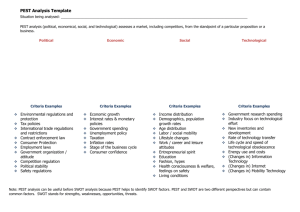
1st residential George Levvy slides
advertisement

Leadership, Change & Strategy George Levvy In pairs Thinking about leadership, strategy & change • What’s front of mind from your work and/or the past 36 hours? • What questions do you have? • What do you want to get out of the next two days? George Levvy Aims • Insight into leadership • Connect that to current context • Prompt reflection about your work and yourself • Enable actions based on learning from these two days George Levvy Manage your learning • Ask • Challenge • Be aware of your needs – pace, energy, space George Levvy Why me? • 10 years chief executive of a national charity • 8 years’ consulting, working with leaders & top teams on leadership and change = practitioner perspective George Levvy Strategy George Levvy What is the purpose of Culture & Sport services? What are they there to achieve? George Levvy Groups of 3 or 4 • Is there a meaningful vision that guides those services? If so what is it? • Are there fundamental values that guide the delivery of those services? If so, what are they? George Levvy Groups of 3 or 4 Thinking about culture & sport services in general • Do a PEST & SWOT analysis • Identify the three key issues in each category George Levvy Strategic issues ‘Fundamental policy questions or critical challenges affecting an organisation’s [ability to achieve its aims]’ John M Bryson 2004 George Levvy In same groups Given the purpose, vision and values agreed earlier and what you’ve identified in the PEST & SWOT analyses, what are the strategic issues for culture & sport services George Levvy George Levvy • Who are the target customers of culture & sport services? • What is the value proposition in relation to those customers? George Levvy • Given the strategic issues, customers and value proposition you have identified how would you sum up the challenge facing culture & sport services? George Levvy Strategy • A diagnosis • A guiding policy / approach • A set of coherent actions George Levvy Change: making it happen George Levvy Groups of 3 or 4 You are the leader of the reorganisation of your service. The criteria for the change are a 25% reduction in costs while serving as many people as now. What are the three most important things you need to do in bringing about this change? George Levvy Kotter’s 8 stage process Establish a sense of urgency Create a guiding coalition Develop a vision and strategy Communicate the change vision Empower broad based action Generate short term wins Consolidate gains and produce more change George Levvy Kotter 1996 Anchor new approaches in the culture George Levvy People and change George Levvy When you have been part of a change project (not as the management / leadership), • What was it like? • How did it make you feel? • What did you think of the management? George Levvy When you have led or managed a significant change • What was it like? • What did you think of how people responded? • How successful was it? George Levvy The transition process (adapted from William Bridges 2003) ending end present beginning The Change Curve Morale Performance Integration - results start to be seen, behaviours start to be the norm denial frustration not fair, why me searching for meaning - why was it needed? Where do I fit in? testing still in ‘old think’ shock letting go Time The J Curve What stakeholders (mistakenly) expect Desired state Performance Current state What actually happens in most cases Time George Levvy NEW ORDER Capability Chaos REGRESSION Change initiative George Levvy Rob Zuijderhoudt In times of major change, what did you need to know? George Levvy What people need to know Purpose………………WHY? Picture……………..…WHAT? Plan…………………....HOW? Part to play………….HOW? To achieve change you need vision skills incentive resource action plan change skills incentive resource action plan confusion vision X incentive resource action plan anxiety vision skills resource action plan slow change vision skills incentive X action plan frustration vision skills incentive resource X Colin Livingstone, Steria Consulting X X false starts George Levvy Think about the best organisation you’ve worked in and the worst. How did they differ? What were the key differences between them? George Levvy The leader’s job Creating the conditions for success George Levvy Ulrich, Zenger & Smallwood (Results-Based Leadership, 1999) Set direction Demonstrate personal character Mobilise individual commitment George Levvy Engender organisational capability Setting (providing?) direction • Understand external events • Focus on the future • Turn vision into action George Levvy Mobilising individual commitment • Build collaborative relationships • Share power and authority • Manage attention George Levvy Engendering capability • • • • • Build organisational infrastructure Leverage diversity Deploy teams Design human resource systems Make change happen George Levvy Demonstrating personal character • Live values by practising what is preached • Have and create a positive self-image • Possess cognitive ability and personal charm George Levvy In current circumstances and looking to the next few years, which of these are the most challenging? George Levvy What could stop you providing that kind of leadership to those you lead? George Levvy What do / will you need in order to provide that kind of leadership? George Levvy ‘Homework’: on your own or in pairs What is your purpose and what are your core values? How do you pursue those in your work? George Levvy Kotter Leadership Management • Setting direction • Planning & budgeting • Aligning people • Organising and staffing • Motivating and inspiring • Controlling and problem solving George Levvy Leadership vs management • What vs how • Doing right thing vs doing things right • Coping with change vs coping with complexity (Kotter) • Etc, etc George Levvy Leadership is not about • • • • • • • • • George Levvy Budgeting Operational planning Strategic planning Running projects Functional tasks Controlling Being ‘productive’ DOING STUFF Etc, etc Friday George Levvy Effectiveness George Levvy • Who is the most effective executive / person you have ever known? • What did they do that made them effective? George Levvy Drucker on effectiveness Effective executives • Ask ‘What needs to be done?’ and ‘What is right for the enterprise?’ • Undertake no more than two top priority tasks • Delegate any other high priority tasks George Levvy In pairs In your work, what’s the one most important thing for you right now? George Levvy Strategy Phase 2 George Levvy Strategy • A diagnosis • A guiding policy / approach • A set of coherent actions George Levvy Developing an approach Think about the diagnosis (the challenge) we reached yesterday regarding Culture & Sport service OR The strategic challenge facing your service How might you tackle it (one or more specific approaches)? George Levvy Approaches • A role (task/purpose/aim) • A destination (A ‘proximate objective’ – Rumelt) George Levvy Critical success factors (CSFs) ‘….the essential areas of activity that must be performed well if you are to achieve the mission, objectives or goals for your business or project.’ www.mindtools.com George Levvy CSFs (2) • Qualitative • ‘areas of activity that should receive constant and careful attention from management.’ • ‘…help everyone in the team to know exactly what's most important ‘ John F Rockart • 3-5 George Levvy OUTCOME CSF George Levvy CSF CSF CSF CSF Managing implementation: Balanced Scorecard (Kaplan & Norton) • • • • Linking strategy to actions Monitoring progress Starts from CSFs Four perspectives – Financial – Customer – Internal business process – Innovation & learning George Levvy Managing implementation (2) Plan Implement Review George Levvy Managing implementation (3) Outcome focus eg Turning the Curve http://www.sunderlandchildrenstrust.org.uk/content/sunderland-turningthe-curve-v1.1.pdf George Levvy Plans are nothing; planning is everything Dwight D Eisenhower George Levvy George Levvy Teams / collaboration George Levvy Groups of 3 or 4 Think of the best & worst teams you have been part of • What were the three key things that made the good team so good? • What were the three key things that made the bad team so bad? George Levvy • Team members openly admit weaknesses & mistakes • The most important - & difficult – issues are put on the table to be resolved during team meetings • Team members leave meetings confident that their peers are completely committed to the decisions that were made, even if there was initial disagreement • Team members challenge one another about their plans & approaches and about their actions & behaviours • Team members willingly make sacrifices in their departments or areas of expertise for the good of the team / organisation George Levvy Inattention to • • The Five Dysfunctions of a Team Patrick Lencioni 2002 RESULTS Absence of ACCOUNTABILITY Lack of COMMITMENT Avoidance of CONFLICT Absence of TRUST Trust • Confidence that other team members’ intentions are good • Hence no reason to be self-protective, so able to be vulnerable with one another – won’t be used against them • Hence able to focus completely on job in hand George Levvy Building Trust • Allow & invest time • Techniques • Personal & professional histories • Team effectiveness exercises • Personality profiling, eg MBTI -> understanding & empathy • Manage emotions • Take the first risk George Levvy Results Team members committed to collective aims & objectives of the team before their individual and functional ones George Levvy George Levvy In groups of 3 or 4 You are a leader of a new collaboration involving other parts of your local authority and also other organisations What are the major challenges of leading a collaboration of this sort? George Levvy How will you carry out your job as leader of the collaboration? What will you concentrate on? George Levvy Collaborative leadership (Arnoud de Meyer) • Collaboration: ‘co-act[ing] with others in order to succeed in implementing change’ • Listening – Weak signals – Internal & external • Influencing • Adapting George Levvy Collaborative leadership: ‘insights’ • Mindset • Reducing transaction costs – trust & informal relationships • Seeing beyond borders of the organisation • Building consensus – ensure and exploit diversity • Networking – weak ties • Managing dualities George Levvy George Levvy Reviewing and planning George Levvy In pairs What have been the most important things you have learned or concluded over the past 3½ days? What actions are you going to take as a consequence? How will you ensure you actually do them? George Levvy George Levvy 07768 601 833 george@levvy.co.uk George Levvy Effective partnerships (Learning Skills & Improvement Service) • • • • • • • • • • involve agencies working together for mutual benefit have an aim that is agreed and understood by all the partners put the learner at the centre of partnership working focus on a high-quality learning experience leading to sustainable progression have clear, effective leadership identify the role of each partner, which is understood by others in the partnership share ownership of the partnership and partners feel they benefit from the collaboration have dedicated time and resources for administration and operation recognise different organisational cultures within the partnership have a supportive atmosphere, where suggestions, ideas and tensions are addressed. George Levvy Situation analysis - some key tools • Stakeholder analysis (NB input into outcomes) • PEST(LIED) • SWOT • Force field analysis • Risk analysis • Scenario analysis • Cost benefit analysis www.mindtools.com George Levvy PESTLIED analysis • • • • • • • • George Levvy Political Economic Social Technological Legal International Environmental Demographic SWOT analysis • • • • George Levvy Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats Risk analysis • Likelihood (H/M/L) • Impact (H/M/L) • Management George Levvy Risk analysis (2) • Human • Operational • Reputational • Procedural • Project George Levvy • Financial • Technical • Natural • Political • Other Context: Stakeholder Analysis High P o w e r Low Keep satisfied Encourage and influence Monitor Keep informed Interest High