Science Starter!
advertisement
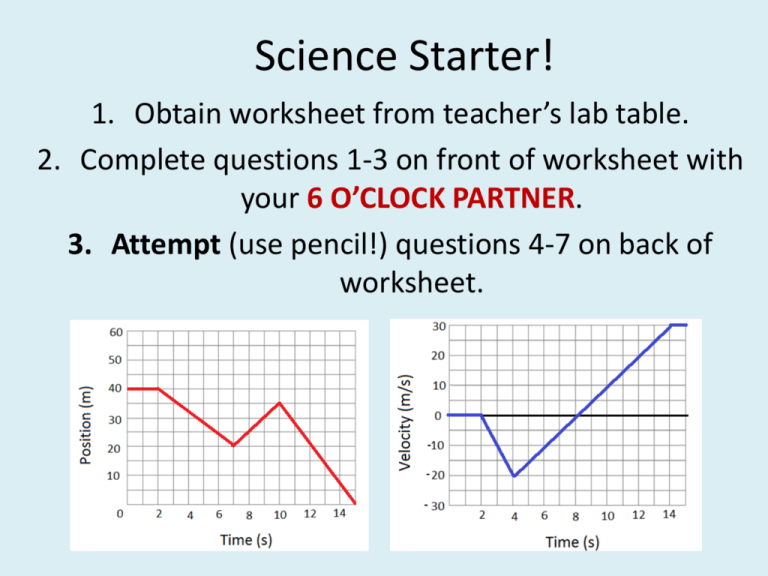
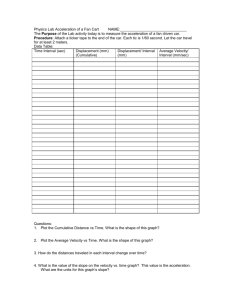
Science Starter! 1. Obtain worksheet from teacher’s lab table. 2. Complete questions 1-3 on front of worksheet with your 6 O’CLOCK PARTNER. 3. Attempt (use pencil!) questions 4-7 on back of worksheet. Key Ideas to Remember On a “Position vs. Time” graph: ∙ Linear Line: Constant Velocity - Positive Slope: Moving in (+) Direction (forward) - Negative Slope: Moving in (-) Direction (backward) - Zero Slope: Not Moving (stopped) * Speed: Distance / Time * Velocity: Displacement / Time - Average Velocity: Slope between any two points - Must include either (+) or (-) ∙ Curved Line: Acceleration Velocity vs. Time Graphs Describe the motion of the object for each interval: a) 0s – 4 s b) 4s – 8s c) 8s – 12s Acceleration Calculate the acceleration from: a) 0s – 4 s b) 4s – 8s c) 8s – 12s d) 0s – 12s Calculate the acceleration from: a) 0s – 4 s b) 4s – 8s c) 8s – 12s d) 0s – 12s Enclosed Area Shade in shape and find area to find displacement. Rectangle = BH Triangle = ½ BH On a “Velocity vs. Time” graph: ∙ Linear Line: Constant Acceleration - Positive Slope: positive acceleration - Negative Slope: negative acceleration - Zero Slope: constant velocity - Average Acceleration: Slope between any two points - Must include either (+) or (-) ∙ Area Between Line and Horizontal Axis - Displacement - Must include either (+) or (-) Kinematics Equations (1) (2) (3) Solving Problems (5 points) 1 point LIST all given variables (with units) and IDENTIFY the unknown (?) 1 point Select and write the appropriate the EQUATION(S) 1 point SUBSTITUTE the given variables into the equation 1 point Show the MATHEMATICAL STEPS 1 point Arrive at the correct ANSWER with correct UNITS 14 hours What is “14” a measurement of? (a) distance (b) speed (c) time (d) temperature KNOW UNITS! “x” (position): m “v” (velocity or speed) : m/s “a” (acceleration): m/s2 “t” (time): s Text Examples # 80 (1) vo = 32 m/s v = 96 m/s t = 8.0 s a=? (3) 96 = 32 + a(8) (4) 96 – 32 = a(8) 64 = a(8) 64 / 8 = a (2) v = vo + at (5) a = 8 m/s2 # 81 (1) vo = 22 m/s t = 6.8 s a = 1.6 m/s2 v=? (3) v = 22 + (1.6)(6.8) (4) v = 22 + (10.88) (5) v = 32.88 m/s (2) v = vo + at # 88 (1) xo = 0 m x = 325 m vo = 0 m/s a = 49 m/s2 v=? (2) v2 = vo2 + 2a (x – xo) (3) v2 = (0)2 + 2(49)(325) (4) v2 = 31850 (5) v = 178 m/s