Price Discrimination and Consumer Surplus
advertisement

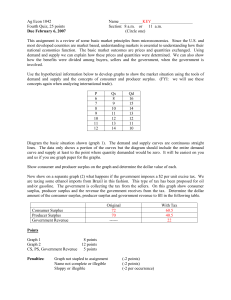
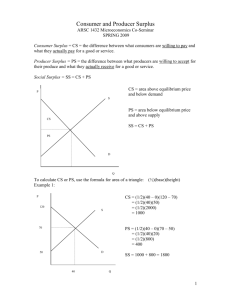
UMAP MODULE 294 - Price Discrimination and Consumer Surplus MA 314 - Project 1 UMAP 294 John Joseph Peter Ivancevic Travis Jegerlehner UMAP MODULE 294 - Price Discrimination and Consumer Surplus Calculus and Economics • Calculus methods can be used to compute consumer surplus and other figures associated with economics. • Calculus can predict approximate figures for large situations, but it can not predict exact figures. • Calculus can be applied to real world economic problems. However, to be applied correctly to economic functions and quantities, a full understanding of economics is required. UMAP MODULE 294 - Price Discrimination and Consumer Surplus Supply Function price • Supply Function: – The supply function represents the given quantity of a good that a supplier will produce at a given price. – Supply is an increasing function. As price rises Supply Function quantity supplied increases (see S(q) graph right). quantity UMAP MODULE 294 - Price Discrimination and Consumer Surplus Demand Function price • Demand Function – The demand function represents the given quantity of a good that is demanded by consumers at a given price. – Demand is a decreasing Demand Function function. As price rises quantity supplied decreases (see graph right). D(q) quantity UMAP MODULE 294 - Price Discrimination and Consumer Surplus Equilibrium Point • The Supply and Demand Function intersect at the equilibrium price (p*) and the equilibrium quantity (q*). • The points can be determined by solving the equation: D(q) = S(q) Equilibrium Point (q*, p*) price S(q) (q*, p*) D(q) quantity UMAP MODULE 294 - Price Discrimination and Consumer Surplus Continuity of D(q) and S(q) • In reality, the Demand and Supply functions are not continuous. They are step or discrete functions because they deal with whole number quantities produced. Discrete Function price price Step Function quantity quantity UMAP MODULE 294 - Price Discrimination and Consumer Surplus Continuity of D(q) and S(q) price • By assuming that the jumps in the Supply and Demand functions are small, continuous functions can be used to approximate the discrete functions. This assumption allows the tools of calculus to be used Continuous Approximaiton to solve problems related to supply and demand. quantity UMAP MODULE 294 - Price Discrimination and Consumer Surplus Calculating Consumer Surplus • To calculate the revenue generated by Demand we can multiply the price each consumer is willing to pay by the quantity demanded (discrete Demand function). Revenue Generated *Area of each rectangle represents how much revenue is generated from the quantity demanded at the given price. price • These amounts are represented by the area of the rectangles formed by the discrete demand function. q1 q2 q3 q4 UMAP MODULE 294 - Price Discrimination and Consumer Surplus Calculating Consumer Surplus • To calculate the total revenue generated by the firm, we use the summation represented by the formula below n i1 D( qi ) ( qi ) • We can then apply calculus to the continuous Demand function to use the integral below to approximate the total revenue. n D( qi ) dq 1 UMAP MODULE 294 - Price Discrimination and Consumer Surplus Calculating Consumer Surplus • In a competitive market consumers do not pay the price they are willing to pay for a good (Perfect Price Discrimination). • Consumers of a good pay the equilibrium price (p*) for the good. Therefore, the total revenue generated is p*q*. • Because some consumers pay less than they were willing to pay for the good, they experience consumer surplus. The consumer surplus can be computed using the following formula: e q 1 D( qi )p e dq UMAP MODULE 294 - Price Discrimination and Consumer Surplus Calculating Consumer Surplus • On the graph, the consumer surplus (yellow) is the area located below the Demand function and above the rectangle that represents the revenue generated (red). Consumer surplus S(q) D(q) Revenue UMAP MODULE 294 - Price Discrimination and Consumer Surplus Calculating Producer Surplus • The supplier also experiences producer surplus. The area (yellow) above the Supply function and still in the rectangle representing income is the producer surplus. Producer Surplus Supplier surplus S(q) Producer Surplus = q D(q) Revenue e e p S( qi ) dq 1 UMAP MODULE 294 - Price Discrimination and Consumer Surplus Elasticity of Supply and Demand • Supply and Demand curve are often approximated as linear functions. • The elasticity of demand measures how changes in price affect changes in quantity demanded. If elasticity is high, small changes in price have a large effect on the quantity demanded. If elasticity is small, the opposite is true. • The elasticity of supply measure how changes in price affect quantity supplied. If elasticity is high, small changes in price have a large effect on quantity supplied. If elasticity is small (just as in the elasticity of demand) the opposite is true. UMAP MODULE 294 - Price Discrimination and Consumer Surplus Two Tier Price Discrimination • Two tier price discrimination occurs when sellers have 2 different prices for products for 2 different consumers. • If the competitive equilibrium price p* is calculated then the Revenue at higher price total revenue to seller is p1*q1 + p*(q*-q1). • Maximizing the Revenue at revenue function lower price reveals what price sellers should charge. UMAP MODULE 294 - Price Discrimination and Consumer Surplus Summary • Using functions to represent Supply and Demand for a good, we can calculate and equilibrium price and quantity that meets supply and demand. • Assuming the discrete functions that represent supply and demand have small increments, we can use continuous functions to approximate them and apply Calculus. • Using Calculus we can calculate consumer surplus, producer surplus, and total revenue. We can also use calculus to determine the price that should be charged for two tier price discrimination to obtain maximum revenue for the producer.