H5_RD100.Poster-2002
advertisement
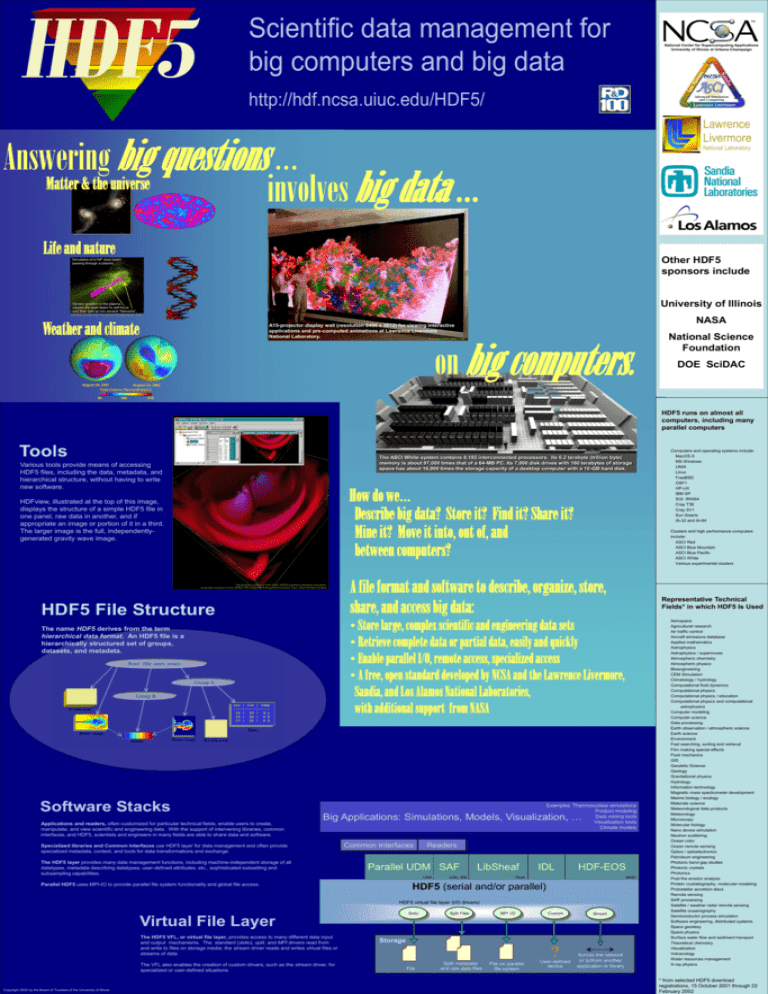
Scientific data management for big computers and big data National Center for Supercomputing Applications University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign http://hdf.ncsa.uiuc.edu/HDF5/ Lawrence Livermore Answering big questions … Matter & the universe involves big data … National Laboratory Life and nature Other HDF5 sponsors include Simulation of a NIF laser beam passing through a plasma. University of Illinois Density gradient in the plasma causes the laser beam to self-focus and then split up into several "filaments". Simulation by Bert Still, Visualization by Steve Langer, LLNL Weather and climate August 24, 2001 NASA A15-projector display wall (resolution 6400 x 3072) for viewing interactive applications and pre-computed animations at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. Courtesy of Arthur Mirin, LLNL on big computers. National Science Foundation DOE SciDAC August 24, 2002 Total Column Ozone (Dobson) 60 385 610 HDF5 runs on almost all computers, including many parallel computers Tools The ASCI White system contains 8,192 interconnected processors. Its 6.2 terabyte (trillion byte) memory is about 97,000 times that of a 64-MB PC. Its 7,000 disk drives with 160 terabytes of storage space has about 16,000 times the storage capacity of a desktop computer with a 10-GB hard disk. Various tools provide means of accessing HDF5 files, including the data, metadata, and hierarchical structure, without having to write new software. How do we… Describe big data? Store it? Find it? Share it? Mine it? Move it into, out of, and between computers? HDFview, illustrated at the top of this image, displays the structure of a simple HDF5 file in one panel, raw data in another, and if appropriate an image or portion of it in a third. The larger image is the full, independentlygenerated gravity wave image. Visualization courtesy of John Shalf, NERSC/Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, using data computed on the NERSC SP2 by Dennis Pollney and the Cactus Team, Albert Einstein Institute HDF5 File Structure Software Stacks Applications and readers, often customized for particular technical fields, enable users to create, manipulate, and view scientific and engineering data. With the support of intervening libraries, common interfaces, and HDF5, scientists and engineers in many fields are able to share data and software. Clusters and high performance computers include: ASCI Red ASCI Blue Mountain ASCI Blue Pacific ASCI White Various experimental clusters A file format and software to describe, organize, store, share, and access big data: Examples: Thermonuclear simulations Product modeling Data mining tools Visualization tools Climate models Big Applications: Simulations, Models, Visualization, … Specialized libraries and Common Interfaces use HDF5 layer for data management and often provide specialized metadata, context, and tools for data transformations and exchange. The HDF5 layer provides many data management functions, including machine-independent storage of all datatypes, metadata describing datatypes, user-defined attributes, etc., sophisticated subsetting and subsampling capabilities. Common Interfaces Readers Parallel UDM SAF LANL Parallel HDF5 uses MPI-IO to provide parallel file system functionality and global file access. LibSheaf LLNL, SNL IDL HDF-EOS TriLab NASA HDF5 (serial and/or parallel) HDF5 virtual file layer (I/O drivers) Stdio Split Files MPI I/O Custom Virtual File Layer The HDF5 VFL, or virtual file layer, provides access to many different data input and output mechanisms. The standard (stdio), split, and MPI drivers read from and write to files on storage media; the stream driver reads and writes virtual files or streams of data. The VFL also enables the creation of custom drivers, such as the stream driver, for specialized or user-defined situations. Copyright 2002 by the Board of Trustees of the University of Illinois Representative Technical Fields* in which HDF5 Is Used • Store large, complex scientific and engineering data sets • Retrieve complete data or partial data, easily and quickly • Enable parallel I/O, remote access, specialized access • A free, open standard developed by NCSA and the Lawrence Livermore, Sandia, and Los Alamos National Laboratories, with additional support from NASA The name HDF5 derives from the term hierarchical data format. An HDF5 file is a hierarchically structured set of groups, datasets, and metadata. Stream Storage ? File Split metadata and raw data files File on parallel file system User-defined device Computers and operating systems include: MacOS X MS Windows UNIX Linux FreeBSD OSF1 HP-UX IBM SP SGI IRIX64 Cray T3E Cray SV1 Sun Solaris IA-32 and IA-64 Across the network or to/from another application or library Aerospace Agricultural research Air traffic control Aircraft emissions database Applied mathematics Astrophysics Astrophysics / supernovae Atmospheric chemistry Atmospheric physics Bioengineering CEM Simulation Climatology / hydrology Computational fluid dynamics Computational physics Computational physics / education Computational physics and computational astrophysics Computer modeling Computer science Data processing Earth observation / atmospheric science Earth science Environment Fast searching, sorting and retrieval Film making special effects Fluid mechanics GIS Geodetic Science Geology Gravitational physics Hydrology Information technology Magnetic mass spectrometer development Marine biology / ecology Materials science Meteorological data products Meteorology Microscopy Molecular biology Nano device simulation Neutron scattering Ocean color Ocean remote sensing Optics / optoelectronics Petroleum engineering Photonic band gap studies Photonic crystals Photonics Post-fire erosion analysis Protein crystallography, molecular modeling Protostellar accretion discs Remote sensing SAR processing Satellite / weather radar remote sensing Satellite oceanography Semiconductor process simulation Software engineering, distributed systems Space geodesy Space physics Surface water flow and sediment transport Theoretical chemistry Visualization Volcanology Water resources management X-ray physics * from selected HDF5 download registrations, 15 October 2001 through 22 February 2002