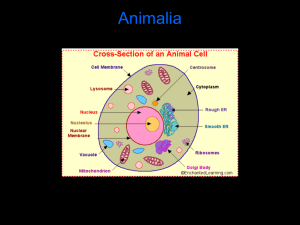
Master Cattleman Program
advertisement

Vaccination Programs for Beef Cow/Calf Operations Dr. Michelle Arnold Ruminant Extension Veterinarian University of Kentucky What diseases am I trying to prevent? VACCINES Scours Pinkeye Clostridials Respiratory Reproductive Respiratory and Reproductive Blackleg 7-way Histophilus Pasteurella Mannheimia Viral 4 or 5way Lepto 5-way Lepto Hardjo Bovis Trich Vibrio Trying to prevent the diseases that lead to Abortion Disease BVD Brucellosis Campylobacter (Vibrio) Chlamydia IBR Leptospirosis Neospora Sarcocystis Trichomoniasis Stage of Gestation Control Method Up to 6 months FP vaccine, cull PI 6+ months Heifer vaccination; test / cull Early embryonic death Vaccinate, antibiotic Last trimester Separation, sanitation Last half Vaccinate Any stage (usually 6+) Vaccinate, antibiotic 4-6 months Canine control Last trimester Canine feces out of feed Early embryonic death < 5 months Cull infected bulls, vaccinate Aim is to prevent the most common diseases as well as enhance colostrum REQUIRED VACCINES Clostridials Respiratory Blackleg 7-way (<2 yrs) Virals 4-way (5-way) Cows Need Annually Reproductive Lepto 5-way HB=Lepto Hardjo-Bovis Treat for internal and external parasites Vibrio Open cows and heifers need a 5 way respiratory vaccine with vibrio (Campylobacter) and lepto 4-6 weeks prior to breeding • Open Cows and Heifers – use modified live FP=Fetal Protection What is BVD? One of the most important and most complicated viral diseases in beef and dairy cattle worldwide Two broad types of infection based on transmission: Transient Infection (TI) Persistent Infection (PI) PI development Persistently Infected Carriers (PI’s) 1 – 4 months gestation Infection 93% of all PI’s produced this way Calf PI’s produce PI’s 100% of the time BVD Virus Courtesy of Dr. John Pickering What does it do? • Effects on fertility Infection early in pregnancy = failure to conceive Early embryonic loss Above - normal embryo Below - a degenerate embryo from a cow infected with BVD in early pregnancy. Abortion • Up to 180 days Mummified Fetus Developmental defects - hydrocephalus, cleft palate, cerebellar hypoplasia (120- 150days). Developmental defects 90 to 150 days Cataracts Retinal Degeneration Optic Neuritis Stillbirths Live born Dummy calves 180 days on Normal calf- fetus is immunocompetent and able to mount a specific immune response Summary of BVD Effects No effect - calf born immune Developmental defects Persistent infection Embryonic loss or abortion Failure to conceive -50 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 Persistent Infection PI Carriers • If fetus becomes a PI and survives - will continuously shed millions of virus all its life from all its secretions - feces - urine - saliva - nasal - milk - semen - uterine secretions - aborted membranes, fluids, fetus - Across fences. Virus survives in environment up to 7 days • If it’s a female and later gets pregnant then its offspring will be a PI and its offspring and so on and so on “FP” means protection against persistent infection and abortion due to BVD virus Unfortunately the fact that a vaccine is licensed and available doesn’t mean it works Ribble CS Assessing vaccine efficacy Can J Vet Med Vol 31 Oct 1990 Vaccines do not work in sick, stressed, thin, or heavily parasitized cattle Two Types of Viral Vaccines: Killed (Inactivated) and Modified Live (Attenuated) Safe for Pregnant: MLV Respiratory Stimulate cell mediated and humoral immunity quickly-longer, stronger Booster recommended but not always required. Do not booster in less than 2 weeks Open Cows Only: Anamnestic (Memory) Response with killed vaccine requires two doses- a primary and a booster 150 100 50 Antibody and T cell response 0 Day 0 Day 14 Day 21 day 28 Booster given on day 21 Killed Viral Respiratory Vaccines A “respiratory vaccine” contains antigens from 4 viruses but the name often depends on the BVD fraction RESPIRATORY "4 or 5 or 6 way" Other Respiratory Mannheimia IBR BVD Type 1 NCP 36% CP 25% PI3 BRSV Pasteurella (-) Type 2 NCP 30% *CP 9% *Not in Vaccines Type 1 and 2 are genotypes; CP and NCP Are biotypes. Pis have noncytopathic BVD Histophilus(-) “HS” stands for Histophilus somni (formerly known as Haemophilus somnus) • Only used if required or if identified as a problem on the farm. While they are in the chute, I’ll give them everything…but they will feel rough the next day • More than two Gram (-) vaccines one time or mishandle vaccine-Excess endotoxin • Mannheimia and Pasteurella • Brucellosis (Bangs) • Moraxella (Pinkeye) • Salmonella, E.coli • Histophilus (Hemophilus) • Vibrio (Campylobacter) The bull needs vaccinating, deworming and a breeding soundness exam before breeding season • Approximately 20% of bulls have some degree of infertility Pregnant cows and heifers need Scours Vaccine before they calve. • Heifers need primary dose and booster. Annual vaccination required Scour Guard 4KC Scour Bos 9 Guardian Scours Vaccines Scour Bos 9 Initial: 5-7 mos; Booster at 8 mos; Annual: 6.5-7 mos Scour Guard 4KC Initial: 7 mos; booster at 8 Annual: 8 months Guardian Initial: 7 mos; booster at 8 Annual: 7.5-8 mos Percent absorption in gut Calf Colostrum Absorption is best in the first 6 hours of life and steadily declines to zero in 24 hours 30% Hours after birth Talk to your veterinarian about your individual herd health program. • Based on exposure to risk • Marketing choices (Cows/calves/stockers/replacements) • Compliance • Expense What if calve year round so cows are in all stages of gestation and all different ages of calves in the pasture • #1 Recommendation-Individually identify cows and calves and record birth dates • #2 Recommendation- Use killed vaccine and give an initial dose followed by a booster 4 weeks later. Continue using killed vaccine twice a year. What about deworming? Use products effective against adult and inhibited Ostertagia but be aware of Cooperia Macrocyclic lactones-Long acting + External parasite control Benzamidazoles • White wormers • Short acting-kill adult worms in the gut and dormant (hypobiotic) larvae • No residual activity but excellent efficacy against Cooperia Results from 2007-2008 FECRT: Free Lab Support to Bovine Practitioners 4765 samples tested Table 1. Efficacy of macrocyclic lactone injectable formulations from FECRTs* conducted by veterinary practitioners and submitted to Intervet’s national database. Number of trials Number of samples Pre-Rx Post-Rx Percent efficacy (%) Injections: Ivomec® Inj. Ivomec® Plus Dectomax® Inj. Cydectin Inj. Ivermectin Inj. 6 6 11 2 1 162 257 362 64 40 55.5 120.4 43.6 246.1 33.0 13.2 69.1 4.4 4.7 16.5 76.2% 42.6% 89.9% 98.1% 50.0% Inj. Summary: 26 884 79.2 21.8 72.5% Product Egg counts/3g** *Fecal egg count reduction tests. ** All samples taken at treatment and again two weeks post-treatment. Results after Pour-Ons: Failure to eliminate worm egg shedding due to lack of Consistent and adequate absorption into the bloodstream. Table 2. Efficacy of macrocyclic lactone pour-ons from FECRTs* conducted by veterinary practitioners and submitted to Intervet’s national database. Number of trials Number of samples Pre-Rx Post-Rx Percent efficacy (%) Pour-ons: Ivomec® PO Ivermectin PO Dectomax® PO Cydectin® PO 8 35 8 9 366 1,437 318 365 45.8 53.6 89.2 45.1 12.7 21.6 18.8 14.8 72.3% 59.7% 78.9% 67.2% Pour-On summary 60 2,486 56.0 19.0 66.1% Product Egg counts/3g** * Fecal egg count reduction tests. **All samples taken at treatment and again two weeks post-treatment. If a macrocyclic lactone (especially ivermectin) is used for external parasite control, it should be used with another dewormer to prevent production losses and the further transfer of resistant parasites to other cattle Table 4. Efficacy of Safe-Guard®/Panacur® in combination with various macrocyclic lactone formulations from FECRTs* conducted by veterinary practitioners and submitted to Intervet’s national database. Combination product Safe-Guard/Panacur Drench plus: Ivomec® Inj. Ivomec® Plus Ivermectin PO Dectomax® Inj. Cydectin® Inj. Summary Number of trials Number of samples 3 1 3 1 1 9 59 40 118 20 24 261 * Fecal egg count reduction tests. **All samples taken at time of treatment and again two weeks post-treatment. Egg counts/3g** Pre-Rx Post-Rx 88.2 30.7 30.8 389.4 583.0 152.1 0 0 0.1 0 0.2 0.1 Percent efficacy (%) 100.0% 100.0% 99.9% 100.0% 99.9% 99.9% LongRange • New dewormer called LongRange • Eprinomectin-similar drug to Eprinex • Delivers 100-150 days of parasite control in a single dose • Prescription only Pinkeye versus IBR Current Pinkeye Facts • Agent – Moraxella bovis, (M. bovoculi) • Transmission – direct contact, face flies • Treat – long acting antibiotics – Long acting tetracycline such as Hexasol or Noromycin 300(LA-200-seeing resistance) – Benzathine Penicillin and Dexamethasone subconjunctival-only with valid VCPR – Excede (off-label) – Draxxin – Nuflor (off label) Predisposing Factors • Lack of pigmentation around the eye ? – Ultraviolet light not absorbed by white hair • Mechanical irritation/Physical trauma – Pollen, seeds, feed dust, dust – Stubble, thorn bushes can scratch cornea • Chemical trauma – Fresh nitrogen applied to pasture • Flies – Face flies feed on eye secretions – Vector of spreading bacteria from animal to animal Predisposing Factors • Ultraviolet light-cell damage to the cornea is initiated by UV burning. This is why the greatest occurrence is in summer. • Viral Infection-Viruses such as IBR can damage the protective cells covering the eye • Stress from shipping, processing, commingling can be immunosuppressive Pinkeye Prevention • Prevent Corneal Damage from sun- need shade. • Control FACE flies-ear tags, face “flyps”,Altosid. Clean up areas where flies breed-spilled feed, old hay in rings. • Clip pastures-mechanical injury from plant awns such as foxtail • Clean Water Source-critical to keep eye clean and moist. • Vaccinate • Antibiotic in feed mix/ free choice mineral – Chlortetracycline (Aureomycin®) is not labeled for pinkeye control. However, it is legal to feed CTC to prevent anaplasmosis. Fly Control-UK ENT-11 Fact Sheet Numerous insecticides and equipment availableMost Permethrin based • Insecticide-impregnated tag • Back rubs and wicks • Dust bags • Sprays • Feed-throughs • Pour-ons • Avoidance of areas with heavy fly infestations Cylence or Python give good face and horn fly control Questions?