Use the following information to fill in the Venn Diagram below. 120
advertisement
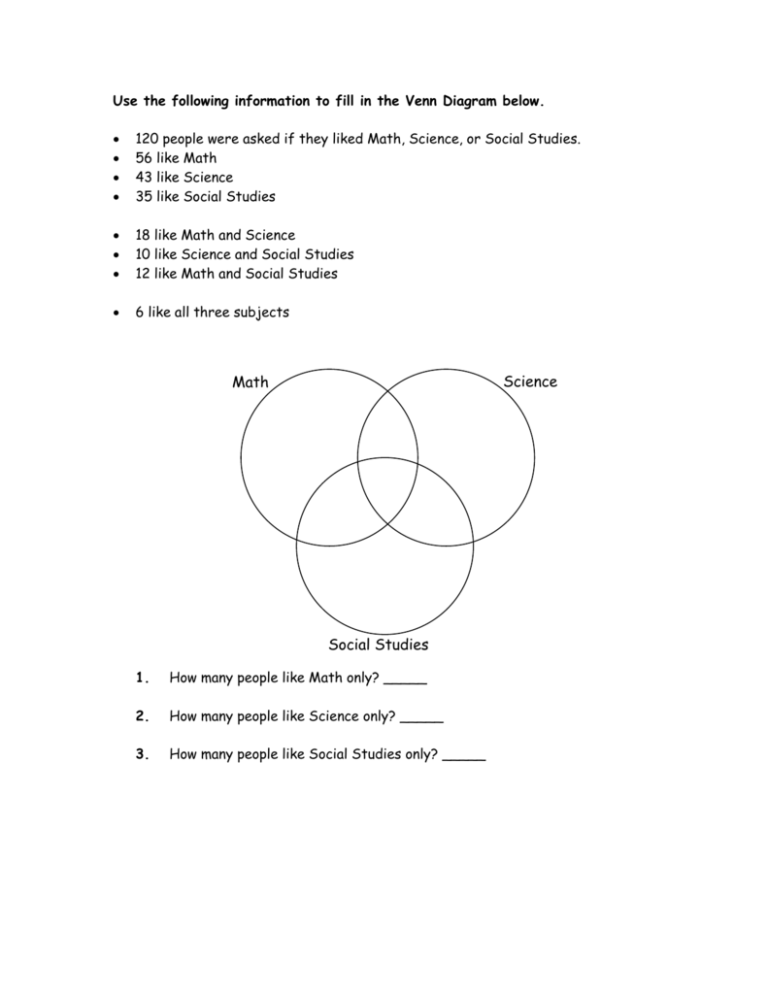
Use the following information to fill in the Venn Diagram below. 120 people were asked if they liked Math, Science, or Social Studies. 56 like Math 43 like Science 35 like Social Studies 18 like Math and Science 10 like Science and Social Studies 12 like Math and Social Studies 6 like all three subjects Science Math Social Studies 1. How many people like Math only? _____ 2. How many people like Science only? _____ 3. How many people like Social Studies only? _____ Objective: Students will be able to construct probability models, compute probability of equal likely events and use the addition rule to find probabilities Example 1: A fair coin is tossed twice, what are the possible outcomes? List them in a set. What is the probability that the outcome is HH? Create a probability model. Example 2: A coin is weighted so that heads is three times as likely to occur as tails. Construct a probability model for this experiment. PROBABILITY FOR EQUAL LIKELY OUTCOMES P(E)=____________________________ Example 3: Calculate the probability that in a 3-child family there are 2 boys and 1 girl. Assume equal likely outcomes. Example 4: One card is drawn from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. What is the probability of drawing… P(ace) = ________ P(face card) = _________ P(a red 10) = ________ P(NOT a diamond) = ______________ Example 5: Consider the experiment of rolling a single fair die. Let E represent the event “roll an even number” and let F represent the event “roll a 1 or 2.” Write the events E and F Write out the event E or F Compute P(E) and P(F) Compute P(E F) Compute P(E F) Example 6: A card is chosen from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. What is the probability that the card will be: a king or a queen? a red jack or a black king? a face card or a card with a prime number? an even card or a red card? a spade or a jack? Example 7: Look at the solution to the following problem and see if you can find the error. Correct the error to find the right answer. P(drawing an ace OR a black card) = P(ace) + P(black) = 4 26 30 15 + = = 52 52 52 26 Example 8: If P(E)=0.2, P(F)=0.3, and P(E F) 0.1, find P(E F) . PROBABILITY OF MUTUALLY EXCLUSIVE EVENTS Look at your Venn Diagram and find P(M)= P(S)= P(SS)= P(SS M) = P(S M) = P(M) =