The Road to the Constitution
advertisement

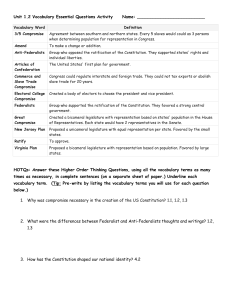
“The Road to the Constitution” Failure of the “Articles of Confederation” Failure of the “Articles of Confederation” By 1787, most realized that the “Articles of Confederation” provided for a weak and ineffective system of government. Under the Articles, the thirteen states operated as a “confederal” government system – whereas, the delegates wanted to create a “federal” system with a strong central government. Return to Philadelphia There were problems with the Articles of Confederation so they met to fix it. The convention was held in Philadelphia in 1787. 55 delegates from 12 states met to determine the future of the U.S. Government. Rhode Island did not attend. They opposed the idea of a stronger central government. America’s “Best and Brightest” The men that attended the Constitutional Convention are called framers. 8 of the delegates had signed the “Declaration of Independence.” 7 of the delegates had been governors. 41 of the delegates had served in the “Continental Congress.” George Washington George Washington is selected as the unanimous choice to preside over the convention. No one in the new “United States” was more respected. Benjamin Franklin Benjamin Franklin was the oldest member of the convention at 81 years old. His wisdom and advice was invaluable to the members. It was decided that the Articles of Confederation would be discarded. They realized that they would need a completely new document. Problems from the Start - “Creating and Ratifying the Constitution” Right away disagreements arose about how the government would be structured. The Two Plans for a Legislature “The Virginia Plan” Proposed by Edmund Randolph / James Madison “The Virginia Plan” Created a “3 branch” government (Legislative, Executive, & Judicial) Created a two house bicameral government based on population. “The Virginia Plan” Representation in the Legislature would be based on POPULATION! Larger states were in favor of this! (Virginia, Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, & New York) Smaller states protested because they would lose power due to their populations. “The New Jersey Plan” Proposed by William Paterson “The New Jersey Plan” Created a “3 branch” government (Legislative, Executive, & Judicial) Called for a one house legislature (unicameral). “The New Jersey Plan” This plan called for equal representation -Each state had ONE vote! Smaller states liked this plan! (New Jersey, Delaware, and Maryland) Opposed by larger states who would only have as much power as smaller states despite having larger populations! Compare & Contrast Virginia Plan and New Jersey Plan There were many compromises at the convention. The “Great Compromise” The “Great Compromise” A way to settle disagreements between two or more groups is a compromise. The “Great Compromise” “The Great Compromise” was proposed by Roger Sherman of Connecticut. Also called the “Connecticut Compromise”. Created a two house government – a bicameral legislature. The “Great Compromise” Created the “Senate” Each state had two (2) votes, both equal. Pleased the smaller states (put them on equal footing with larger states in this house). Created the “House of Representatives”. Each state’s voting status was based on population. Pleased the larger states (gave them more power in this house). Other Compromises Question of Counting Slaves? Southern states wanted to count their slave populations (nearly 550,000) The “3/5th Compromise” settled the issue. It was agreed to count each slave as 3/5ths of a person for representation AND taxation purposes. “Slave Trade Compromise” Northern states wanted the U.S. Government to regulate trade between both states AND foreign nations. Southern states feared this would impact their exports of rice, cotton, & tobacco. It was agreed that slavery would be left alone for 20 years in terms of commerce and trade. They would revisit the issue in 1808. “Electoral College” Some delegates wanted Congress to choose the president. Others felt that the people should elect him. They decided each state legislature would chose the # of electors, known as the electoral college, who would elect the President and Vice President. Still used today, but voters choose the electors now. Ratification of the Constitution Ratifying the “U.S. Constitution” Only 42 of the delegates remained. They gathered for the last time on September 17, 1787. The Constitution would become law if f 9 out of the 13 states ratified it at their ratifying conventions. Debate Breaks Out: “Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists” Each wrote a series of papers in support of their side!!! “Anti-Federalists” “Anti-Federalists” opposed the Constitution as it was written. They felt that it gave too much power to the national government and took too much from the states. Each side wrote papers that argued their position. “Federalists” “Federalists” were supporters of the Constitution as it was written. Believed in a strong central government and wanted the document ratified (approved) as is. “Federalists” In essays entitled “The Federalist Papers”, they argued that the U.S. could not survive without a strong federal government. They were led by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, & John Jay “Anti-Federalists” “Anti-Federalists Papers” demanded that the new Constitution protect the basic individual rights of the people – they wanted a “bill of rights” added. “Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists” Federalists supported the Constitution- they argued that the nation wouldn’t survive without a strong national government. Famous papers written in support of the Constitution were the Federalist Papers. Anti-federalist Papers: demanded that the new Constitution protect the basic individual rights of the people- they wanted a Bill of Rights. This was led by Patrick Henry. Federalists promised that if the Constitution was adopted it would adopt a Bill of Rights. “The U.S. Constitution” “The U.S. Constitution” On June 21, 1788, New Hampshire becomes the 9th state to ratify the Constitution. Rhode Island is the 13th. The 13 independent states became one nation, the “United States of America.” For the first time it was written with a capital “U.”