Math 1 Name_________________________ U1 L2 I3 Intro to
advertisement

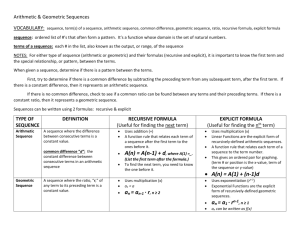
Math 1 U1 L2 I3 Intro to Sequences Name_________________________ Learning goals: I can convert a sequence into a recursive or explicit formula. I can use a formula to find missing terms in a sequence. I can determine the common difference/ratio from a sequence. I can identify linear and exponential situations and distinguish between the two. I can construct a linear or exponential function from an arithmetic sequence, table of values or verbal description. A sequence is an ordered list of numbers. The sequence is named with a letter and a subscript, for example an . The letter is used to name the sequence, and the subscript (“n”) refers to the position of a number in the sequence. For instance, a4 would refer to the 4th term in sequence a. an would be the nth term in the sequence. Suppose an was the 8th term in a sequence. an-1 would be the ____________ term. Given the sequence 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, ... Find the following terms: a4 _____ ; a1 _____ ; a9 _____ ; Formulas for Sequence Some sequences have formulas that generate them. Formulas can be either explicit or recursive. An explicit formula is a formula that allows direct computation of any term in the sequence. A recursive formula requires the computation of all previous terms in order to find the value of term an . Consider the sequence 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, ... The explicit formula for this sequence is an 2n a1 2 The recursive formula for this sequence is an an 1 2 Note that for the recursive formula, you must know the first term, then you define the rest of the terms in relation to the first term. Write out the first five terms of the following sequences: g n 2n 1 ______, ______, ______, ______, ______ ki i 2 1 ______, ______, ______, ______, ______ q1 3 qn 2 qn1 ______, ______, ______, ______, ______ b1 4 bn 2 bn 1 3 ______, ______, ______, ______, ______ III. Arithmetic Sequences An arithmetic sequence is a sequence in which the difference between two consecutive terms is the same. The common difference is found by subtracting any term from its succeeding term. The nth term ( an ) of an arithmetic sequence with first term a1 and the common difference is d is given by the following formula: A. Name the first five terms of each arithmetic sequence defined below. An example is given. Example: B. an a1 d n 1 a1 2, d 3 1. a1 4, d 3 2. a1 7, d 5 3. 4 a1 , d 1 5 Name the next four terms of each of the following arithmetic sequences: Example: 5, 9, 13 1. 21, 15, 9 2. 11, 14, 17 3. 9.9, 13.7, 17.5 C. Write out the first four terms of the following arithmetic sequences; then write an explicit and recursive formula. Example: D. a1 7, d 3 1. a1 1, d 10 2. a1 2, d 3. a1 27, d 16 1 2 Find the indicated term in each arithmetic sequence: Example: a12 for -17, -13, -9, . . . 1. a21 for 10, 7, 4 2. a10 for 8, 3, -2 3. a12 for 3, 4.1, 5.2, 6.3 E. Determine the desired term? Example: F. Which term of -2, 5, 12, . . . is 124? 1. Which term of -3, 2, 7, . . . is 142? 2. Which term of 7, 2, -3, . . . is -28? Find the missing terms of the following arithmetic sequences: Example: 55, ______, ______, ______, 115 1. -10, ______, ______, ______, ______, -4 2. 2, ______, ______, ______, ______, ______, 20 II. Geometric Sequences A geometric sequence is a sequence in which each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous term by a constant. In any geometric sequence, the constant or common ratio is found by dividing any term by the previous term. The nth term ( an ) of a geometric sequence with first term a1 and constant ratio r is given by the formula an a1 r n 1 Consider the sequence 4, 12, 36, 108, ... n1 The explicit formula for this sequence is g n 4 3 g1 4 The recursive formula for this sequence is g n 3 g n 1 A. Determine which of the following sequences are geometric. If it is a geometric sequence, find the common ratio. Example: B. 4, 20, 100, 500 1. 7, 14, 28, 56, . . . 2. 2, 4, 6, 8, . . . 3. 3, 9, 27, 54, . . . 4. 9, 6, 4, 8 3 Find the next two terms for each geometric sequence: Example: 729, 243, 81, . . . 1. 20, 30, 45, . . . 2. 90, 30, 10, . . . 3. 2, 6, 18, . . . C. Find the first four terms of each geometric sequence described below: Example: D. 1. a1 3, r 2 2. a1 12, r 3. a1 27, r 1 2 1 3 Find the nth term of each geometric sequence described below: Example: E. 3 a1 , r 2 2 a1 4, r 5, n 3 1. a1 4, r 2, n 3 2. a1 2, r 2, n 5 3. 1 a1 32, r , n 6 2 Find the missing terms of the following geometric sequences: Example: 1. 3, ______, ______, ______, 48 243, ______, ______, ______, 3