Isotopes and Average Atomic Mass
advertisement

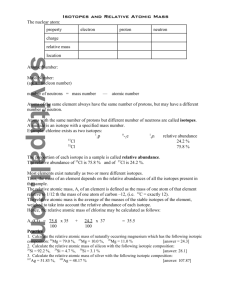
Isotopes and Average Atomic Mass Chemistry 11- Chapter 1 Section 4 Isotopes The number of protons define the type of atom: 6 protons is carbon 1 proton is hydrogen 8 protons is oxygen 92 protons is uranium However the number of neutrons can vary within a given type of atom Trend in the number of neutrons as atomic number increases Hydrogen Isotopes There are three main isotopes of hydrogen Hydrogen – 1p, 0n, 1e Deuterium – 1p, 1n, 1e Tritium – 1p, 2n, 1e Relative Mass of an Atom The mass of an atom is expressed in atomic mass units (u) In the past, hydrogen was used as a standard of 1 u but because of the isotopes, the standard was changed to carbon Atomic mass is determined based upon carbon12 as a standard with a mass exactly equal to 12u. One twelve of C-12 is equal to 1u Using this, the relative mass of every atom on the periodic table can be determined (i.e. oxygen 16 would have a mass of 16u) Isotopic Abundance Because elements as a combination of different isotopes, it is useful to consider the isotopic abundance For example, magnesium is composed of: Magnesium-24 – 79% Magnesium-25 – 10% Magnesium-26 – 11% Regardless of where you find magnesium, it will be composed of these percentages Mass spectrometer Highly specialized piece equipment that can identify the mass of an element or compound in a mixture and its relative abundance It directs the element in gas form across a tube and the beam is deflected by a magnetic field…heavy elements keep going straight, light elements veer of quickly. The detector plate senses the elements as they hit it. Isotopes and radioisotopes Some isotopes are stable but not all All elements after Bismuth are unstable Unstable isotopes break down- the nucleus, and transmutate to new elements and give off radiation in the process. They are described as radioactive and break down in a predictable way called half life There are many uses for radioisotopes especially in the medical and research field Nuclear radiation 3 types: alpha, beta and gamma Alpha= heavy, positive helium nucleus = 2 P and 2 N, can be stopped by paper Beta= negatively charged electron = can be stopped by aluminum or plexiglass (thick see-through plastic) Gamma= high energy electromagnetic radiation = no mass or charge, can be stopped by thick lead Average Atomic Mass and the Periodic Table The average atomic mass that appears on the periodic table is the average of the mass of all the element’s isotopes Therefore, even carbon, which is used as the standard, does not have an average atomic mass of 12 but rather 12.01 due to the presence of carbon-14 Carbon-14 is about 1.1% of all carbon while carbon-12 is the remaining 98.1% Average Atomic Mass Calculation mass 12 carbon12 masscarbon14 14 abundancecarbon12 98.1% abundancecarbon14 1.1% M C mC12 aC12 mC14 aC14 M C 12(.981) 14(.011) M C 12.02 Average Atomic Mass Naturally occuring silver exists as two isotopes. From the mass of each isotope and the isotopic abundance listed below, calculate the average atomic mass of silver Isotope Atomic mass (u) Abundance (%) Silver-107 106.9 51.8 Silver-109 108.9 48.2 Average masssilver107Atomic 106.9 Mass masssilver109 108.9 abundancesilver107 51.8% abundancesilver109 48.2% M Ag m Ag107a Ag107 m Ag109a Ag109 M Ag 106.9(.518) 108.9(.482) M Ag 107.9 You try 1. Chlorine has two naturally occurring isotopes. One has a mass of 34.969 and an abundance of 75.77% and the other a mass of 36.966 and abundance of 24.34%. Calculate the average atomic mass. 2. Calculate the average atomic mass of oxygen given the three isotopes abundance are 99.759%, 0.037%, 0.204% for the masses 15.995, 16.995 and 17.999 respectively. 1. 35.494 2. 15.999