Review_Final
advertisement

I can:
- multiply when I see brackets
- follow BEDMAS
We are learning to expand and simplify polynomial expressions
- write a bracket twice if it is squared
- collect like terms using the signs in front and only if their
variables are identical
1.
Expand and then simplify.
a.
(𝑥 + 4)(2𝑥 − 7)
b.
3(𝑥 − 4)(𝑥 + 2)
c.
4(𝑥 + 2)2 − 9
d.
(𝑥 − 2) − (3𝑥 + 4)2
We are learning to factor polynomial expressions using
I can:
methods of: common factoring, differences of squares, perfect - write a multiplication question (with brackets)
square, simple and complex trinomials
- find a common factor first (numbers that divide evenly or
letters that are everywhere)
2.
Factor.
a.
6𝑥 2 − 11𝑥
b.
𝑥 2 + 7𝑥 − 44
•
•
write down my common factor outside
write down what's left when I divide inside
- factor a simple trinomial (1x^2)
•
•
find two numbers that x to c and + to b
write my two special numbers in the brackets
- factor a complex trinomial (anything but 1)
c.
2
5𝑥 + 15𝑥 + 10
d.
6𝑥 2 + 13𝑥 − 5
e.
6𝑥 2 − 24
•
•
•
find two numbers that x to ac and + to b
•
•
see a subtract sign between TWO terms
•
factor as root + root and root - root
replace the x-term with my two special numbers
factor by grouping
- factor a difference of squares
recognize both terms as perfect squares because I
know their square roots
I can:
We are learning to solve quadratic equations
3.
Solve.
a.
(6𝑥 − 1)(3𝑥 + 5) = 0
b.
𝑥 2 + 5𝑥 + 4 = 0
c.
4𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 = 3𝑥 2 − 2𝑥 − 4
d.
6𝑥 2 + 7𝑥 − 11 = 2𝑥 + 4
- set my equation equal to zero
- factor; everything is in brackets OR formula; ax^2+bx+c
- set each bracket to zero if I chose to factor
To be able to use function notation accurately
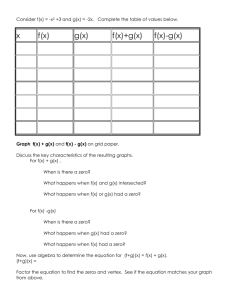
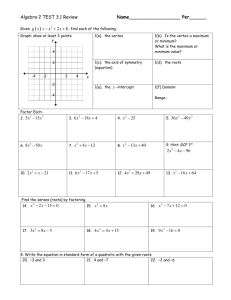
4. Consider the relation 𝑓(𝑥) = 3(𝑥 − 2)2 + 8.
a. Calculate f(2) and f(6)
b. Write a mapping statement and use it to
describe the transformations that have
been applied.
c.
I can:
calculate f(x) by replacing all of the xs
with a value
write a mapping statement to transform
points
insides are for xs (brackets lie)
outsides are for ys
describe transformations
negatives mean reflections
multiplications mean
stretches/compressions
additions mean shifts
identify domain as xs that are part of
the relation
write notation D:{x|xER, any restriction}
identify range as ys that are part of the
relation
write notation R:{y|yER, any restriction}
identify a function as having no
cheating xs (ys can have as many
partners as they like)
State the domain and range.
5. Consider the relation {(3,5), (2,5), (3,9)}
a. State the domain and range.
b. Is this a function?
To be able to sketch parabolas
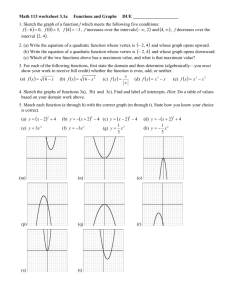
1. Sketch the parabolas:
a. 𝑓(𝑥) = 3𝑥 2 + 12𝑥 − 4
b. 𝑔(𝑥) = −2(𝑥 + 5)2 -6
c.
ℎ(𝑥) = 4(𝑥 + 3)(𝑥 − 7)
I can:
use two brackets to find two xintercepts
find the x of my vertex halfway between
my x-intercepts
find the y of my vertex as f(xvertex)
use the odd as to step from the vertex
OR
I can:
use one bracket to find my one vertex
use odd as to step from my vertex
OR
I can:
use -b/2a (from no brackets) to find the
x of the vertex and sub it in to find y
use odd as to step from my vertex
To be able to write equations for parabolas in vertex and factored
forms
I can:
2. Write the equation of a parabola with x-intercepts at -6 and 10. The parabola passes through (4,9).
use two x-intercepts to fill
in my two brackets
use one other point as x
and y and some algebra
to find a
use one vertex to fill in
one bracket
use one other point as x
and y and some algebra
to find a
OR
3. Write the equation of a parabola that passes through (7,11).
This parabola has a vertex of (4, -10).
To be able to find xs, ys and the vertex, given a
quadratic function in any of the three forms
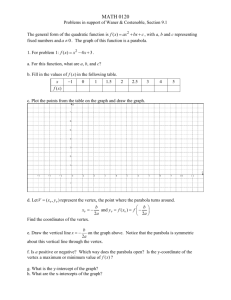
1. The height of a ball is given by the function
ℎ(𝑡) = −4.9𝑡 2 + 19.6𝑡 + 24.5.
a. How high was the ball initially?
b. When did the ball hit the ground?
c.
What was the maximum height of
the ball?
I can:
find x-intercepts by setting y=0 and solving
(factor or formula or algebra)
find y-intercept by setting x=0 and using
BEDMAS
find any xs given a y (sometimes it's
hidded) by setting it to zero then factoring
or formula or using algebra
find any y given x using BEDMAS
find the vertex because it's halfway
between xs or it's -b/2a
We are learning to solve RATs
2. Solve the triangle below.
x
70
1.8m
I can
- use 180 - - to find the third
angle
- use PYTHAGOREAN
THEOREM to find the third side
long side add or short
side subtract
- label my sides H then O then
A after selecting my THETA to
find a second side or second
angle
- Pick a formula (SOH CAH
TOA) that I have two numbers
for
there is usually a side I
don't care about
- Sub in my values so I only
have one variable and then
solve
angles require 2nd, sides
to do not
We are learning to solve non-RATS
3. Solve the triangle below.
6cm
x
50
8cm
I can:
- use 180 - - to find the third
angle
- use sine law when I have a full
pair (still need 2nd Function to
get an angle)
find the third angle first
when possible
- use cosine law when I do not
have a full pair
use c^2= for sides
use cosC = for angles
To be able to sketch the graph of a periodic function to solve problems
4.
Sketch graphs of each of the following:
a. 𝑓(𝑥) = 6 sin(5(𝑥 − 20)) + 10
I can identify the period as:
the pattern in a periodic function
when the graph starts to repeat
360/the horizontal stretch or
compression (multiplication inside)
in the equation
the time it takes to go once around
twice as much time as it takes to go
from max to min
I can find the amplitude because:
b.
it's the height it goes up or down
from the axis of the curve (max +
min)/2
it's the size of the wave on my
graph
it's the vertical stretch
(multiplication outside) in my
equation
𝑓(𝑥) = 10 sin(2𝑥) − 5
I can find the start of the period (phase shift)
because:
c.
𝑓(𝑥) = −50 sin(180(𝑥 − 3)) + 100
it is where the pattern starts/stops
it's the horizontal shift (addition
inside) in the equation
I can find the axis of the curve because:
it's the midline on a graph
it's the (max + min) / 2
it's the vertical shift (addition
outside) in the equation
I can skect the y-axis using the amplitude and
the axis of the curve (outsides are ys)
5.
Write the equation of the sine function the represents a Ferris I can sketch the x-axis using the start of a
wheel with a radius of 50m on a 2m platform that goes around period, it's length and then middle, middle,
middle (insides are xs and they lie)
10 times an hour.
I can sub in ys to get xs (ALGEBRA)
using my x and my curve I can find
more xs.
We are learning to use mapping notation
1.
Write a mapping statement for 𝑦 = 3 sin(2𝑥) + 5.
a.
Describe the transformations that have been applied.
b.
State the domain and the range,
I can use numbers in the brackets (liars)
on my x and numbers outside brackets
on y
I can
see reflections as negatives
stretches as multiplications
shifts as additions
We are learning to simplify exponential
expressions using the exponent laws
2.
I can:
add the exponents when asked to multiply
(exponent law 1)
Simplify each of the following.
75 72
72
subtract exponents when asked to divide
(exponent law 2)
multiply exponents when asked to raise a
power to a power
write anything raised to zero as 1
write negative exponents as positive if i flip
the base
write fraction exponents as radicals
(−9)4 ((−9)2 )10
1 3
3 2
(24 ) (24 )
5−6 (5−1 )2
5−3
We are learning to solve exponential equations
3.
Solve.
a.
b.
100 = 2 × 2𝑥
36 = 6 × 6
I can:
simplify the equation by combining like bases
through the laws
drop the bases and set the exponents equal
use trial and error when all else fails!
do regular algebra to solve for the base
3𝑥
I can:
We are learning to solve problems using the graph
of an exponential function
4.
𝑥⁄10
sketch the graph of 𝑦 = 15(2)
it to approximate when y=1000
+ 15. Use
write an equation of the form y=ab^x where y is
future, a is starting, b is what happens each
period and x is number of periods
graph using a table of values by picking nice
values of x (make sure you consider the fraction)
find y given an x using BEDMAS
find x given a y using my graph