Chapter 7: Creating the Constitution Workbook & Notes
advertisement

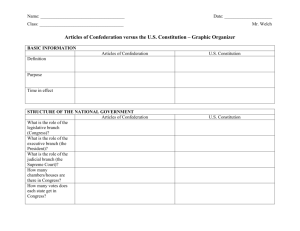
Name: Date: Pd: Chapter 7: Creating the Constitution Workbook & Notes 1. Articles of Confederation _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Land Ordinance of 1785 _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Northwest Ordinance of 1787 _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Shays’ Rebellion _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Annapolis Convention-1786 meeting after Shay’s Rebellion to discuss revising the Constitution. 6. James Madison _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Roger Sherman _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 8. James Wilson _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Governuer Morris _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 10. George Washington _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Benjamin Franklin _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 12. The Virginia Plan _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 13. The New Jersey Plan _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 14. The Great Compromise _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 15. The Three-Fifths Compromise _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 1 Name: Date: Pd: 16. Federalists _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 17. Anti-Federalists _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 18. Alexander Hamilton _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 19. John Jay _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 20. George Mason _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 21. Bill of Rights _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 22. The Federalist Papers _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Colonists’ Beliefs About Government What do you think the colonists believed about government? One way to find out is to look at this important document. Any ideas? Underline your guesses. When, in the course of human events, it becomes necessary for one people to dissolve the political bonds which have connected them with another, and to assume among the powers of the earth, the separate and equal station to which the laws of nature and of nature's God entitle them, a decent respect to the opinions of mankind requires that they should declare the causes which impel them to the separation. We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable rights that among these are life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. That to secure these rights, governments are instituted among men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed. That whenever any form of government becomes destructive to these ends, it is the right of the people to alter or to abolish it, and to institute new government, laying its foundation on such principles and organizing its powers in such form, as to them shall seem most likely to effect their safety and happiness. Prudence, indeed, will dictate that governments long established should not be changed for light and transient causes; and accordingly all experience hath shown that mankind are more disposed to suffer, while evils are sufferable, than to right themselves by abolishing the forms to which they are accustomed. But when a long train of abuses and usurpations, pursuing invariably the same object evinces a design to reduce them under absolute despotism, it is their right, it is their duty, to throw off such government, and to provide new guards for their future security. --Such has been the patient sufferance of these colonies; and such is now the necessity which constrains them to alter their former systems of government. The history of the present King of Great Britain is a history of repeated injuries and usurpations, all having in direct object the establishment of an absolute tyranny over these states. To prove this, let facts be submitted to a candid 2 world. Name: Date: Pd: Governing a New Nation States began to set up new governments by writing ______________________________________ __________ of 13 states wrote new constitutions Rhode Island and Connecticut used their __________________ but removed references of the ____________ State constitutions tried to avoid problems they had _______________ Limited ________________________ o Take power away from_______________ (state governor) and gave power to _______________ (elected by the people) o Most legislatures were _________________ (two houses: a senate and house of representatives) o Allowed more people to vote o All but a few states barred ____________________ o In New Jersey, ___________ allowed to vote till 1807 o Most states: Had to be a ________, male, _______ or older and ______________________ o 7 states added ________________ o Used to protect individual __________ o Virginia was first to add one o All 13 agreed that government only existed _______________________________ Articles of Confederation Adopted in _________ by the Continental Congress ______________ by last state in 1781 To all to whom these Presents shall come, we the undersigned Delegates of the States affixed to our Names send greeting. Articles of Confederation and perpetual Union between the states of New Hampshire, Massachusetts-bay Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina and Georgia. I. The Stile of this Confederacy shall be "The United States of America". II. Each state retains its sovereignty, freedom, and independence, and every power, jurisdiction, and right, which is not by this Confederation expressly delegated to the United States, in Congress assembled. III. The said States hereby severally enter into a firm league of friendship with each other, for their common defense, the security of their liberties, and their mutual and general welfare, 3 binding themselves to assist each other, against all force offered to, or attacks made upon them, or any of them, on account of religion, sovereignty, trade Name: Date: Pd: Confederation? A ___________association of ___________ states for a common _________________ Set up the government for the United States as a “____________________” Largest share of power given to _________________ States retained their “_______________, ________________, and ________________” Government Set-Up __________ branch of government: the legislature or __________ One-house legislature (_______________) All states have a __________ _____________ _____ states had to agree for law to go into effect ________ ________ had to agree before Articles could be ____________ A Limited Government Congress could not o ___________ o ___________ o ___________ Congress could o Deal with foreign nations and Native Americans o _____________ o _____________ o Coin or borrow money o __________________ Settling Western Lands Disputes over ownership of western lands slowed __________ of _____________ States did not want to ___________________ to national government (___________ was last to agree) Land Ordinance of 1785 o Surveyors divided land into 6 sq. mile ______________ o 1 sq. mile _____________ sold within the township o One section in each township set aside for _________________ Northwest Ordinance of 1787 o Guaranteed ______________ of settlers and ________________ o Set up a three-step process for admitting states Beginning of Settling: Governor, Secretary, 3 Judges 5,000 free adult male settlers: ______________ 60,000 people: _______________ 4 Name: Date: Articles of Confederation Pd: U.S. Constitution What type of legislature, unicameral or bicameral? Number of votes per state in the legislature? Who can levy taxes, the central government or states? What are the powers of the Congress? Number and name of the branches of Government? Number of votes needed to amend the Constitution? Number of votes needed to pass laws? Which has more power, the central government or states? What are the possible problems that could happen in the U.S. because of the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation? 5 Name: Date: Pd: Now that you have read Arty’s story, you should have a good idea of the answer to the question “What were the successes and failures of the Articles of Confederation?” Here’s your task – make a list of all of the weaknesses of the new government under the Articles of Confederation, and then describe the problems that could be caused by those weaknesses. Make a list of the successes as well. An example has been provided! SUCCESSES United the colonies WEAKNESS No national court system Brainstorm! What are problems that will occur with the weaknesses? Successes? 6 Name: Date: Pd: After watching the cartoon, what are some of the complaints delegates have about the Constitution? Compromises of the Constitutional Convention How will the states be represented in the Legislature? ___________________________________ o Created a _______________________________________ House of Representatives Votes (or representatives) based on population Senate 2 votes (or representatives) per state o This satisfied the people who wanted the New Jersey Plan o Also satisfied people who wanted the Virginia Plan Should everyone be allowed to vote or just a select group? ___________________________________________ o People would vote for representatives (or legislators) to represent them in Congress ___________________________________________ o Each state chooses Electors o The number of Electors per state is equal to the ____________________________________ from the House and Senate o The Electors usually decide based on the popular vote, but ___________________________ How should slaves be counted for representation in Congress? o _____________________________________________ Each enslaved person counted as _________________________ So for every __________________________________________ would count towards representation in the House of Representatives This compromise was overturned when slavery was banned in 1865 7 Name: Date: Pd: Debating the Constitution Once the Constitution was written by the delegates, each state had to hold a __________________ to _______________(approve) the _________________ The Constitution would go into effect once ______ states ratified it Not everyone agreed that the Constitution ___________________________ Issue Should the Constitution be ratified? Federalists Anti- Federalists Favored a ___________ or national _________________ Felt that for the Union to last there must be a _____________________ ______________________________ Wanted the central government to have ___________ it did not have under the___________, like the power to _______________ laws Felt the Constitution made the government _____________ Main Arguments: ______________________________ o Felt the too-strong central government would take away state power and individual freedom _______________________________ o Many state constitutions had one o No protection of basic freedoms ________________________________ o If president could be reelected again, may act like a king 8 Name: Date: Pd: Important Federalists Alexander Hamilton John Jay James Madison Strong supporters of the ___________________ To try to gain public support, they published a series of 85 newspapers essays called the _____________________________ The essays were very influential Important Anti-Federalists George Mason The author of Virginia’s __________________________________ Felt so strongly that the Constitution should have a Bill of Rights that he ______________________________________ Also felt that the Constitution took away too many ________________ rights Patrick Henry Felt the president would become too much _____________________ Thought the power was not ________________ enough Led the _______________ on the Constitution in ________________ Beginning the New Government In June 1788, _________________ became the 9th state to ratify the Constitution, allowing it to _______________________ In May of 1790, _______________ was the last state to ratify the Constitution ___________________ was elected President with _____________ as Vice President The first Congress passed a series of ___________________ which have become our _____________________________ Protect people from the ____________________ of the federal government Many come out of ____________________ with Britain 9 Name: Date: Pd: The Bill of Rights Using pgs. 240-242, look over the ten amendments in the Bill of Rights, and then write them in your own words. I will show you how I remember the amendment, and then you need to come up with your own way that helps you remember it! Amendment (in your words) How Mrs. Hoachlander Remembers it How you Remember it 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 10