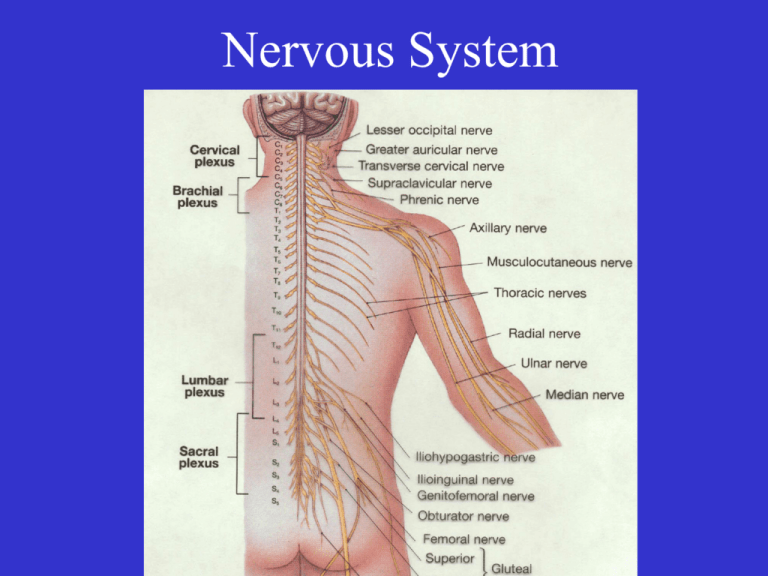
Nervous System
advertisement
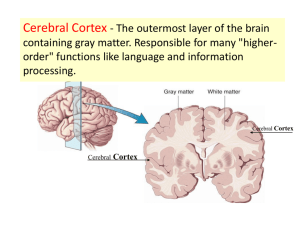
Nervous System • Anatomical Divisions – CNS • Brain • Spinal Cord • Anatomical Divisions – CNS • Brain • Spinal Cord – PNS • Spinal Nerves & Plexi • Anatomical Divisions – CNS • Brain • Spinal Cord – PNS • Spinal Nerves & Plexi • Cranial Nerves • Peripheral Nerves • Functional Divisions – Afferent – Efferent • Somatic • Autonomic – Sympathetic – Parasympathetic • Principle Parts of the Brain – Cerebrum (Telencephalon) • Principle Parts of the Brain – Cerebrum (Telencephalon) – Diencephalon • Principle Parts of the Brain – Cerebrum (Telencephalon) – Diencephalon • Thalamus • Hypothalamus • Pineal Gland • Principle Parts of the Brain – Brain Stem • Midbrain (Mesencephalon) • Principle Parts of the Brain – Brain Stem • Midbrain (Mesencephalon) • Pons (Metencephalon) • Principle Parts of the Brain – Brain Stem • Midbrain (Mesencephalon) • Pons (Metencephalon) • Medulla Oblongata (Myelencephalon) • Principle Parts of the Brain – Brain Stem • Midbrain (Mesencephalon) • Pons (Metencephalon) • Medulla Oblongata (Myelencephalon) – Cerebellum • Protection of the Brain – Skull • Protection of the Brain – Skull – Meninges • Protection of the Brain – Skull – Meninges – CSF • Ventricles of the Brain – Lateral Ventricles • Ventricles of the Brain – Lateral Ventricles rd – 3 Ventricle • Ventricles of the Brain – Lateral Ventricles rd – 3 Ventricle • Ventricles of the Brain – Lateral Ventricles rd – 3 Ventricle th – 4 Ventricle • Ventricles of the Brain – Lateral Ventricles rd – 3 Ventricle th – 4 Ventricle • The cerebral aqueduct links rd th the 3 and 4 ventricles • CSF Circulation • If the cerebral aqueduct were blocked: CSF would build up in the lateral and 3rd ventricles CSF would not be able to reach the subarachnoid space Both Neither • If the cerebral aqueduct were blocked: Correct! CSF would build up in the lateral and 3rd ventricles CSF would not be able to reach the subarachnoid space Both Neither • Normal • Hydrocephalus • Blood-Brain Barrier – Only lipid soluble substances can diffuse across capillary endothelium • Blood-Brain Barrier – Water soluble substances cross only by active or passive transport • selective • directional • Brain regions without a bloodbrain barrier – portions of hypothalamus – pineal gland – choroid plexus • Organization of Neural Tissue – gray matter • arranged as nuclei; often around ventricles and cerebral aqueduct • Organization of Neural Tissue – gray matter •Arranged as nuclei, often around ventricles and cerebral aqueduct OR •As thin outer layer of cerebrum and cerebellum (cortex) • Organization of Neural Tissue – White matter • arranged as “tracts” • Found everywhere gray matter isn’t Structure and Functions of Selected Brain Regions • Medulla oblongata Structure and Functions of Selected Brain Regions • Medulla oblongata • Pons Structure and Functions of Selected Brain Regions • Medulla oblongata • Pons Structure and Functions of Selected Brain Regions • Medulla oblongata • Pons • Midbrain 1 Structure and Functions of Selected Brain Regions • Medulla oblongata • Pons • Midbrain Structure and Functions of Selected Brain Regions • Medulla oblongata • Pons • Midbrain • Diencephalon • Thalamus book Structure and Functions of Selected Brain Regions • Medulla oblongata • Pons • Midbrain • Diencephalon Structure and Functions of Selected Brain Regions • Medulla oblongata • Pons • Midbrain • Diencephalon • Cerebellum Structure and Functions of Selected Brain Regions • Medulla oblongata • Pons • Midbrain • Diencephalon • Cerebellum • Cerebrum • Cerebrum – sulci and gyri • Cerebrum – sulci and gyri • Cerebrum – sulci and gyri – lobes • Cerebrum – sulci and gyri – lobes • Cerebrum – sulci and gyri – lobes – cerebral gray matter • Cerebrum – sulci and gyri – lobes – cerebral gray matter • Cerebrum – sulci and gyri – lobes – cerebral gray matter • cerebral cortex • Cerebrum – sulci and gyri – lobes – cerebral gray matter • cerebral cortex – motor and sensory cortex • Cerebrum – sulci and gyri – lobes – cerebral gray matter • cerebral cortex – motor and sensory cortex – association cortex – cerebral gray matter, continued – cerebral gray matter, continued • cerebral nuclei – cerebral gray matter, continued • cerebral nuclei – corpus striatum – cerebral gray matter, continued • cerebral nuclei – corpus striatum – cerebral gray matter, continued • cerebral nuclei – corpus striatum – amygdala – cerebral gray matter, continued • cerebral nuclei – corpus striatum – amygdala – cerebral gray matter, continued • cerebral nuclei – corpus striatum – amygdala – hippocampus – cerebral white matter • association fibers • commissural fibers • projection fibers – Limbic System – Limbic System – Functions: – Limbic System – Functions: memory, – Limbic System – Functions: memory, emotions, – Limbic System – Functions: memory, emotions, and survival behaviors – Limbic System – Functions: memory, emotions, and survival behaviors – Examples of components – Limbic System – Functions: memory, emotions, and survival behaviors – Examples of components – parts of thalamus and hypothalamus – Limbic System – Functions: memory, emotions, and survival behaviors – Examples of components – parts of thalamus and hypothalamus – hippocampus and fornix • hippocampus, fornix, etc. movie – Limbic System – Functions: memory, emotions, and survival behaviors – Examples of components – parts of thalamus and hypothalamus – hippocampus and fornix – septal nuclei *** • Limbic System – Functions: memory, emotions, and survival behaviors – Examples of components • parts of thalamus and hypothalamus • hippocampus and fornix • septal nuclei • reticular formation • Lateralization of Cerebral Function Cranial Nerves I - Olfactory II - Optic III – Oculomotor IV – Trochlear VI - Abducens V - Trigeminal VII - Facial VIII - Vestibulocochlear IX - Glossopharyngeal X - Vagus XI - Spinal Accessory XII - Hypoglossal Blood Supply to the Brain 558