Module 61 - Introduction to Monopoly
advertisement

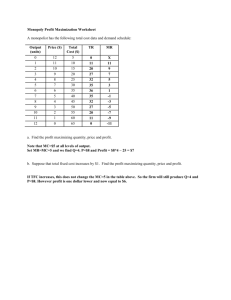
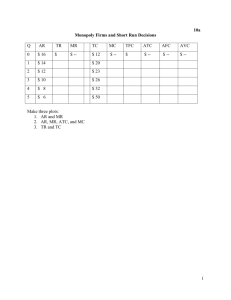
AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Module 61: Introduction to Monopoly November 2015 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Monopoly vs. Perfect Competition • Monopolist maximizes profit where MR=MC • Perfectly Competitive firm also maximizes profit where MR=MC • Monopolist sets price • Perfectly Competitive firm is a price taker • Monopolist has barriers to entry • Perfectly Competitive firms have free entry and exit • Monopolist has opportunity to earn profits in long run • Perfectly Competitive firm will earn zero profit in long run 2 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Monopoly Demand and MR • Monopolist MR curve is below D curve because they must reduce price to sell more • Unlike perfect competition, DFIRM = DINDUSTRY 3 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Monopoly Profit-Maximizing P and Q • As with perfect competition, p is maximized where MR=MC • Optimal Output Rule – Know the Concept, own the Concept! 4 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Monopoly Profit-Maximizing P and Q • Monopolies create $ inefficiencies; P>MC • Also notice Qm is Pm= $14 lower than Qc would be (where D and MC Pc = $10 Intersect) Profit = $12 MC = ATC D MR Qm= 3 Output 5 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Monopoly Profit-Maximizing P and Q • With barriers to entry $ there are no new entrants and no Pm= $14 adjustment to new equilibrium with zero Pc = $10 economic profits at long-run equilibrium Profit = $12 MC = ATC D MR Qm= 3 Output 6 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Classic Monopoly Graph • Qm is found where MR=MC • But Pm is found by extending Qm vertically to D curve • Be sure you can find Monopolist’s p area 7