Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
advertisement

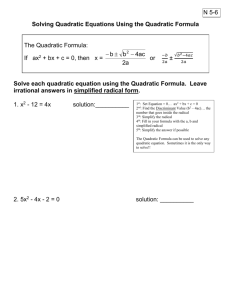
Solving Quadratic Equations by the Quadratic Formula THE QUADRATIC FORMULA 1. When you solve using completing the square on the general formula ax 2 bx c 0 you get: b b2 4ac x 2a 2. This is the quadratic formula! 3. Just identify a, b, and c then substitute into the formula. WHY USE THE QUADRATIC FORMULA? The quadratic formula allows you to solve ANY quadratic equation, even if you cannot factor it. An important piece of the quadratic formula is what’s under the radical: b2 – 4ac This piece is called the discriminant. WHY IS THE DISCRIMINANT IMPORTANT? The discriminant tells you the number and types of answers (roots) you will get. The discriminant can be +, –, or 0 which actually tells you a lot! Since the discriminant is under a radical, think about what it means if you have a positive or negative number or 0 under the radical. WHAT THE DISCRIMINANT TELLS YOU! Value of the Discriminant Nature of the Solutions Negative 2 imaginary solutions Zero 1 Real Solution Positive – perfect square 2 Reals- Rational Positive – non-perfect square 2 Reals- Irrational Example #1 Find the value of the discriminant and describe the nature of the roots (real,imaginary, rational, irrational) of each quadratic equation. Then solve the equation using the quadratic formula) 1. 2 x 2 7 x 11 0 Discriminant = a=2, b=7, c=-11 b 2 4ac (7) 2 4(2)( 11) 49 88 Discriminant = 137 Value of discriminant=137 Positive-NON perfect square Nature of the Roots – 2 Reals - Irrational Example #1- continued Solve using the Quadratic Formula 2 x 2 7 x 11 0 a 2, b 7, c 11 b b 2 4ac 2a 7 7 2 4(2)(11) 2(2) 7 137 4 2 Reals - Irrational Solving Quadratic Equations by the Quadratic Formula Try the following examples. Do your work on your paper and then check your answers. 1. x 2 x 63 0 2 2. x 8 x 84 0 2 3. x 5 x 24 0 2 4. x 2 7 x 13 0 5. 3 x 2 5 x 6 0 1. 9, 7 2.(6, 14) 3. 3,8 7 i 3 4. 2 5 i 47 5. 6