Endocrine System & Visual/Auditory System
advertisement

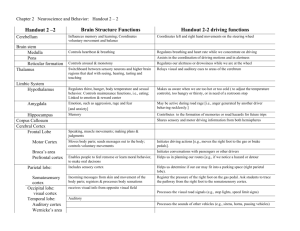
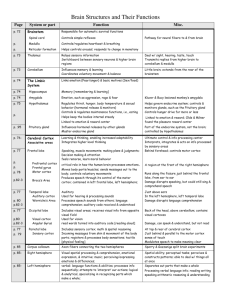
Endocrine System & Visual/Auditory System Describe how the Endocrine System is linked to the nervous & describe the visual and auditory sensory system Pituitary Gland Is called the “master gland.” The anterior pituitary lobe releases hormones that regulate other glands. The posterior lobe regulates water and salt balance. Pituitary Gland Is called the “master gland.” anterior pituitary lobe releases hormones that regulate organs and other glands. posterior lobe regulates water and salt balance. Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands Regulate metabolic and calcium rate. Diet & Bone Health • Normal blood pH ~7.4 • required for effective transport of Oxygen • Excessive protein and not enough fruits and veggies causes your blood to become acidic • Soda causes your blood to become acidic • Your body must restore normal pH • Parathyroid hormone is released causing calcium to leach from your bones into blood. • This restores pH Adrenal Glands Adrenal glands consist of the adrenal medulla and the cortex. The medulla secretes hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) during stressful and emotional situations, while the adrenal cortex regulates salt and carbohydrate metabolism. Adrenal Glands The adrenal cortex regulates salt and carbohydrate metabolism. The medulla secretes hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) during stressful and emotional situations. Gonads Sex glands are located in different places in men and women. They regulate bodily development and maintain reproductive organs in adults. Visual Function Visual Function • Notice the visual cortex is located in the occipital lobe. Courtesy of V.P. Clark, K. Keill, J. Ma. Maisog, S. Courtney, L.G. Ungerleider, and J.V. Haxby, National Institute of Mental Health • The functional MRI scan shows the visual cortex is active as the subject looks at faces. Auditory Function • The auditory cortex contains distinct subregions that are important for decoding complex sound. • Auditory cortex is in the temporal lobe. 5. The motor cortex is involved in sensory–motor feedback, in controlling movements needed to produce music using an instrument. 5 3 2. information travels through the brainstem and midbrain to the 1 auditory cortex. 1. Sound waves enter ear, and are turned into neural impulses by the inner ear 2 4 4. The frontal lobe is involved in emotional evaluation. 3. information from the auditory cortex interacts with many other brain areas, especially the frontal lobe, for memory formation and interpretation. Auditory Hallucinations The functional MRI scan shows the auditory cortex is active in patients who hallucinate. Association Areas More intelligent animals have increased “uncommitted” or association areas of the cortex. Language Aphasia is an impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca’s area (impaired speaking) or to Wernicke’s area (impaired understanding). Specialization & Integration Brain activity when hearing, seeing, and speaking words The Brain’s Plasticity The brain is sculpted by our genes but also by our experiences. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to modify itself after some types of injury or illness. Our Divided Brain Our brain is divided into two hemispheres. The left hemisphere processes reading, writing, speaking, mathematics, and comprehension skills. In the 1960s, it was termed as the dominant brain. Splitting the Brain A procedure in which the two hemispheres of the brain are isolated by cutting the connecting fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) between them. Martin M. Rother Courtesy of Terence Williams, University of Iowa Corpus Callosum Split Brain Patients With the corpus callosum severed, objects (apple) presented in the right visual field can be named. Objects (pencil) in the left visual field cannot. Try This! Try drawing one shape with your left hand and one with your right hand, simultaneously. BBC