1.4 Notes Power Point - Science with Mrs. Lambert

Science and Measurement
Chapter 1.4
The Foundations of Physical
Science
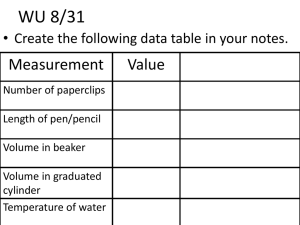
Working With Measurements
All measurements involve a degree of uncertainty
How much error or uncertainty is acceptable?
In the real world, it is IMPOSSIBLE to make measurement of the exact true value of anything (except counting)
Significant Digits
Significant Digits or Significant Figures (or Sig
Figs for short) are the meaningful digits in a measured quantity
If you measure a paperclip and it is between
2.6 and 2.7. We usually say 2.65 cm
But to a scientist 2.65 means between 2.62 and 2.67
The final digit in 2.65 is the 5, it represents the smallest amount and is always considered to be rounded up or down
Rules for Significant Digits
Digits that are ALWAYS significant
1. Non-zero numbers
Examples: 54982 = 5 2365149898= 10
2. Zeros between two significant digits
Examples: 93100008= 8 1001= 4
3. All final zeros to the right of a decimal point
Examples: 4451.630= 7 5012677.26090= 12
Rules for Significant Digits
Digits that are NEVER significant
1. Leading zeros to the right of a decimal point
Examples: 0.002= 1 0.000456= 3
2. Final zeros in a number that does not have a decimal point
Examples: 9900000= 2 8765210= 6
WANT A SHORT CUT???
This method depends on a question .
When you are attempting to determine the number of sig fig’s in a number, ask yourself:
Is the decimal point PRESENT or
ABSENT ?
Is the decimal point PRESENT or ABSENT?
If the decimal point is NOT WRITTEN in the number, start on the RIGHT side of the number, go through any zero until you get to the first nonzero digit, underline it and all other numbers.
The number of underlines is the number of sig fig’s!
300 = __ 1 ___ 2100 = __ 2 ___ 7890900 = __ 5 ___
Is the decimal point
PRESENT or ABSENT?
If the decimal point IS WRITTEN in the number, start on the LEFT side of the number, go through any zero until you get to the first nonzero digit, underline it and all other numbers. The number of underlines is the number of sig fig’s!
0.0033 = __ 2 ___ 0.000 000 4040 = __ 4 ___
2.0000 = ___ 5 __
Significant Figures
Addition/Subtraction Rule
For addition or subtraction, your answer should be rounded off to the LEAST number of decimal places in the problem.
325.471
+ 77.210
402.681 Using the rule, this answer should be reported
as 402 .68
1207.2
- 756.739
450.461 Using the rule, this answer should be reported
as 450.5
Significant Figures
Multiplication/Division Rule
For multiplication and division problems, your answer should have the same number of sig. figs. as the LEAST number of sig. figs. in the problem.
How many sig. figs.? 3 2 = 2 .
2.51
61 = __ 153.11
_____ Final Answer _ 150 ___
How many sig. figs.? 2 / 3 = 2 .
450/32.1 = 14.0186915
Final Answer ___ 14 ___
Accuracy, Precision, and
Resolution
Accuracy- how close a measurement is to an accepted or true value
Precision- describes how close together or reproducible reproducible repeated measurements are
Resolution- refers to the smallest interval that can be measured
Significant Differences
In everyday conversation, “ same ” means two numbers that are the same exactly, like 2.56 and 2.56.
When comparing scientific results “same” means “ not significantly different ”.
Significant differences are differences that are MUCH larger than the estimated error in the results
Error and Significance
How can you tell if two results are the same when both contain
(uncertainty)?
error
When we estimate error in a data set, we will assume the average is the exact value .
If the difference in the averages is at least three times larger than the average error , we say the difference is “ significant” .
Error
How you can you tell if two results are the same when both contain error.
Calculate error
Average error
Compare average error