The Unit Organizer Routine
advertisement

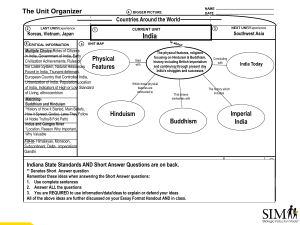
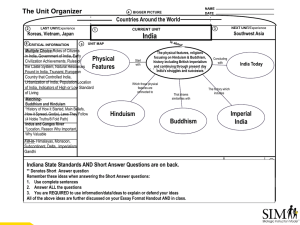
The Unit Organizer 4 NAME DATE BIGGER PICTURE Countries Around the World 2 LAST UNIT/Experience Koreas, Vietnam, Japan 8 CRITICAL INFORMATION 5 3 CURRENT CURRENT UNIT UNIT 1 India NEXT UNIT/Experience Southwest Asia UNIT MAP Multiple Choice-Roles of Citizens in India, Government of India, Early Physical Civilization Achievements, Rules of the Caste System, Natural Resources Features Found in India, Tsunami defenses, European Country that Controlled India, Urbanization of India, Population Location of India, Indicators of High or Low Standard of Living, ethnocentrism MatchingBuddhism and Hinduism *History of How it Started, Main Beliefs, How it Spread, God(s), Laws They Follow (4 Noble Truths/8 Fold Path) Indus and Ganges River *Location, Reason Why Important, Why Valuable Start with The physical features, religions focusing on Hinduism & Buddhism, history including British Imperialism and continuing through present day India's struggles and successes Which those physical features are connected to Hinduism That shares similarities with Buddhism Concluding with India Today The history which includes Imperial India 6 UNIT ** Denotes Short Answer question Remember these ideas when answering the Short Answer questions: 1. Use complete sentences 2. Answer ALL the questions 3. You are REQUIRED to use information/data/ideas to explain or defend your ideas 7 All of the above ideas are further discussed on your Essay Format Handout AND in class. Other Important Ideas Indiana State Standards AND Short Answer Questions are on back. RELATIONSHIPS UNIT SELF-TEST QUESTIONS Fill-in- Himalayas, Monsoon, Subcontinent, Delta, Imperialism, Gandhi Indiana State Standards **Denotes Short Answer Questions 1. Identify and compare the rise of early agricultural river valley civilizations in Africa and Asia. Example: Indus River Valley (7.1.1) 2. Describe the historical origins, central beliefs and spread of major religions. Example: Hinduism, Buddhism (7.1.2) 3. Explain the reasons for European colonization of Africa, Asia and the Southwest Pacific and analyze the long and short term impact that colonization and imperialism had on the social, political, and economic development of these societies from both the European and indigenous perspectives. Example British in India (7.1.11) 4. Create and compare timelines that identify major people and events and developments in the history of civilization and/or countries of Africa, Asia and the Southwest Pacific. Example: India from 1950 to the present (7.1.15) 5. Analysis and Interpretation, Research: Analyze cause-and-effect relationships, bearing in mind multiple causation in the role of individuals, beliefs and chance in history. Example: Independence movements in India (7.1.16) 6. Distinguish between unsupported expressions of opinion and informed hypotheses grounded in historical evidence. (7.1.17) 7. Compare and contrast perspectives of history in Africa, Asia and the Southwest Pacific using fictional and nonfictional accounts. (7.1.18) 8. Compare, contrast, and evaluate different routes to independence from colonial rule taken by countries in Asia, Africa and the Southwest Pacific. Example: India (7..2.1) 9. Compare and contrast historical and contemporary governments in India. (7.2.2) 10. Describe how major forms of governments of India currently protect or have protected citizens and their civil and human rights. (7.2.3) 11. Define and compare citizenship and the citizen's role in selected countries of Africa, Asia and the Southwest Pacific. Example: Compare methods of voting, participation in voluntary organizations and participation in government in India (7.2.5) 12. Identify and describe major physical characteristics of regions in Africa, Asia and the Southwest Pacific. Example: mts, rivers (7.3.4) 13. Identify and explain the importance of the early cultural hearths in the Indus River Valley. (7.3.11) 14. Identify current trends and patterns of rural and urban population distribution in selected countries of Africa, Asia and the Southwest Pacific. Example: Life expectancy, income, industry, education, natural resources, climate and land forms in India. (7.3.8) 15. Provide examples of ethnocentrism and how this attitude affected the relationships between different people in Africa, Asia, and the Southwest Pacific. (7.3.9) 16. **Compare and contrast the standard of living in various countries (India) in Africa, Asia, and Southwest Pacific using Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita, life expectancy, literacy rate as an indicators; hypothesize how factors including urbanization, industrialization, and globalization, could affect differences in the standard of living statistics. (7.4.4) 2 University of Kansas Center for Research on Learning 2006