Doc
advertisement

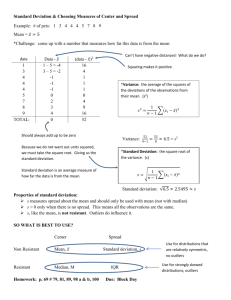
S O C S Shape Outliers Center Spread We can use a graphs to look at the shape of the quantitative variable distribution. An example of a bell-shaped or normal distribution which appear often in nature: Symmetric Mean, median, mode roughly equal Scores from an easy exam, skewed left. Non-symmetric Mean < Median < Mode Scores from a hard exam, skewed right. Non-symmetric Mean > Median > Mode Shape described by number of peaks (mode) An outlier is an extreme value of the data (extremely high or extremely low). It is an observation value that is significantly different from the rest of the data. There may be more than one outlier in a set of data. Possible Reasons for Outliers: 1. An error was made while taking the measurement or entering it into the computer. 2. The individual belongs to a different group than the bulk of individuals measured. 3. The outlier is a legitimate, though extreme data value. We can identify an outlier if it is • Less Q1 – 1.5×IQR or • Greater than Q3 + 1.5×IQR Make a box and whisker plot of the data and identify any outliers. • 10, 12, 11, 15, 11, 14, 13, 17, 12, 22, 14, 11 Australia: $2.20 Canada: $2.02 Germany: $4.58 Mexico: $2.09 United States: $1.59 Japan: $3.47 Taiwan: $2.16 a. Make a box and whisker plot for the gasoline prices. a. Which countries, if any, had gasoline prices that can be considered outliers? Measures of center: mean, median, mode Mean Average of the data set Median The middle value of a data set arranged from smallest to largest Mode The data value that occurs the most often, is a common measure of center for categorical data When describing data, you must decide which number is the most appropriate description of the center. Mean Median applet: http://bcs.whfreeman.com/tps3e/content/cat_020/applets/mea nmedian.html Use the mean on symmetric data and the median on skewed data or data with outliers Range Max value subtract minimum value (spread of all data) Interquartile Range Mean Absolute Deviation Variance and Standard Deviation Interquartile range (IQR) : shows middle 50% of data Average distance between each data value and the mean a measure of the “average” deviation of all observations from the mean. IQR = Q3 – Q1 Not affected as much by outliers Use when measure of center is median Use when measure of center is mean Complete a 5 number summary and box and whisker plot for the following data. • Number of hours spent on internet per week: 12, 4, 16, 18, 1, 6, 10, 8 To calculate Mean Absolute Value Deviation: Calculate the mean for the data set. Find the distance between each data value and the mean. That is, find the absolute value of the difference between each data value and the mean. Find the average of those distances. Find the mean absolute value of the following data set: • 52, 48, 60, 55, 59, 54, 58, 62 A measure of spread is the Standard Deviation: a measure of the “average” deviation of all observations from the mean. The symbol for Standard Deviation is σ (the Greek letter sigma). To calculate Standard Deviation: Calculate the mean for the data set. Determine each observation’s deviation: subtract the mean from each data point. (𝑥 − 𝑥). Square each deviation. “Average” the squared-deviations by totaling the squareddeviation and dividing the total squared deviation by (n-1). This quantity is the Variance. Square root the result to determine the Standard Deviation. Calculate the standard deviation of the following test scores: • 15, 20, 21, 20, 36, 15, 25, 15 The shape of the data’s distribution! If data are symmetric, with no serious outliers, use range and standard deviation. If data are skewed, and/or have serious outliers, use IQR. Quantitative Data: through graphs Categorical Data: through two way frequency tables Multiple bar graphs Multiple box and whisker plots These tables examine the relationships between the two categorical variables. A two-way frequency table will deal with two variables Relative frequency is the ratio of the value of a subtotal to the value of the total. Create a two-way frequency table for the following problem.