File - Taran D. Thompson
advertisement

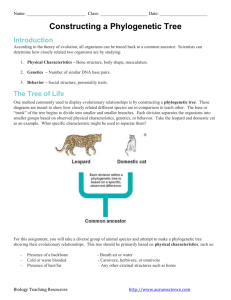
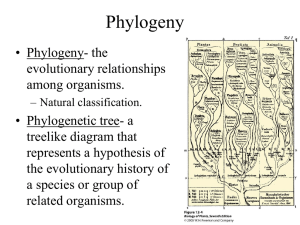
Ch. 10 Classification and Phylogeny of Animals ORDER from DIVERSITY! 1.5 million species of animals named, thousands added every year “Natural System” of classification: Animals grouped according to evolutionary relationships based on shared features Systematic Classification Based on Comparative biology Studies variations among animal populations 3 goals of Systematic Zoologists: – Discover all species of animals – Reconstruct their evolutionary relationships – Classify them accordingly Linnaeus & Classification Each level is called a taxon. This is the taxonomy of a human. Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Primates Family: Hominidae Genus: Homo Species: sapiens These are the 7 mandatory taxons To Remember… Use a memory sentence to remember the order of the taxa, like… Kings King Play Phillip Chess Came On Over Fine For Green Great Silk Spaghetti Naming Scientific names or Latin names 2 names = BINOMIAL NOEMNCLATURE of the last two taxa – Genus species – Ex. Thunnus albacares Naming TRINOMIAL NOMENCLATURE? Subspecies Examples: Animals: breeds, races, ethnicity Plants: breeds, varieties Somateria mollissima dresseri Somateria mollissima borealis What is a species? GENERAL DEFINITION An interbreeding population Smallest phylogenetic grouping Has a geographic range (where it is found) Has a evolutionary duration (when it has lived) Species COSMOPOLITAN – large, even worldwide distribution ENDEMIC – small or restricted range of habitat Wallaroos Typological Species Concept Species defined by fixed, immutable morphological features Defined a species with a Type Specimen Pre-dates Darwin but many features of this system still used. Biological Species Concept -Based on interbreeding populations of common descent that occupies a specific niche and share morphology. -Sibling Species: morphologically identical populations that do not interbreed (ecological races) Evolutionary Species Concept - Addresses time dimension lacking in biological concept - Can include fossils - Single lineage of ancestor-descendant populations distinct from other lineages Phylogenetic Species Concept Based on groupings that cannot be subdivided further with physical AND evolutionary characteristics Emphasizes common descent Most useful in Modern Cladistics Phylogeny Study of the phyla, evolutionary “tree” that relates extant and extinct species. Accomplished by studying characters, features used for comparison Characters Homology – similar characteristics that come from a similar ancestry (divergent evolution) Homeoplasy - similar characteristics that come from a different ancestry (convergent evolution) Ancestral (relictual) – trait shared with ancestors Derived – “new” trait, different from ancestors Sources of Characters (Phylogenetic Info) Morphology/ anatomy/physiology Evolution Biochemistry (enzymes, DNA) Environmental aspects Comparative cytology Organization/Diagrams Clades – species that share derived characteristics form groups called clades, unit of evolutionary common descent Cladogram – a branching classification diagram that shows NESTED hierarchies of organisms; branch length arbitrary Simple cladogram Characteristics to the right indicate what groups branch out, and when Branches to the left show the groups that do not have the necessary characteristics to continue on the “family tree” http://dragon.seowon.ac.kr/~bioedu/bio/ohp/t-130.jpg Cladogram based on characters science.kennesaw.edu/.../LecIntro/CladVert.GIF Characters are listed in the table to the left Cladogram shows how these characteristics and groups branching off are sorted Sphyraena Pomatomus Acanthocybium Sarda Auxis rochei Scombridae Auxis thazard Scomber Lepidocybium Ruvettus Neoepinnula Gempylus Thyrsites Nesiarchus Rexea Gempylidae Paradiplospinus Diplospinus Promethichthys Nealotus Assurger Cladogram made from genetic characteristics Lepidopus altifrons Trichiurus Lepidopus caudatus Aphanopus Benthodesmus Trichiuridae Organization/Diagrams Phylogenetic Tree – diagram representing REAL evolutionary lineages; branch length indicate ancestors, relative amount of changes in characters Phylogenetic Tree – distances depict changes Phylogenetic Trees Kingdoms Whittaker’s Five-Kingdom classification