GEOLOGICAL TIME SCALE - Liberty Union High School District

Intro to Earth Systems and Earth Science
GEOLOGICAL TIME SCALE
AND
EARTH’S STRUCTURE
Textbook pages 207-209, 212
GEOLOGY
The study of the nonliving parts of the Earth such as rocks, soil, and land features
GEOLOGIST study Geology
JAMES HUTTON
“FATHER OF MODERN GEOLOGY”
Figured out sedimentary rock gets compacted and compressed over time
PRINCIPLE OF UNIFORMITARIANISM= changes in the Earth’s surface happened slowly. Example: gradual shifting across different continental land forms https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lMfPSdrrjZI
RELATIVE TIME MEASUREMENTS
Measurements that give you the age of rock and soil layers by comparing them to layers above and below
RELATIVE DATING
Dates an unknown sample to a certain time period when compared to samples of a known time period
Top layers are youngest
Bottom layers are oldest
PRINCIPLE OF
SUPERPOSITION
Strata are laid down in succession
(layers are piled on top of each other over time)
ABSOLUTE DATING
Process of determining an approximate age of rocks by using radiometric methods https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=phZeE7Att_s
GEOLOGICAL TIME SCALE
*The history of the Earth is measured in Geological Time
*It is organized according to major events
*The largest unit of time is EON
EON
ERA
PERIOD
EPOCH
IMPORTANT STAGES IN EARTH’S HISTORY
* 4.6 BILLION YEARS AGO
(HADEAN EON)
= ORIGIN OF EARTH- NO LIFE
* 3.5 BILLION YEARS AGO
(ARCHEON EON/PRECAMBRIAN ERA)
= FIRST PROKARYOTIC CELL- LIFE
* 2.5 BILLION YEARS AGO
( PROTEROZOIC EON/PRECAMBRIAN ERA )
= ATMOSPHERIC OXYGEN EXISTS
* 1.5 BILLION YEARS AGO
(PROTEROZOIC EON/PRECAMBRIAN ERA)
= FIRST EUKARYOTIC CELL
* 550 MILLION YEARS AGO(
PROTEROZOIC EON/
PALEOZOIC ERA/CAMBRIAN PERIOD)
= PRIMITIVE ALGAE/MARINE INVERTEBRATES
*450 MILLION YEARS AGO
(PHANEROZOIC EON/PALEOZOIC ERA/
= FIRST MARINE VERTEBRATES (FISH)
ORDOVICIAN PERIOD)
*400 MILLION YEARS AGO
(PHANEROZOIC EON/
PALEOZOIC ERA/SILURIAN PERIOD)
*200 MILLION YEARS AGO
(MESOZOIC ERA/TRIASSIC PERIOD)
*150 MILLION YEARS AGO
(MESOZOIC ERA/JURASSIC PERIOD)
= FIRST LAND INVERTEBRATES & PLANTS
= FRIST BIRDS/ROCKY MOUNTAINS FORM
= AGE OF DINOSAURS
*65 MILLION YEARS AGO
(CENOZOIC ERA/TERTIARY PALEOGENE PERIOD)
=EXTINCTION OF DINOSAURS
PALEOCENE EPOCH)
1.8 MILLION YEARS AGO
(CENOZOIC ERA/QUATERNARY PERIOD)
=FIRST MAN/MAMMALS/INSECTS/FLOWERS
PLEISTOCENE EPOCH)
Geologic Time Scale Music Video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7PQURsc2SYs
Earth and our Solar System
• _________ planet from the Sun
EARTH’S INTERACTIVE COMPONENTS
LITHOSPHERE = makes up the Earth’s interior (rock)
ATMOSPHERE = makes up the gases surrounding Earth (air)
HYDROSPHERE= makes up the areas of water
BIOSPHERE = makes up all the living things within the other parts
EARTH IS AN INTEGRATED SYSTEM OF
4 INTERACTING COMPONENTS
HOW EARTH FORMED
- CAME FROM COSMIC DUST IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM (BIG BANG THEORY)
- ALL THE ELEMENTS FOUND ON EARTH ARE AS OLD AS EARTH
- EARLY EARTH WAS A HOT, MOLTEN SPHERE
- AS MOLTEN MATERIAL COOLED, THE ELEMENTS SEPARATED INTO LAYERS
BASED ON MASS (HEAVY IRON TOWARDS THE CENTER) https://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=BBwqendK8zc
EARTH LAYERS
BECAUSE EARTH’S ELEMENTS SETTLED INTO PLACE
BASED ON MASS…… EARTH IS DIVIDED INTO LAYERS
2 GROUPS OF LAYERS:
COMPOSITIONAL LAYERS
&
PHYSICAL LAYERS
KNOWLEDGE OF EARTH’S LAYERS
*SEISMIC WAVES ANALYSIS
*LAVA ANALYSIS
*METERITE COMPOSITION
COMPOSITIONAL LAYERS OF EARTH
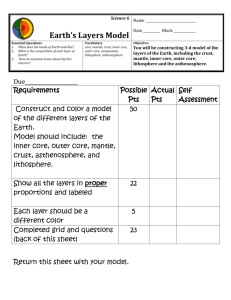
CRUST = thinnest (only 0.5% of earth’s total mass), outermost layer, solid, brittle, coolest layer, mostly oxygen, oceanic & continental
MANTLE = medium density, has magma that circulates in convection cells, mostly iron, magnesium, aluminum
CORE = innermost layer, greatest density, hottest, mostly iron and nickel
PHYSICAL LAYERS OF EARTH
1. LITHOSPHERE = outer layer, includes crust and uppermost mantle, divided into tectonic plates
2. ASTHENOSPHERE = middle part of mantle, flexible, rock flows slowly
3. MESOPHERE = lower part of mantle
4. OUTER CORE = outer part of core, dense liquid nickel and iron
5. INNER CORE = inner most part of core, dense solid nickel and iron due to pressure, over 4000 ° C
Comparison of the Compositional and
Physical Layers
Physical Layers
What is plate tectonics?
If you look at a map of the world, you may notice that some of the continents could fit together like pieces of a puzzle.
• The Earth’s crust is divided into 12 major plates which are moved in various directions.
• This plate motion causes them to collide, pull apart, or
scrape against each other.
• Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of
Earth structures or “tectonic” features.
• The word, tectonic, refers to the deformation of the crust as a consequence of plate interaction.
World Plates
What are tectonic plates made of?
• Plates are made of rigid
lithosphere.
The lithosphere is made up of the crust and the upper part of the mantle.
What lies beneath the tectonic plates?
• Below the lithosphere
(which makes up the tectonic plates) is the asthenosphere.
• The plastic layer below the lithosphere
• The plates of the lithosphere float on the asthenosphere
Plate Movement
• “Plates” of lithosphere are moved around by the underlying hot mantle convection cells
Plate Tectonics Excel Graph
Activity
On our class webpage is the link for the activity (word document) and the data (excel document)
Work on the webquest when you are done