Scientific Method PPT
advertisement

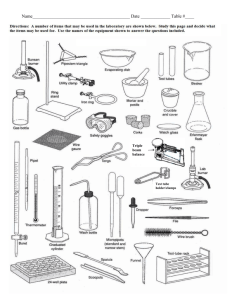
Unit 01: Lab Safety, Lab Equipment & Scientific Method Safety Symbols Reactive material could react when exposed to air and/or water, or when the material is disturbed, heated, or illuminated A Corrosive material is one which causes damage to skin, eyes or other parts on the body on contact. The technical definition is written in terms of "... destruction, or irreversible damage to living tissue at the site of contact". Lab Equipment Beaker Beakers hold solids or liquids that will not release gases when reacted or are unlikely to splatter if stirred or heated. Beaker Tongs Beaker tongs are used to move beakers containing hot liquids Erlenmeyer Flask Erlenmeyer flasks hold solids or liquids that may release gases during a reaction or that are likely to splatter if stirred or heated. Florence Flask Rarely used in first year chemistry, it is used for the mixing of chemicals. Narrow neck prevents splash exposure. Graduated Cylinder A graduated cylinder is used to measure volumes of liquids. Triple Beam Balance A balance is used to measure the mass of solid substances. Test Tubes 13 x 100 mm test tubes Ignition tube 10 x 75 mm test tubes Test Tube Holder A test tube holder is useful for holding a test tube which is too hot to handle. Test Tube Brushes Test tube brushes are used to clean test tubes and graduated cylinders. Forcing a large brush into a small test tube will often break the tube. Test Tube Racks Test tube racks are for holding and organizing test tubes on the laboratory counter. After washing flip test tube over on wooden peg to dry. Rubber Stoppers Rubber stoppers are used to close containers to avoid spillage or contamination. Containers should never be heated when there is a stopper in place. Spot Plates Spot plates are used when we want to perform many small scale reactions at one time. Glass Stir Rod A glass rod is used to manually stir solutions. It can also be used to transfer a single drop of a solution. Scoopula A scoopula is used to transfer solid materials. Forceps Forceps (or tweezers) are used to pick up small objects. Funnel A funnel is used to aid in the transfer of liquid from one vessel to another. Watch Glass A watch glass is used to hold a small amount of solid, such as the product of a reaction. Wash Bottle A wash bottle has a spout that delivers a wash solution to a specific area. Distilled water is the only liquid that should be used in a wash bottle. Weighing Boat Weighing boats are used to weigh solids that will be transferred to another vessel. Bunsen Burner Bunsen burners are used for the heating of nonvolatile liquids and solids. Strikers Strikers are used to light Bunsen burners. The flints on strikers are expensive. Do not operate the striker repeatedly just to see the sparks! Ringstands and their Components Ringstand Ringstands are a safe and convenient way to perform reactions that require heating using a Bunsen burner. Ringstands and their Components Utility Clamps Utility clamps are used to secure test tubes, distillation columns, and burets to the ringstand. Ringstands and their Components Iron Ring Iron rings connect to a ringstand and provide a stable, elevated platform for the reaction. Ringstands and their Components Wire Gauze Wire gauze sits on the iron ring to provide a place to stand a beaker. How to properly write up a lab. Must be on a sheet of paper. Requirements: • • • • • Name, Title, Date Objective Data Analysis Conclusion Labs will be graded using a rubric. Laboratory Report Format Title: Start with your name, the title and date of the lab. Mrs. Owen Using the Scientific Method to Solve Problems 8-28-2007 Laboratory Report Format Objective: Write the objective. Mrs. Owen Using the Scientific Method to Solve Problems 8-28-2007 Objective: To make observations. To observe and record how a system changes over time. To develop a hypothesis that fits the evidence you collect. Laboratory Report Format Data: Follow procedures. A data table may need to be copied or created. Mrs. Owen Using the Scientific Method to Solve Problems Data: Part A First Observations Coke Diet Coke Part B Experiment One Observations Similarities Differences 8-28-2007 Laboratory Report Format Analysis: Answer the questions, graph data or show calculations. Using the Scientific Method to Solve Problems Analysis: Sodium bicarbonate solution: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Sodium bicarbonate solution and raisins: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Mrs. Owen 8-28-2007 Solution with acetic acid: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Laboratory Report Format Conclusion: Answer questions in complete sentences in paragraph form. Refer back to purpose/objective. Concisely state findings. Using the Scientific Method to Solve Problems Conclusion: Mrs. Owen 8-28-2007 Scientific Method • The scientific method is a logical approach to the solution of scientific problems. • It uses a systematic method of solving problems based on experiments and observations. Scientific Method • An observation is the information obtained through the senses. • A hypothesis is the proposed explanation for the observation. • An experiment is carefully controlled, repeatable procedure for gathering data to test a hypothesis. Scientific Method • A theory is a thoroughly tested model that explains why experiments give certain results. It is possible that a new experiment could disprove it. Scientific Method • A scientific law is a concise statement that summarizes the results of many observations and experiments. Laws describe a natural phenomenon without explaining it. Scientific Method In early summer of 1965, a University of Florida assistant coach sat down with a team of university physicians and asked them to determine why so many of his players were being affected by heat and heat related illnesses. The researchers — Dr. Robert Cade, Dr. Dana Shires, Dr. H. James Free and Dr. Alejandro de Quesada — soon hypothesized two key factors that were causing the Gator players to ‘wilt’: the fluids and electrolytes the players lost through sweat were not being replaced, and the large amounts of carbohydrates the players’ bodies used for energy were not being replenished. The researchers then took their observation into the lab, and scientifically formulated a new, precisely balanced carbohydrate-electrolyte beverage that would adequately replace the key components lost by Gator players through sweating and exercise. They called their concoction ‘Gatorade’ Experimental Groups • Control Group- the group in an experiment used as a comparison. • Test Group- group in which one variable is changed at a time. – Variables • Independent Variable- Variable that stands alone and continues in the same way. Example: time • Dependent Variable- Depends on the independent variable. Example: Solubility