Chapter 2

The Biological Perspective
Chapter 2
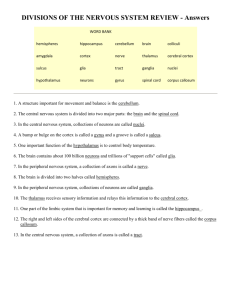
LO 2.1 What are the nervous system, neurons and nerves
Overview of Nervous System
• Nervous System an extensive network of specialized cells that carry information to and from all parts of the body.
• Neuroscience – deals with the structure and function of the brain, neurons, nerves, and nervous tissue.
• Relationship to behavior and learning.
The Nervous System
Nervous
System
Central
Nervous
System
Peripheral nervous system
Autonomic
(Involuntary)
Somatic
(Voluntary)
The Nervous System
Central Nervous System
Peripheral Nervous System
LO 2.3 Brain and spinal cord
Central Nervous System
• Central nervous system (CNS) part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord.
Nervous
System
• Spinal cord a long bundle of neurons that
• carries messages
• is responsible for very fast, lifesaving reflexes.
Central
Nervous
System
Autonomic
(Involuntary)
Peripheral nervous system
Somatic
(Voluntary)
LO 2.4 Somatic and autonomic nervous systems
Peripheral Nervous System
• Peripheral nervous system (PNS) all nerves and neurons that are not contained in the brain and spinal cord but that run through the body itself
Central
Nervous
System
Nervous
System
Peripheral nervous system
• Divided into the:
• Somatic nervous system
• Autonomic nervous system
Autonomic
(Involuntary)
Somatic
(Voluntary)
LO 2.4 Somatic and Autonomic nervous systems
Autonomic Nervous System
• Autonomic nervous system (ANS) division of the PNS consisting of nerves that control all of the involuntary muscles, organs, and glands
Central
Nervous
System • Composed of:
• Sympathetic division Reacts to stressful events and bodily arousal.
Nervous
System
Autonomic
(Involuntary)
Peripheral nervous system
Somatic
(Voluntary)
• Parasympathetic division – restores body to normal functioning after arousal
Autonomic Divisions
Parasympathetic
Eyes
Sympathetic
Lungs
Heart
Stomach
Blood Vessels
LO 2.4 Somatic and Autonomic nervous systems
Somatic Nervous System
• Somatic nervous system division of the PNS consisting of nerves that carry information from the senses to the CNS and from the CNS to the voluntary muscles of the body.
Nervous
System
Central
Nervous
System
Peripheral nervous system
Autonomic
(Involuntary)
Somatic
(Voluntary)
LO 2.1 What are the nervous system, neurons and nerves
Structure of the Neuron
• Neuron – cell in the nervous system that receives and sends messages.
• Parts of a Neuron
• Dendrites branch-like structures that receive messages.
• Soma – contains the nucleus and keeps the cell alive and functioning
• Axon long tube-like structure that carries messages out to other cells
Structure of the Neuron
LO 2.1 What are the nervous system, neurons and nerves
Glial Cells
• Glial cells - grey fatty cells that:
• Provide support for the neurons to grow
• Deliver nutrients to neurons
• Produce myelin to coat axons Glial Cell
Myelin Sheath
Myelin - fatty substances that coat the axons of neurons to insulate, protect, and speed up the neural impulse.
• Clean up waste products and dead neurons.
Myelin
The Synapse
• Space between Axon and Dendrite of a receiving cell
• The location where
Neurotransmitters are released
LO 2.2 Neuron communication
Neuron Communication
• Excitatory neurotransmitter neurotransmitter that causes a receiving cell to fire.
Excitatory
• Inhibitory neurotransmitter neurotransmitter that causes a receiving cell to stop firing.
Inhibitory
How Drugs Work
• Drugs similar in shape to neurotransmitters can stimulate receptor cites just like neurotransmitters do
• Agonistsmimic or enhance the effects of neurotransmitters
• Antagonistsblock or reduce the effects of neurotransmitters
LO 2.2 Neuron communication
Neurotransmitters
LO 2.5 Study of the brain
Peeking Inside the Brain
• Deep lesioning – sending electrical current via a wire, which destroys the brain cells at the tip of the wire.
• Electrical stimulation of the brain (ESB) – sending milder electrical current via a wire to explore the activity of the brain
• http://www.youtube.com/watchv=IOHtUzW02cg&feature=related
• Electroencephalograph (EEG) – Records brain wave patterns produced by electrical activity of the surface of the brain.
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t6XeCwFQrCA&NR=1
LO 2.5 Study of the brain
Peeking Inside the Brain
• Computed tomography (CT) brain-imaging method using computer controlled X-rays of the brain.
• Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain-imaging method using radio waves and magnetic fields. FMRImore detailed
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Cwda7YWK0WQ
• Positron emission tomography (PET) brain-imaging method in which an injected radioactive sugar shows the activity of the brain with lighter colors indicating more activity.
FMRI Scans
LO 2.6 Structures of the bottom part of brain
The Brain Stem
• Medulla – Forms the lowest part of the brain
• Responsible for lifesustaining functions such as breathing, swallowing, and heart rate.
Medulla
The Brain Stem
• Pons – Structure above the medulla
• Connects the top of the brain to the bottom
• Plays a part in sleep, dreaming, left –right body coordination, and arousal.
Pons
LO 2.6 Structures of the bottom part of brain
The Brain Stem
• Cerebellum part of the lower brain located behind the Pons
• Controls and coordinates involuntary, rapid, fine motor movement.
• Controls voluntary movements that happen in rapid succession
Cerebellum
LO 2.7 Structures controlling emotion, learning, memory, and motivation
The Limbic System
• Limbic system a group of several brain structures involved in learning, emotion, memory, and motivation.
Thalamus
Olfactory bulbs
Amygdala
Hypothalamus
Hippocampus
LO 2.7 Structures controlling emotion, learning, memory, and motivation
The Limbic System
• Hypothalamus located below the thalamus and directly above the pituitary gland
• Regulates body temperature, thirst, hunger, sleeping, waking,
• Responsible for motivational behavior
Hypothalamu s
The Limbic System
• Thalamus part of the limbic system located in the center of the brain Thalamus
• Relays sensory information from the lower part of the brain to the proper areas of the cortex
• Processes some info prior to relaying it
The Limbic System
• Hippocampus curved structure located within each temporal lobe
• Formation of longterm memories and the storage of memory for location of objects.
Hippocampus
The Limbic System
• Amygdala - brain structure located near the hippocampus
• Responsible for fear responses and memory of fear.
Amygdala
The Limbic System
• Olfactory bulbs two projections just under the front of the brain
• Receive information from the receptors in the nose located just below.
Olfactory bulbs
LO 2.7 Structures controlling emotion, learning, memory, and motivation
The Cortex
• Cortex outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons
• responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input.
The Cortex: Various Primates
LO 2.8 Parts of cortex controlling senses and movement
Cerebral Hemispheres
• Cerebral hemispheres the two sections of the cortex on the left and right sides of the brain.
• Corpus callosum thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres.
Corpus callosum
Corpus callosum
Kim Peek
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NJjAbs-
3kc8&p=C74C071676B9229C&playnext=1&index=1 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Auufbu_ZdDI&feature=related
LO 2.8 Parts of cortex controlling senses and movement
Four Lobes of the Brain
• Occipital lobe – section containing the visual centers of the brain.
• Primary visual cortex – processes visual information from the eyes.
• Visual association cortex – identifies and makes sense of visual information.
Four Lobes of the Brain
• Parietal lobes – sections containing centers for touch, taste, and temperature sensations.
• Somatosensory cortex – responsible for processing information from the skin and receptors for touch, temperature, body position, and possibly taste.
LO 2.8 Parts of cortex controlling senses and movement
Four Lobes of the Brain
• Temporal lobes – areas containing the neurons responsible for the sense of hearing and meaningful speech.
• Primary auditory cortex – processes auditory information from the ears.
• Auditory association cortex – identifies/ makes sense of auditory information.
Four Lobes of the Brain
• Frontal lobes – areas responsible for higher mental processes, decision making, and the production of fluent speech.
• Motor cortex – responsible for sending motor commands to the muscles of the somatic nervous system.
Four Lobes: Summary
LO 2.9 Parts of cortex responsible for higher thought
Association Areas of Cortex
• Association areasareas responsible for interpreting information
Wernicke’s aphasia
Broca’s aphasia
• Broca’s aphasia – result of damage to Broca’s area-Inability to speak fluently, to mispronounce words, and to speak haltingly.
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fw6d54gjuvA
• Wernicke’s aphasia – result of damage to Wernicke’s area-
Inability to understand or produce meaningful language.
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aVhYN7NTIKU&feature=relat ed
Association Areas of the Brain
• Spatial neglect condition produced by damage to the association areas of the right hemisphere
• Inability to recognize objects or body parts in the left visual field.
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ADchGO-0kGo&feature=related
LO 2.10 Left side and right side of brain
Split Brain Research
• Split brain research
• Study of patients with severed corpus callosum.
• Involves sending messages to only one side of the brain.
• Demonstrates right and left brain specialization.
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aCv4K5aStdU
LO 2.10 Left side and right side of brain
Results of Split Brain Research
• Left side of the brain:
• seems to control language, writing, logical thought, analysis, and mathematical abilities,
• processes information sequentially,
• Right side of the brain
• controls emotional expression, spatial perception, recognition of faces, patterns, melodies, and emotions,
• processes information globally