The Lottery PowerPoint
advertisement

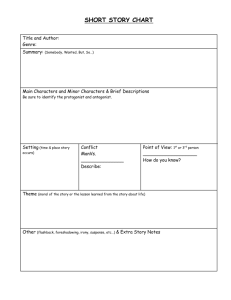
Short Story Unit A Theme The theme in a story is its underlying message, or 'big idea.' In other words, what critical belief about life is the author trying to convey in the writing of a novel, play, short story or poem? This belief, or idea, transcends cultural barriers. It is usually universal in nature. When a theme is universal, it touches on the human experience, regardless of race or language. It is what the story means. Often, a piece of writing will have more than one theme. Theme is an element of a story that binds together various other essential elements of a narrative. It is a truth that exhibits universality and stands true for people of all cultures. Theme gives readers better understanding of the main character’s conflicts, experiences, discoveries and emotions as they are derived from them. Through themes, a writer tries to give his readers an insight into how the world works or how he or she views human life. Foreshadowing Foreshadowing is a literary device in which a writer gives an advance hint of what is to come later in the story. Foreshadowing often appears at the beginning of a story or a chapter and helps the reader develop expectations about the coming events in a story. There are various ways of creating a foreshadowing. A writer may use dialogues of characters to hint at what may occur in future. In addition, any event or action in the story may throw a hint to the readers about future events or action. Even a title of a work or a chapter title can act as a clue that suggests what is going to happen. Foreshadowing in fiction creates an atmosphere of suspense in a story so that the readers are interested to know more. Characterization Characterization is a literary device that is used step by step in literature to highlight and explain the details about a character in a story. It is in the initial stage where the writer introduces the character with noticeable emergence and then following the introduction of the character, the writer often talks about his behavior; then as the story progresses, the thought-process of the character. The next stage involves the character expressing his opinions and ideas and getting into conversations with the rest of the characters. The final part shows how others in the story respond to the character’s personality. Irony Irony is a figure of speech in which words are used in such a way that their intended meaning is different from the actual meaning of the words. It may also be a situation that may end up in quite a different way than what is generally anticipated. In simple words, it is a difference between the appearance and the reality. Irony (continued) On the grounds of the above definition, we distinguish two basic kinds of irony i.e. verbal irony and situational irony. • A verbal irony involves what one does not mean. When in response to a foolish idea, we say, “what a great idea!” it is a verbal irony. • A situational irony occurs when, for instance, a man is chuckling at the misfortune of the other even when the same misfortune, in complete unawareness, is befalling him. Difference between Dramatic Irony and Situational Irony • Dramatic irony is a kind of irony in a situation, which the writers frequently employ in their works. • In situational irony, both the characters and the audience are fully unaware of the implications of the real situation. In dramatic irony, the characters are oblivious of the situation but the audience is not. Symbolism Symbolism is the use of symbols to signify ideas and qualities by giving them symbolic meanings that are different from their literal sense. Symbolism can take different forms. Generally, it is an object representing another to give it an entirely different meaning that is much deeper and more significant. Sometimes, however, an action, an event or a word spoken by someone may have a symbolic value. For instance, “smile” is a symbol of friendship. Similarly, the action of someone smiling at you may stand as a symbol of the feeling of affection which that person has for you. Symbols do shift their meanings depending on the context they are used in. “A chain”, for example, may stand for “union” as well as “imprisonment”. Thus, symbolic meaning of an object or an action is understood by when, where and how it is used. It also depends on who reads them Mood In literature, mood is a literary element that evokes certain feelings or vibes in readers through words and descriptions. Usually, mood is referred to as the atmosphere of a literary piece, as it creates an emotional situation that surrounds the readers. Mood is developed in a literary piece through various methods. It can be developed through setting, theme, tone and diction. Satire Satire is a technique employed by writers to expose and criticize foolishness and corruption of an individual or a society by using humor, irony, exaggeration or ridicule. It intends to improve humanity by criticizing its follies and foibles. A writer in a satire uses fictional characters, which stand for real people, to expose and condemn their corruption. A writer may point a satire toward a person, a country or even the entire world. Usually, a satire is a comical piece of writing which makes fun of an individual or a society to expose its stupidity and shortcomings. In addition, he hopes that those he criticizes will improve their characters by overcoming their weaknesses.