1.4% NS ELBW (< 1000 grams) 0.6% 0.7% 0.7% NS Small for Gestational Age 10.6% 7.0% 13.4% < .001 Large for Gestational Age 9.1% 10.8% 8.2% < .001 p value Morbidity Rates of LBW and especially Small for Gestational Age are significantly higher in Medicaid Insured births. Mortality Using the Fetal-Infant Morbidity/Mortality Review/Registry (FIMMRR), we also explored the Fetal/Infant death rates among Medicaid and Non-Medicaid insured women. Standard Calculation of Death Rates (all ≥ 300 grams) Overall number of total deaths/total live births + fetal deaths Fetal number of intrauterine deaths/total live births + fetal deaths Neonatal number of deaths ≤ 28 days of life/total live births Post-Neonatal number of deaths 29 -365 days of life/total live births Infant Neonatal + Post-Neonatal Central New York Region 2006-2007 Total Live Births + Fetal Deaths = 38962 14 * Total Non-Medicaid Insured Medicaid Insured rate/1000 12 10 * 8 6 4 * 2 0 Overall Fetal Neonatal PostNeonatal * p< .001 Non-Medicaid Insured vs Medicaid Insured Infant Central New York Region 2006-2007 Total Live Births + Fetal Deaths = 38962 Overall Fetal Neonatal Post Neonatal Infant Total 11.4 5.7 4.3 1.4 5.7 Non-Medicaid 9.4 5.2 3.7 0.5 4.2 Medicaid 13.7 6.3 5.0 2.5 7.5 ≥ 300 grams Findings The significant difference in mortality is concentrated within the Infant Deaths, most strikingly the PostNeonatal Deaths. The lack of a significant difference in mortality for both Fetal and Neonatal Deaths, suggests a potential protective effect by Medicaid. Further analysis, using the Perinatal Periods of Risk approach, provided a different prospective. Total Central New York Region 2006-2007 Live Births + Fetal Deaths = 38962 Overall Fetal-Infant Mortality Rate 11.3 per 1, 000 Live Births & Fetal Deaths Age at Death Fetal Death Post- neonatal Birthweight Maternal Health/ Prematurity 6.9 300-1499 g 1500+ g Neonatal Maternal Care Newborn Care Infant Health 1.9 1.4 1.1 Non-Medicaid Insured Central New York Region 2006-2007 Live Births + Fetal Deaths = 21277 Overall Fetal-Infant Mortality Rate 9.4 per 1, 000 Live Births & Fetal Deaths Age at Death Fetal Death Post- neonatal Birthweight Maternal Health/ Prematurity 6.1 300-1499 g 1500+ g Neonatal Maternal Care Newborn Care Infant Health 2.0 0.9 0.4 Medicaid Insured Central New York Region 2006-2007 Live Births + Fetal Deaths = 17685 Overall Fetal-Infant Mortality Rate 13.7 per 1, 000 Live Births & Fetal Deaths Age at Death Fetal Death Post- neonatal Birthweight Maternal Health/ Prematurity 8.0 300-1499 g 1500+ g Neonatal Maternal Care Newborn Care Infant Health 1.8 1.9 2.0 Perinatal Periods of Risk (PPOR) Central New York Region 2006-2007 Non-Medicaid Medicaid Insured Insured ≥ 300 grams Total Live Births + Fetal Deaths 38962 21277 17685 Live Births 38739 21166 17573 Overall Fetal-Infant Mortality Rate 11.3 9.4 13.7 S Maternal Health/Prematurity 6.9 6.1 8.0 S Maternal Care 1.9 2.0 1.8 NS Newborn Care 1.4 0.9 1.9 NS Infant Health 1.1 0.4 2.0 S sig Perinatal Periods of Risk (PPOR) Central New York Region 2006-2007 Reference Non-Reference sig Group Group ≥ 300 grams Total Live Births + Fetal Deaths 38962 26806 12156 Live Births 38739 26667 12072 Overall Fetal-Infant Mortality Rate 11.3 9.6 15.2 S Maternal Health/Prematurity 6.9 5.9 9.3 S Maternal Care 1.9 1.8 2.1 NS Newborn Care 1.4 1.2 1.7 NS Infant Health 1.1 0.7 2.2 S Perinatal Periods of Risk (PPOR) Central New York Region 2006-2007 Non-Medicaid Medicaid Reference Insured Insured Group ≥ 300 grams Total Live Births + Fetal Deaths 38962 21277 17685 26806 Live Births 38739 21166 17573 26667 Overall Fetal-Infant Mortality Rate 11.3 9.4 13.7 9.6 Maternal Health/Prematurity 6.9 6.1 8.0 5.9 Maternal Care 1.9 2.0 1.8 1.8 Newborn Care 1.4 0.9 1.9 1.2 Infant Health 1.1 0.4 2.0 0.7 Perinatal Periods of Risk (PPOR) Central New York Region 2006-2007 Excess Mortality Rates in comparison with Reference Group Total Non-Medicaid Insured Medicaid Insured Overall Fetal-Infant Mortality Rate 1.70 -0.20 4.1 Maternal Health/Prematurity 1.00 0.20 2.10 Maternal Care 0.10 0.20 0.00 Newborn Care 0.20 -0.30 0.70 Infant Health 0.40 -0.30 1.30 ≥ 300 grams Perinatal Periods of Risk (PPOR) Central New York Region 2006-2007 Excess Mortality Numbers in comparison with Reference Group Total Non-Medicaid Insured Medicaid Insured Overall Fetal-Infant Mortality Rate 66 -4 73 Maternal Health/Prematurity 39 4 37 Maternal Care 4 4 0 Newborn Care 8 -6 12 Infant Health 16 -6 23 ≥ 300 grams Perinatal Periods of Risk (PPOR) Central New York Region 2006-2007 Comparison to Reference Group supports our previous Findings. It is also useful to examine the distribution of various causes of death in each PPOR category. Fetal-Infant Morbidity/Mortality Review & Registry Central New York Region 2006-2007 Dominant Cause of Death: rate/1000 live births + fetal deaths ≥ 300 grams Abruptio/Placental Infarct Other Placental Problems Cord Accident/Prolapse Congenital Anomaly/ Chromosomal Abnormality Prematurity Overwhelming Immaturity Other Sepsis SIDS/SUID Trauma Unexplained Maternal Health/Prematurity Maternal Care Non-Medicaid 6.1 0.66 0.47 0.29 1.34 Medicaid 8.0 1.41 0.56 0.45 1.02 Non-Medicaid 2.0 0.23 0.33 0.38 0.33 Medicaid 1.8 0.45 0.39 0.11 0.06 0.52 2.05 0.15 0.19 0 0 0.43 0.96 2.25 0.34 0.34 0.11 0.06 0.50 0 0 0.14 0 0 0 0.57 0.17 0 0.11 0.06 0 0 0.45 Fetal-Infant Morbidity/Mortality Review & Registry Central New York Region 2006-2007 Dominant Cause of Death: rate/1000 live births + fetal deaths ≥ 300 grams Abruptio/Placental Infarct Other Placental Problems Cord Accident/Prolapse Congenital Anomaly/ Chromosomal Abnormality Prematurity Overwhelming Immaturity Other Sepsis SIDS/SUID Trauma Unexplained Newborn Care Infant Health Non-Medicaid 0.9 0 0.22 0 0.54 Medicaid 1.9 0 0.06 0.06 1.34 Non-Medicaid 0.4 0 0 0 0.13 Medicaid 2.0 0 0 0 0.46 0 0 0.09 0.05 0 0 0 0 0 0.06 0.17 0.11 0.11 0 0 0 0 0.04 0.18 0.04 0 0 0 0.29 0.11 0.74 0.4 0 Cause of Death Conclusions These findings support our earlier Findings that pre-pregnancy and early pregnancy factors, along with post neonatal factors play the largest role in the disparity between death rates among Medicaid and Non-Medicaid insured women. A protective effect of Medicaid Status is suggested regarding Fetal and Neonatal deaths. Sharing the Results CNY Regional Perinatal Forum CNY Regional Perinatal Program/Affiliate Hospitals Onondaga County Health Department/Syracuse Healthy Start SUNY Upstate Medical University Departmental Grand Rounds (OB-GYN/Pediatrics) Masters in Public Health courses Resultant Targeted Interventions Improve preconceptional/interconceptional care Facilitate access to early/quality prenatal care Implement stronger smoking cessation programs Improve maternal post partum supports and counseling about importance of Safe Sleep Environment Contact Information: Center for Maternal & Child Health www.upstate.edu/cmatch/ 315-464-5706 Richard H. Aubry, MD, MPH Pamela Parker, BA Kristen Luke-Houseman, RN, BA aubryr@upstate.edu parkerp@upstate.edu lukehouk@upstate.edu Preliminary Data. Not for release without permission.