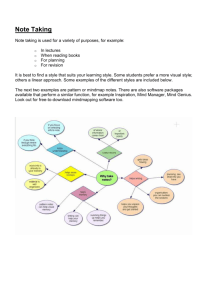
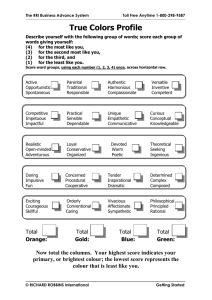
Slides of the presentation.
advertisement

“It's always incumbent on a researcher to make the effort to reach out to the community to engage with the population they're serving.” Experiments with the See ColOr Interface Guido Bologna CVML, University of Geneva, Switzerland Outline • • • • • Introduction Local Perception Module Experiments in the past New experiments Conclusion 3 Introduction • Blind people 40 millions in 2020 (90% after the age of 1 year) 4 millions in OCDE countries • Long term goal : sensing the environment with sounds Action is key to perception • A number of pixels are directional sound sources 4 Local Perception Module See ColOr Seeing Colours with an Orchestra head-centric colour encoding 2D sound spatialization distance stereovision video piano saxophone 25 points headphones 6 7 Colour encoding • Colour system: HueSaturation-Luminance • Hue: musical instrument • Saturation: 4 instrument notes • Luminance: 2 instruments with different notes 8 Hue Oboe Saxophone Viola Violin pizzicato Piano Flute Trumpet 9 Saturation and luminance • 4 levels of saturation Low High • 8 levels of luminance Double bass Human voice 10 Prototypes – – – – – – Stereoscopic or Kinect camera Sonification of a row containing 25 points CIPIC Kemar HRTFs (2D spatialization) HSL colour coding Two depth coding schemes Lower peripheral resolution [15 12 9 7 5 3 3 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 5 7 9 12 15] 11 Depth coding (first mode) For all sonified pixels (25) : • 90 ms for undetermined depth (D); • 160 ms for 0 <D<1 • 207 ms for 1<D<2 • 254 ms for 2<D<3 • 300 ms for D > 3 12 Depth coding (second mode) • The strategy here is to sonify the dominant colour of the row with only 1 sound source (providing average depth) • The centroid of the first red area is laterally spatialized [R R R R R B B J B B B R R G G G J J B B B G G G G] [R R R R R ] • The volume V after 3 meters starts to decrease: F(V) = V * exp(-k*D) 13 Experiments in the Past 15 Left picture : the 6 experiment participants interpreted the major colours as the sky the sea and the sun; clouds were more difficult to infer (2 subjects); instead of ducks, all the subjects found an island (with yellow sand) or a ship. Right picture : 4 participants correctly recognised the tree with the sky and the grass; one subject qualified the tree as a strange dark object and finally the last individual imagined a nuclear explosion ! 16 • All individuals found one of the red doors in a time range between 4 and 9 minutes. 17 Pairing colored socks 18 Participant P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 Average Time (mn) 12 24 7 6 16 13.0 (7.3) Success rate (pairs) 5 5 5 3 5 4.6 (0.9) Participant P6 P7 P8 P9 P10 Average Time (mn) 5 10 4 4 18 8.2 (6.0) Success rate (pairs) 5 5 5 5 5 5.0 (0.0) 19 Following a red path • In this experiment the goal was to follow a coloured path in an outdoor environment. 20 Participant P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 P7 P8 P9 P10 Average Path Length (m) M+C = 88 M = 84 M+B = 110 M+A = 93 M = 84 M+A+C = 97 M+A+C = 97 M = 84 M = 84 M = 84 90.5(8.7) Speed Average (m/h) 723 710 485 656 484 600 451 869 1326 1096 740.0(284.6) 21 Find a red tee shirt New Experiments Current Prototype with Kinect Local Perception Object Recognition 15/03/2016 Alerting System Global Perception Text reading 25 See ColOr – CVML (2013) EXPERIMENT ONE: The Spinning Chair Spinning Chair Time (minutes) 5 6 Time(minutes) 5 4 3 2 1 4 1 3 2 1 0 Test4 Part. 1 Part. 2 Test3 Part. 3 Part. 4 Part. 5 Test2 Part. 6 Part. 7 Part. 8 Test 1 Part. 9 Part. 10 Test 1 Part. 1 2.8 Part. 2 3 Part. 3 4.2 Part. 4 2 Part. 5 5.1 Part. 6 1.9 Part. 7 2.1 Part. 8 2.8 Part. 9 1.4 Part. 10 2.3 Test2 2.4 3.4 3.7 2.2 4.3 1.7 2 2.6 1.8 1.9 Test3 2.5 3.1 3.8 2.7 3.9 2.5 2.2 3.1 1 1.7 Test4 2.7 3.3 4.5 2.3 3.5 2.2 2.2 2.4 0.8 2 EXPERIMENT THREE: Finding Juan 10 Time (minutes) Finding a Person 12 6 4 2 10 Time(minutes) 8 1 8 6 4 2 0 Test 4 Part. 1 Part. 2 Test 3 Part. 3 Part. 4 Part. 5 Test 2 Part. 6 Part. 7 Part. 8 Test 1 Part. 9 Part. 10 Test 1 Part. 1 5.4 Part. 2 5.8 Part. 3 10.2 Part. 4 6.3 Part. 5 2.6 Part. 6 3.1 Part. 7 9.5 Part. 8 0.7 Part. 9 1.2 Part. 10 8.7 Test 2 5.8 6.6 4.2 2.1 1.8 4.5 4 1.2 0.7 6.5 Test 3 5.6 5.9 5.2 1.8 3.5 6.2 4.2 2.2 1.5 3.3 Test 4 5.6 6.5 4.8 2.1 2 1.2 1.7 3 4 5.1 EXPERIMENT TWO: Walking Towards a Wall EXPERIMENT FOUR: Grasping Objects Conclusions • Sonification of two very important vision features (colour and depth) made it possible to achieve a number of tasks related to mobility and recognition. • We will pursue to define new challenging experiments requiring the activation of several See ColOr modules. • We hope that new small 3D RGB cameras will be in the market soon (like the new Kinect Capri) ! 35