Chapter 12 _B_ John Marshall
advertisement

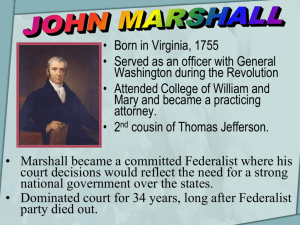
Most Important Justice in Supreme Court history Significantly strengthened the Supreme Court in Marbury v Madison(1803) and other cases. His decisions greatly increased power of the federal government over the states. Born in Virginia, 1755 Served as an officer with General Washington during the Revolution Attended College of William and Mary and became a practicing attorney. 2nd cousin of Thomas Jefferson. Marshall became a committed Federalist where his court decisions would reflect the need for a strong national government over the states. Dominated court for 34 years, long after Federalist party died out. Strengthened the federal government His decisions at times and helpeddemocracy create a hampered stable environment just when America for business. was becoming more democratic. Checked the excesses (Jacksonian Period) of the popularly elected state legislatures. Examined cases from a Federalist philosophy and found legal precedents to support his Hamiltonian views.. Jeffersonian attempts to balance the Court with Republicans failed. Republicans came to accept the Federalist ideal of strong central government.. Evolves As A Federalist 1. US troops suffer at Valley Forge Need a strong government to tax which AOC could not provide 2. Merchants refused to pay debts to British Need strong to government to demand obedience AOC could not provide 3. Shay’s Rebellion “mobocracy” Need a strong government to maintain order AOC could not provide Evolves As A Federalist 4. French Revolution Importance of US Government to maintain order. 5. Controversial: Neutrality/Whiskey Rebellion Individuals should respect the office of the presidency even if one disagrees with decisions. 6. XYZ Affair US Government needed to be powerful enough to command respect from other nations. Evolves As A Federalist 7. Kentucky/Virginia Resolutions States not the final authority over law but SC. 8. Appointed as Chief Justice Increase powers of SC and national government. 9. Republicans took control of US Congress As chief justice, implements Federalist principles. Protection of Property Rights Against Popular Pressures Issue: new Georgia legislature canceled a contract which granted 35 million acres in the Yazoo River county to land speculators as a form of graft Decision: Court ruled Constitution forbids state from "impairing contracts" One of earliest examples of Court asserting its right to invalidate state laws Court stated the legislative grant was a contract (albeit fraudulently secured) “Steamboat Case" Setback to States' Rights Issue: In 1808 the State of New York An attempt state monopoly of New York granted by an the exclusive to to grant to anavigation private company a monopoly of a privileges of waterway between NewNew York andto New the waterway from York Jersey. (Meaning no other company Newthat Jersey. could use the channel.) “Steamboat Case" Setback to States' Rights Decision: Only Congress had the An attempt by theinterstate state of New York to right to regulate commerce. grant to a private company a monopoly of a waterway between New rivers York and New Court ruled interstate were to Jersey. (Meaning that no not other company regulated by Congress, individual could usestates. the channel.) Issue: Maryland tried to destroy its branch of the Bank of the U.S. by taxing its notes. Decision: Marshall declared Bank of U.S. constitutional, denying the right of Maryland to tax the Bank. Marshall invoked Hamilton's doctrine of implied powers (elastic clause of the constitution ) “Necessary & Proper" "the power to tax involves the power to destroy” and "that a power to create implies the power to preserve." "Loose Construction" given major boost. Argued the Constitution derived from the consent of the people and thus permitted the government to act for their benefit. Protection Of Property Rights From The States Issue: New Hampshire had reversed a charter granted to the college by the British king in 1769. Republicans sought to remove "private" aspect of school & make it a state institution. Dartmouth appealed; defended by Daniel Webster, an alumnus. Decision: Charter was a contract; states could not cancel a legal agreement. Significance Positive: safeguarded business from domination by the states. Negative: set precedent giving corporations ability to escape government control. Argued Federalist and nationalist views before the Supreme Court. He actually "ghost wrote“ some of the Marshall’s opinions. Classic speeches in the Senate, challenging states' rights and nullification, were similar to arguments he earlier made to the Supreme Court. Virginia sought to disregard Treaty of Paris (1783) and Jay’s Treaty (1794) regarding confiscation of Loyalist lands. Issue Did the Supreme Court (as stated in Judiciary Act of 1789) have the right to review decisions of state supreme courts where federal statutes or treaties were involved or when state laws had been upheld under the Constitution? Decision Supreme Court rejected "compact theory“ and state claims that they (the states) were equally sovereign with the federal government. Significance Upheld Supremacy Clause of the Constitution and federal judicial supremacy over the states. Involved the Cohen brothers appealing to the Supreme Court for being found guilty of illegally selling lottery tickets by the state of Virginia. Issue: whether the Supreme Court had jurisdiction to hear an appeal in a criminal case decided by the courts of the state of Virginia. Virginia won and the conviction was upheld. Significance: Decision affirmed the Court's assertion of its power to review state supreme court decisions in criminal law matters when the defendant claims that their Constitutional rights have been violated. JUDICIAL AUTHORITY Marbury vs. Madison NATIONALISM McCulloch vs. Maryland Gibbons vs. Ogden Cohens vs. Virginia PROPERTY RIGHTS Dartmouth College vs. Woodward Fletcher vs. Peck JUDICIAL AUTHORITY Supreme Court has the power to declare a law unconstitutional with the principle of judicial review. NATIONALISM The National Government has supremacy over the states. PROPERTY RIGHTS Private property is sacred and contracts legal.