Math Vocabulary Project

Math Vocabulary Project
By: J’amezz Martin
Integer
• A whole number; a number that is not a fraction.
Rational Number
• A number that can be written as a fraction.
Scientific Notation
• Where a number is written in two parts:
First: just the digits (with the decimal point placed after the first digit),
Followed by: ×10 to a power that would put the decimal point back where it should be.
Perfect Square
The product of a rational number multiplied by itself.
• a real number that cannot be expressed as a rational number.
Irrational Number
Real Numbers
a rational number or the limit of a sequence of rational numbers, as opposed to a complex number.
Also called real .
Density Property
The density property tells us that we can always find another real number that lies between any two real numbers
Adjacent angles
• angles that have a common ray coming out of the vertex going between two.
• A numerical or constant quantity placed before and multiplying the variable in an algebraic expression
Coefficient
Distance Formula
• which is used to find the distance between two points is called the
Distance Formula.
Domain
• domain of a function is the set of "input" or argument values for which the function is defined
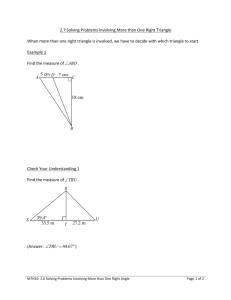
Hypotenuse
• The longest side of a right triangle, opposite the right angle.
Legs of a right Triangle
• a triangle in which one angle is a right angle
(that is, a 90-degree angle).
Rational Number
• any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction p/q of two integers
• range of a set of data is the difference between the largest and smallest values.
Range
Slope
• The slope of a line in the plane containing the x and y axes is generally represented by the letter m, and is defined as the change in the y coordinate divided by the corresponding change in the x coordinate, between two distinct points on the line. This is described by the following equation
• A solid geometric figure whose two end faces are similar, equal, and parallel rectilinear figures, and whose sides are parallelograms.
Prism
Scatter plot
• type of mathematical diagram using
Cartesian coordinates to display values for two variables for a set of data.
Slope intercept form
• The slope-intercept form is one way to write a linear equation
(the equation of a line). The
slope-intercept form is written as y = mx+b
Absolute Value
• The magnitude of a real number without regard to its sign. The absolute value of a complex number a 2 + ib
Exponent
• The exponent of a number shows you how many times the number is to be used in a multiplication.
It is written as a small number to the right and above the base number.
Pythagorean Theorem
• square of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other...
Product
• product is the result of multiplying.
Acute Triangle
• Less than 90° - all three angles are acute and so the triangle is acute
Probability
• The extent to which something is probable
Factor
• numbers you can multiply together to get another number
Variable
• A variable is a symbol that stands for a value that may vary; the term usually occurs in opposition to constant
Evaluate
• to determine or set the value
Quotient
• The answer after you divide one number by another dividend ÷ divisor = quotient
Acute Angle
• an angle less than 90 degrees but more than 0 degrees.
Congruent
• Identical in form.
Reciprocal
• A mathematical expression or function so related to another that their product is one; the quantity obtained by dividing the number one
Vertex
• The highest point; the top or apex.
Polygon
• A plane figure with at least three straight sides and angles, and typically five or more.
Diameter
• A straight line passing from side to side through the center of a body or figure, esp. a circle or sphere.
• Adding two numbers and getting the answer is the sum.
Sum
• Dividend is the number to be divided.
Dividend
Divisor
• Is the number that divides the dividend in a division problem.
Median
• The middle number in a number set.
• The mean is the average.
Mean
• is the most frequently occurring value in a data set
Mode
Pyramid
• A pyramid is a solid figure with a polygon base and all other faces triangles that meet at a common vertex.
Quadrilateral
• A polygon with four sides.
Parallelogram
• A four-sided plane rectilinear figure with opposite sides parallel.
• A parallelogram having four rectangles.
Rectangle
• Reflection is the change in direction of a wave front at an interface between two different media
Reflection
• Rate is a ratio that compares two quantities
Rate
Trapezoid
• A trapezoid is a four-sided figure with one pair of parallel sides.
Cylinder
• A surface or solid bounded by two parallel planes and generated by a straight line moving parallel to the given planes.
• A plane figure with eight straight sides and eight angles.
Octagon
• A plane figure with five straight sides and five angles.
Pentagon
• A triangle with a right angle.
Right Triangle
• an equilateral parallelogram, including the square as a special case.
Rhombus
Lowest Terms
• Simplest form; when the GCF of the numerator and the denominator of a fraction is 1.
X-axis and Y-axis
• Y axis: The vertical axis in a coordinate system.
• X axis: The horizontal axis on a coordinate plane.