TOSHA Update: Emphasis Areas for New Fiscal Year
advertisement

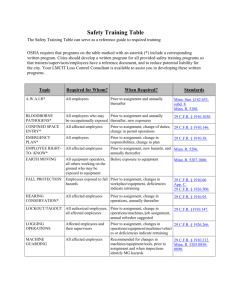
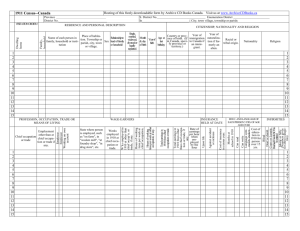
A DIVISION OF THE DEPARTMENT OF LABOR AND WORKFORCE DEVELOPMENT James G. Neeley, Commissioner TOSHA STAFFING 102 Total Positions 42 Occupational Safety Specialists 30 Industrial Hygienists 21 Support Staff 2 Chemists Remaining positions Administrative, Legal, etc. Will request a Compliance Asst. Position in 2007 TOSHA Coverage 131,000 Employers 2,638,000 Workers Private & Public Sector Agriculture, Construction, & General Industry 4th Q 2005 New Public Sector Participation 72 23 43 1 Utilities Schools Systems Cities County 10,024 Total Employees Covered New TOSHA Lab AIHA Accredited Lab Located in Murfreesboro Plan to partner with MTSU to allow student access State of the art facility Staffed presently by two chemists Building shared with local Career Center TOSHA Advisory Committee Gary Watkins Jim Williams Becky Morris Kent Carter John Lawhon Bob Walker IBEW UAW/Ford Glass CWA Marvin Windows Blaine Construction Bridgestone/Firestone Tennessee OSH Review Commission J. Russell Farrar, Chairman Marsha Vaughn, Member James Cunningham, Member Review Commission Activity 1999 Inspections Contested 220 Current Inspections Contested 20 – 2006 18 – 2005 2 – 2004 0 13 of the 20 cases contested are pending settlement. – 2006 11 – 2005 2 TOSHA Inspection Activity, Recognition Programs, Recent Changes to the TOSHA Act Inspection Activity July 2005-June 2006 Safety & Health – 2,212 – 8,018 – $2,075,374 Compliance Program Inspections Conducted Hazards Identified Penalties Assessed Consultative Assistance Program – 397 Visits – 3,040 Hazards Identified –$ 0 Penalties Assessed Special Emphasis Programs Excavation Safety Fall Protection Carbon Monoxide Noise Amputations Targeting Initiatives Sharps Injury Reduction in Hospitals & Ambulatory Surgical Treatment Centers Construction Metal Working Industries TOSHA Recognition Programs Volunteer Star (VPP) SHARP Governor’s Award Commissioner’s Award Volunteer Star 24 sites 19,000+ employees •Smurfit-Stone - Lewisburg - 1996 •DuPont - New Johnsonville – 1996 •Bridgestone/Firestone - Morrison - 1997 •Tennessee Eastman - Kingsport -1998 •International Paper - Memphis - 1998 •MSC Corp. - Oak Ridge - 2000 •Frito-Lay - Fayetteville – 2000 •Johnson Controls - Athens - 2001 24 sites 19,000+ employees •Eaton-Inoac - Livingston - 2001 •Marvin Windows and Doors - Ripley - 2002 •Olin Chlor-Alkali – Charleston – 2002 •Frito-Lay – Pulaski – 2002 •John Deere – Greeneville – 2002 •TRW – Cookeville – 2003 •International Paper- Pioneer – 2003 •Schering-Plough – Cleveland – 2003 24 sites 19,000+ employees •Osmose Chemical – Millington – 2004 •DuPont – Old Hickory - 2004 •Frito-Lay – Chattanooga - 2005 •ITW Dynatec – Hendersonville - 2005 •Performance Pipe – Knoxville – 2005 •Denso Manufacturing – Athens – 2005 •Huber – Spring City – 2006 •Lucite International – Memphis – 2006 Governor’s & Commissioner’s Award of Excellence Recognizes manufacturing and construction firms Commissioner’s Award No Lost Time Injuries/Illnesses Governor’s Award No Lost Time or Restricted Duty Injuries/Illnesses The man-hour requirements are dependent upon number of employees and are defined in the application package. SHARP Program S - Safety H - Health A - Achievement R - Recognition P - Program SHARP Program 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Venture I Cassemco Inc Fastec Industrial Tindell’s Inc Fi-Shock Inc Entec, Inc Cumberland Lumber MI Metals Inc Capstan Tennessee Inc ARJ Manufacturing LLC DH Compounding Nichirin TN Inc Yorkville Cookeville Johnson City Knoxville Knoxville Manchester McMinnville Smyrna Rockwood Jackson Clinton Lewisburg October 1998 October 1998 March 1999 October 2000 July 2003 January 2004 January 2005 August 2005 September 2005 October 2005 January 2006 January 2006 Changes to the TOSHA Act No legislative changes during 2006 May request changes in citation delivery options for 2007 Standards Development Completed Actions Occupational Exposure to Hexavalent Chromium Slip Resistance of Skeletal Structural Steel Rollover Protective Structures: Overhead Protection Standards Development Final Rule Stage Electrical Standards (1910) - Complete revision using latest National Electrical Code – last revision in 1981. Employer Payment for PPE - Evaluation of Public Comment Assigned Protection Factors (1910) Amendments to the final rule on respiratory protection Standards Development Proposed-Rule Stage Confined Spaces in Construction (1926) Preventing suffocation/explosions Electric Power Transmission and Distribution (1910) - Electrical protective equipment, foot protection and fall protection (PPE). Explosives (1910) - Complete revision of 30 year old standard. Exposure to Crystalline Silica - New standard needed Updating OSHA Standards based on National Consensus Standards – Continued work on project started in 2004. Standards Development Pre-Rule Stage Excavations - (1926.650-652) Review to determine continued need Beryllium Exposure - Develop proposed rule Cranes and Derricks - Review to determine need for changes to 30 year old standard Power Presses - Revision of the current standard to cover other presses (hydraulic and pneumatic) Standards Development Pre-Rule Stage Emergency Response and Preparedness - No current standard Lead in Construction - Review to determine continued need Standards Improvement Phase III Elimination of duplicative and unnecessary standards Hazard Communication - Revise to conform to Globally Harmonized System (GHS) of classification and labeling Standards Development Long Term Action Walking Working Surfaces and PPE (Slips, trips and falls) Hearing Conservation for Construction Ionizing Radiation Regularly Scheduled Fall Seminars 10-Hr. General Industry Course—2 days 30-Hr. General Industry Course—4 days Safety Committee Strategies—1/2 day Effective Safety Programs—1 day Maintenance Related Standards—1 day Basic Safety—1 day TOSHA 101—1/2 day – TOSHA Requirements for Monitoring, Evaluation, & Inspection—1 day – Industrial Hygiene Made Easy—1/2 day Training Videos Currently Available – Hazard Communication – Bloodborne Pathogens – Special Emphasis Programs – Personal Protective Equipment – How to Develop a PPE Program In Development – PPE Training for Employees New Requirements & Most Cited Health Standards Hexavalent Chromium Published in Federal Register February 28, 2006 General Industry, Construction, Agriculture (.1026) Start-up dates the same in Tennessee as published in the standard Includes provisions for: – – – – – – Methods for controlling exposure Respiratory protection Protective work clothing and equipment Hygiene areas and practices Medical surveillance Hazard communication and recordkeeping Sharps Injury Reduction Targeting Initiative Hospitals and Ambulatory Surgical Treatment Centers Tennessee Law signed in 1999 Changes to Federal Law (1910.1030) in 2001 Oct. 2005 to Sept. 2006-free training classes across the state Oct. 1, 2006-programmed inspection – Focused on sharps injuries Cost of Sharps Injuries American Hospital Association – Cost of follow-up for a high-risk exposure is about $3000 per needlestick injury even when no infection occurs – One case of serious infection caused by a bloodborne exposure can cost over $1M For follow-up testing, lost time, disability payments – Safer needle device average cost is 28 cents higher TB Respirators Occupational Exposure to Tuberculosis – Inspections only conducted in five types of workplaces identified by the CDC as having a higher incidence of TB than the general population Must conduct initial fit test No requirement to conduct annual fit test – Appropriations restriction in the Consolidated Appropriations Act for 2006 All other respirator requirements remain the same as required by 1910.134 Most Cited General Industry-Health by Average Penalty 1910.94 1910.1025 0800-1-1 1910.151 1910.146 1910.1048 1910.134 1910.95 1910.1030 1910.120 Ventilation Lead Air Contaminants Medical Services & First Aid Permit-Required Confined Space Formaldehyde Respiratory Protection Occupational Noise Exposure Bloodborne Pathogens Hazardous Waste & Emergency Response Most Cited Construction-Health by Average Penalty 1926.62 1926.1101 1926.59 1926.50 1926.103 1926.52 1926.55 1926.57 1926.28 1926.51 Lead Asbestos Hazard Communication Medical Services & First Aid Respiratory Protection Occupational Noise Exposure Gases, Vapors, fumes, dusts, mists Ventilation Personal Protective Equipment Sanitation Most Cited Safety Standards & Fatality Review Top 10 Cited Safety Standards in General Industry by Average Penalty 50-3-105 1910.333 1910.176 1910.212 1910.217 1910.67 1910.23 1910.219 1910.179 1910.147 General Duty Electrical Work Practices Material Handling/Housekeeping/Clear aisles Machine Guarding Mechanical Power Presses Vehicle Mounted Rotating Work Platforms Guarding Floor and Wall Openings Mechanical Power Transmission Apparatus Overhead and Gantry Cranes Control of Hazardous Energy (Lockout/Tagout) Top 10 Cited Construction Standards by Average Penalty 1926.269 1926.652 1926.454 1926.21 1926.651 1926.760 1926.501 1926.550 1926.451 1926.453 Electric Power Generation, Trans., Dist. Excavations (Collapse Protection) Fall Protection Training Safety and Health Training Excavations (General Requirements) Steel Erection Fall Protection General Fall Protection Cranes and Derricks Scaffolding Aerial Lifts Fatalities investigated in 2005...28 Struck-by 12 Falls 6 Burns (fires, explosions, etc.) Overturned equipment 2 3 Caught in/Crushed by 2 Excavation Collapse Chemical Overexposure 1 2 – (trees, vehicles, steel beams, etc.) – (stairs, bucket truck, roof, skylight, etc.) – (skidder, scraper, mower) – (wall& track drill, dock plate) – (CO while buffing floors) Catastrophes investigated in 2005…..4 8 employees admitted to hospital from smoke inhalation due to grinding operation fire 4 employees admitted to hospital from smoke inhalation due to fighting wildland fires 4 employees struck by roof trusses when a block wall collapsed during construction of a building 4 employees admitted to hospital due to smoke inhalation from a fire while demolition of powder coat spray booth Fatalities investigated to date in 2006…..30 Struck-by (forklifts, vehicle, elevator, tree, elephant,logs) Falls (from ladder, cell tower) Drowning Explosion (disposing of explosives, reactor vessel, storage vessel cleaning) Gas explosion (lighting pilot) Electrocution Overturned Equipment (skid steer) Crushed by/caught in (hopper, coil of steel, robot) Equipment failure (pole broke ‘ee was climbing, scaffold) 11 6 2 3 1 1 1 3 2 Catastrophes investigated to date in 2006…..2 4 employees hospitalized for exposure to hydrogen flouride 4 employees hospitalized for exposure to hydrogen flouride