Lecture 22
advertisement

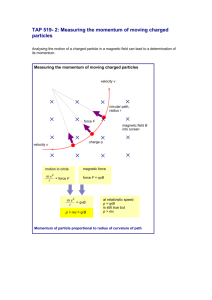
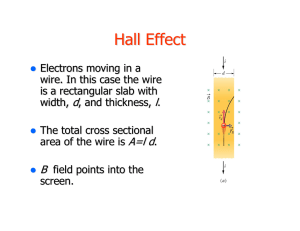
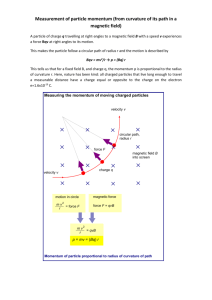
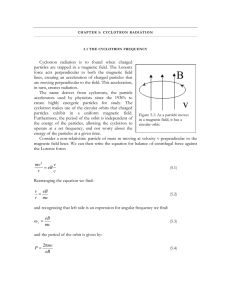
Charged Particles in Electric and Magnetic Fields • Motion of charged particles • Lorentz Force • Examples: cyclotron, mass spectrometer Recall: F qE in an electric field F qv B in a magnetic field F qv B qE in general, “Lorentz Force” Example: A positive charge q=3.2x10-19 C moves with a velocity v=(2i+3j-k) m/s through a region where both a uniform magnetic and electric field exist. Calculate the force on the charge if B=(2i+4j+k) T and E=(4i-j-2k) V/m. Magnetic Fields: F = qvB q The force is perpendicular to x the velocity (and path), so: • no work is done by B • kinetic energy is constant • speed is constant x v + x x F x x Only the direction of the motion changes due to the magnetic force. Let’s look at these two special cases: x Bx 1) Uniform B, v perpendicular to B Magnetic force (v ) is x Fm = qvB (constant) v x x + q x F x But Fc = mv2/r , so the radius of circle is : mv r qB x Motion is a circle. x r x Example: A proton is moving in a circular orbit of radius 14cm in a uniform magnetic field of 0.35T directed perpendicular to the velocity of the proton. Find the orbital speed of the proton. 2) Uniform B, v not perpendicular to B x z v + y -path is a circular helix along a field line -the component v (parallel to B) is constant On a large scale, the particles follow the field lines. Frequency Angular frequency v qBr qB r mr m [rad/s] = "cyclotron frequency f " is independent of speed 2 and radius. = 1/T (period) 1 1 qBr q B r KE mv m 2 2 m 2m qBr sin ce v m 2 The kinetic energy of a particle at radius r is 2 2 2 2 The Cyclotron : accelerates particles to very high velocities x “dees” x Bx x x x x x + + x x AC Voltage Supply The electric field across the gap is reversed each time the proton arrives, so that its speed in the gap continually increases. Because the time for each half-circle is the same for any proton speed, the voltage supply can just be set to a constant frequency. Example: A cyclotron needs to accelerate electrons to a speed of 0.95c for experiments. Given that it can provide a magnetic field of 0.5T: a) what is the cyclotron frequency? b) what is the radius of the cyclotron? Quiz A cyclotron can accelerate protons to a maximum kinetic energy of 1 MeV. You want to design a new, improved model with a higher maximum proton energy. Which of the following changes would help? A) B) C) D) Double Double Double Double the magnetic field the diameter of the dees the proton current the voltage of the voltage supply The Velocity Selector: allows to select particles that move at the same velocity E x Source x + x x v x x x x x Detector B x E, B, v all Find: Conditions so that the path is straight. Free-body diagram: FM qvB x B + E FE qE v Need F 0 for straight path qvB qE E for straight path v B Question: FM qvB x B + E FE qE v How are the charges deflected that are either traveling too slow or too fast to travel in a straight line? Mass Spectrometer : separates ions according to their mass:charge ratio Ion Source Exercise: x x x x x x x x x x x x Uniform B radius depends on mass Assume 12C and 14C have same charge. Find the ratio of the diameters of the circular paths if the ions have the same speeds