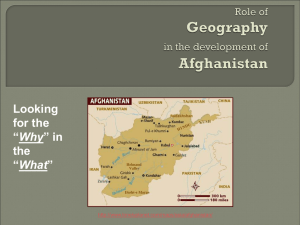
gender_and_change1
advertisement

What’s the story? Women are on the rise? • https://www.ted.com/talks/hanna_rosin_new _data_on_the_rise_of_women As population has changed what has happened to women? • Key question – what gender imbalances exist globally? Labour force participation of women http://hdrstats.undp.org/en/indicators/489 06.Html USA 0.82 UK 0.81 Philippines 0.62 This compares how many women work for every man working Population with secondary education – male-female ratio • http://hdrstats.undp.org/en/indicators/24806.htm USA 1.004 UK 1.015 Philippines 1.035 This means that USA has more females finishing secondary school than men. Female members of government http://hdrstats.undp.org/en/indicators/83506.html USA 0.2 UK 0.28 Philippines 0.285 So Philippines parliament is 28% women Literacy (can people read and write) http://www.prb.org/DataFinder/Topic/Rankings.aspx?ind=20 USA Men 99% Female 99% UK Men 99% Female 99% Philippines Men 96% Female 94% USA – women’s wages as % of men UK Salaries favour men? Gender and change Objective – to understand gender inequalities in culture, status, education, birth ratios, employment, empowerment, life expectancy, family size, migration, legal rights and land tenure Surely in The Philippines women earn as much as men? Women earn an average wage that is 7.3 percent lower than men’s average wages. Female factory workers earn on an average P296.36 daily, lower than men’s daily rate of P319.75 http://www.eiler.ph/2-3-million-filipino-women-render-unpaid-work-prone-to-abuse-%E2%80%93-think-tank/ Is there anywhere on the planet where women are equal? • In some or all of these areas? Its not just the poor or Muslim countries… • In 2011, women ran only 12 of the Fortune 500 companies. • In 2010, women made up 31.5% of all lawyers but were only 19.5% of partners in U.S. law firms according to Catalyst. Additionally, 11% of the largest law firms in the U.S. had no women on their governing committees. • No state has ever achieved federal or state judgeships gender equality. Women held only 23% of all federal judgeships and only 27% of state judgeships in 2010. In its 220-year history, only four women justices have served on the Supreme Court although we currently have the all time high of three justices out of nine. • Today in the 112th Congress women hold 17 Senate seats out of 100 and hold 92 out of 435 House seats. • USA has never had a woman President. • Men outnumber women at a rate of 73% vs. 27% in all sectors of employment for science and engineering as of 2009. http://www.wrc.org.uk/resources/facts_and_statistics_on_womens_inequality_in_the _uk.aspx UK • • • • • In 2007/08, only 19% of MPs, and 20% of the House of Lords were female. From 2006 to 2007/8, the number of female members of the cabinet fell from 35% in 2006 to 26%. In 2007/08, women made up 0.4 in senior ranks in the armed forces, 27% in civil service top management, 21% of trade union General Secretaries or equivalent, 20% of local authority Chief Executives and only 14% of local authority Council Leaders. In 2007, there were 34.4% of women in public appointments and 6.5% women from ethnic minority women in Public Appointments. In 2006 it was reported that the gender pay gap in the UK is one of the highest in Europe: women who work full-time earned 17% less per hour than men. Women working part-time earned 39% less per hour than men working fulltime. In 2007, median weekly earnings of full-time employees for women of £394 were 21% less than those for men (£498). In 2007, median weekly earnings of fulltime employees for women of £394 were 21% less than those for men (£498). Model in Malaysia to Be Caned for Drinking Beer • KUALA LUMPUR, Malaysia (AP) -A Muslim part-time model will be caned next week, becoming the first woman in Malaysia to be given the punishment under Islamic law, after she pleaded guilty to drinking beer, a prosecutor said Wednesday. • An Islamic court in July ordered that Kartika Sari Dewi Shukarno, 32, be lashed six times with a rattan cane after she was caught drinking alcohol in a raid on a hotel night club in eastern Pahang state last year. Gender and population growth • In many countries high rates of population growth are associated with a low status of women • The UN Decade For Women, from 1975 to 1985, recommended 3 important points for action: • There should be legal equality for women • Further development needs to improve on the substandard role that women play • Women should receive an equal share of power Estimated adult literacy by region and gender, 1995… has it improved? Number of girls per 100 boys in primary school Proportion of seats held in national parliament by women (%) Labour force participation rate, female (% of female population ages 15-64) Gender pay gap in the EU, 2005 • gender pay uk.docx • saudi olympics.docx 1 of 5 Case Study: Afghanistan • 1920s - King Amanullah and Queen Soraya began reforming strict social customs that disenfranchised women • These included the wearing of head-to-toe veils in public, seclusion of women, arranged marriages, FGM, restricted access to education and work, and other harsh traditions • However, from the end of the 20s through the beginning of the 60s, the old codes were once again enforced 2 of 5 Gender Inequality: Afghanistan • mid 1960s - change began to be felt in Afghanistan, resulting in the election of the first woman cabinet member, a relaxing of dress codes and even the adoption of the far less restrictive clothing of Western women • Many freedoms were granted while the communists were in power from 1978 to 1996, including the right of women to work 3 of 5 Afghanistan case study Taliban Rule • But when the Taliban took over in 1996, they brought with them the harshest restrictions on women's rights of the century. • These included severe restrictions on participation in public life and extremely limited access to education, work, travel, health care, legal resources and recreation 4 of 5 Afghanistan case study • the literacy rate, which was only 27% for men, dropped to a 5.6% for women. • The Taliban issued edicts forbidding women from working outside the home except under limited circumstances in the medical field; hardest hit were the 30,000 widows who were sole providers for their families • women and girls in certain regions were required to wear a head to toe covering called the burqa when out in public. Women were also forbidden to appear in public with a male who was not their relative 5 of 5 Case Study: Afghanistan • the Taliban has been removed from rule in Afghanistan. But, as many Afghan women and political observers are quick to point out, their successors, the Northern Alliance, are also implicated in many human rights violations and must be pressured by the international community if women are to have a greater role in the future of Afghanistan. Index of gender equality Why does the Philippines score so well? GDI (gender-related development index) • Gender-related development index (GDI) measures the inequality between the sexes in life expectancy, education and the standard of living Gender-related development index (GDI) rank HDI Rank Country 1 Iceland 2 Norway 3 Australia 4 Canada 5 Ireland 6 Sweden 7 Switzerland 8 Japan 9 Netherlands 10 France 2005 1 3 2 4 15 5 9 13 6 7 GDI (gender-related development index) Gender-related development index (GDI) rank HDI Rank Country 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 2005 Congo (Democratic Republic of the) Ethiopia Chad Central African Republic 152 Mozambique Mali Niger Guinea-Bissau 155 Burkina Faso Sierra Leone 147 148 151 149 150 154 153 156 Gender inequalities Task: • Complete the table to show the various factors and their influence on gender inequalities. As we work through….. • Make reference to place specific examples. • Resources: • Powerpoint slides which you can share amongst yourselves • IB Geography text p 23-27 • Planet geography p.48-58 Explain the relationship between _______ and the status of women [5 marks] Examine gender inequalities in culture, status, education, birth ratios, employment, empowerment, life expectancy, family size, migration, legal rights and land tenure How to answer the exam question • State the relationship [1] e.g. higher the status the lower the fertility level • Explain the relationship for higher status [1] give an example [1] e.g. higher status more educated therefore have sex ed and may be career driven e.g UK fertility rate is 1.6 • Explain the relationship for lower status [1] give an example [1] Updating case studies • • • • • Saudi – driving protests Philippines – recent elections and pay divide China – do they own their own bodies now? Norway – the best place to be a woman? Afghanistan - better now Taliban has gone? Objective – to understand gender inequalities in culture, status, education, birth ratios, employment, empowerment, life expectancy, family size, migration, legal rights and land tenure