Planktotrophic larvae - University of Washington
advertisement
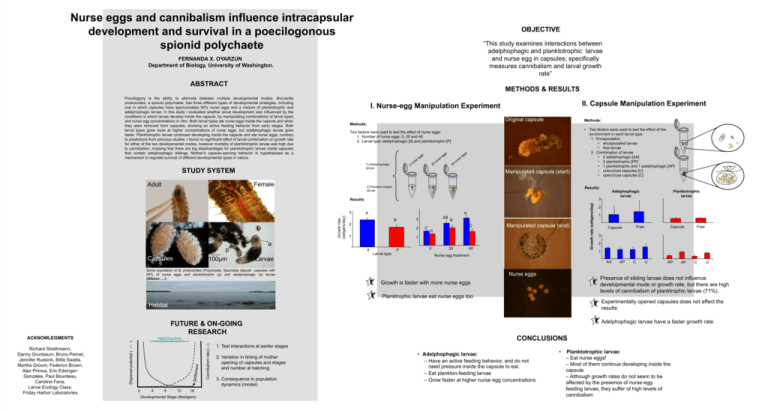
Nurse eggs and cannibalism influence intracapsular development and survival in a poecilogonous spionid polychaete OBJECTIVE “This study examines interactions between adelphophagic and planktotrophic larvae and nurse egg in capsules; specifically measures cannibalism and larval growth rate” FERNANDA X. OYARZUN Department of Biology, University of Washington. ABSTRACT METHODS & RESULTS Poecilogony is the ability to alternate between multiple developmental modes. Boccardia proboscidea, a spionid polychaete, has three different types of developmental strategies, including one in which capsules have approximately 90% nurse eggs and a mixture of planktotrophic and adelphophagic larvae. In this study I evaluated whether larval development was influenced by the conditions in which larvae develop inside the capsule, by manipulating combinations of larval types and nurse egg concentrations in vitro. Both larval types ate nurse eggs inside the capsule and when they were removed from capsules, showing an active feeding behavior from early stages. Both larval types grew more at higher concentrations of nurse eggs, but adelphophagic larvae grew faster. Planktotrophic larvae continued developing inside the capsule and ate nurse eggs, contrary to predictions from previous studies. I found no significant effect of larval combination on growth rate for either of the two developmental modes, however mortality of planktotrophic larvae was high due to cannibalism, implying that there are big disadvantages for planktotrophic larvae inside capsules that contain adelphophagic siblings. Mother’s capsule-opening behavior is hypothesized as a mechanism to regulate survival of different developmental types in nature. Original capsule Methods: Methods: Two factors were used to test the effect of nurse eggs: 1. Number of nurse eggs: 0, 20 and 40 2. Larval type: adelphophagic [A] and planktotrophic [P] 1) Adelphophagic larvae STUDY SYSTEM Female Adult II. Capsule Manipulation Experiment I. Nurse-egg Manipulation Experiment Manipulated capsule (start) 2) Plankton-trophic larvae • Two factors were used to test the effect of the environment in each larval type: 1. Encapsulation • encapsulated larvae • free larvae 2. Combination of larvae • 2 adelphophagic [AA] • 2 planktotrophic [PP] • 1 planktotrophic and 1 adelphophagic [AP] • untouched capsules [U] • open/close capsules [C] Results: 3 Growth rate (setigers/day) A A B 2 Capsules 100μm A P Larval type Larvae C B C Manipulated capsule (end) C 1 a p 3 2 1 AB 0 20 40 Growth rate (setigers/day) Results: 3 Adelphophagic larvae Planktotrophic larvae 2 1 Free Capsule Capsule Free 3 2 1 Nurse egg treatment AA Some population of B. proboscidea (Polychaeta: Spionidae deposit capsules with 90% of nurse eggs and planktotrophic (p) and adelphophagic (a) larvae (Gibson…..). Nurse eggs AP C U PP AP C U Presence of sibling larvae does not influence developmental mode or growth rate, but there are high levels of cannibalism of planktrophic larvae (71%). Growth is faster with more nurse eggs Planktrophic larvae eat nurse eggs too Experimentally opened capsules does not affect the results Habitat Adelphophagic larvae have a faster growth rate FUTURE & ON-GOING RESEARCH ACKNOWLEGMENTS Cannibalism rate (---) Dispersal potential ( –– ) Richard Strathmann, Danny Grunbaum, Bruno Pernet, Jennifer Ruesink, Billie Swalla, Martha Groom, Federico Brown, Alex Primus, Eric EdsingerGonzales, Paul Bourdeau, Caroline Faria, Larval Ecology Class, Friday Harbor Laboratories CONCLUSIONS Hatching time 0 4 8 12 16 Developmental Stage (#setigers) 1. Test interactions at earlier stages 2. Variation in timing of mother opening of capsules and stages and number at hatching 3. Consequence in population dynamics (model) • Adelphophagic larvae: – Have an active feeding behavior, and do not need pressure inside the capsule to eat. – Eat plankton-feeding larvae – Grow faster at higher nurse egg concentrations • Planktotrophic larvae: – Eat nurse eggs! – Most of them continue developing inside the capsule – Although growth rates do not seem to be affected by the presence of nurse-egg feeding larvae, they suffer of high levels of cannibalism