Internet Information Server
advertisement

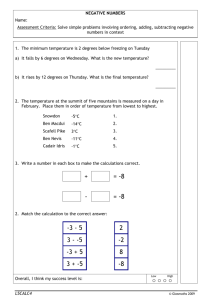
Project Report Microsoft Internet Information Server Group 4 Javier Ek, Jimmy Phung, Ben Lee, Tom Truong CIS 454- FALL QUARTER 1999 Internet Information Server Group 4 Overview -Jimmy Phung Installation - Tom Truong Troubleshooting TCP/IP - Benjamin Lee Web Applications -Javier Ek What is a Microsoft Internet Information Server? It is Microsoft’s Web server that allows for the management of Web-related applications, files and data. By Jimmy Phung 3 What is a Web Server? A Web server is a specialized program that uses the client/server model and the World Wide Web's Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) to present files in the form of Web pages to the users. – Source: www.whatis.com By Jimmy Phung 4 Example of the Use of a Web Server When we type in: www.calstatela.edu/ats/cbt.htm, we are directed to the web server with the domain name www.calstatela.edu. The web server then finds the ats directory and the cbt.htm file. It then forwards the file directly back to us. By Jimmy Phung 5 Uses of the Internet Information Server (Examples) Corporate workgroups using intranets Corporate partners using extranets Customers logging on to a Web site By Jimmy Phung 6 Where can you find the Microsoft Internet Information Server? The Internet Information Server is found in the Microsoft Option Packs All NT Servers shipped after January 1998 come with Internet Information Sever By Jimmy Phung 7 How Much Does the Internet Information Server Cost? FREE You can download it form the Microsoft Web site Tom will tell you how By Jimmy Phung 8 Where Can You Install Internet Information Server? Windows 95 Windows 98 Windows NT Workstation Window NT Server By Jimmy Phung 9 Features of the Internet Information Server Setup and Management – Use the Graphical User Interface (GUI) – Easy to learn; relatively short learning curve By Jimmy Phung 10 Features of the Internet Information Server Building Web sites – Integrates fully with Microsoft Front Page, which allows for the creation of Web pages – Contain assorted Web-building Wizards – Facilitates the development of Active Server Pages (ASP), which allow the creation of active and interactive Web pages. VB Scripts in HTML file Java Scrips in HTML file By Jimmy Phung 11 Features of the Internet Information Server Support the writing of web-based applications that access databases – Integrate fully with Microsoft SQL Server, which facilitates the the manipulation of databases – ODBC driver support By Jimmy Phung 12 Features of the Internet Information Server Security – Prohibit access by user and group using passwords – Prohibit access to directories and files By Jimmy Phung 13 Features of the Internet Information Server Security Continued – Security rules – Security rules can be based on URLs – Can hide part of a document based on security rules – Can change user access control list without restarting server – Supports Secure Socket Layer (SSL) v. 2 and v. 3 By Jimmy Phung 14 Features of the Internet Information Server Reliability – Each Internet applications running on the Internet Information Server can run on a separate memory space – When one application crashes, it will not crash the whole system. Only the affected application crashes, the server and the other applications keep on working By Jimmy Phung 15 Features of the Internet Information Server Reliability Continued – Contains Integrated Message Queuing, which provides a way for applications to send and receive messages over a network - even when part of the application or the network becomes unavailable. This increases reliability. By Jimmy Phung 16 Features of the Internet Information Server Scripting support – Script debugging, which helps debug ASP scripts – Supports JAVA By Jimmy Phung 17 Features of the Internet Information Server Web Management – Programmable Management Console – Ability to customized management tools – Browser-Based Administration – Remote administration – GUI interface/command line interface – Has the Configuration Rollback feature, which helps to bring the server back to previously saved configurations. By Jimmy Phung 18 Minimum Requirements 80x86-Based Computers – 486 Computer – 66 MHz RAM – 32 Meg Ram minimum – 64 Meg highly recommended Hard Disk – 200 Meg of free space By Jimmy Phung 19 Minimum Requirements Internet Explorer 4.0 Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT Workstation or Window NT Server Service Pack 3 or later for NT By Jimmy Phung 20 IIS Installation Process There are a number of ways to install IIS 4.0. You can download the Windows NT Option Pack from the Internet, or your can install it from CD. To download the Option Pack from the Internet, you use the URL shown here: http://backoffice.microsoft.com/downtrial/optionpack.asp To install the Option Pack from the CD, you insert the CD in the drive and run the appropriate setup.exe. By Tom Truong 21 By Tom Truong 22 By Tom Truong 23 By Tom Truong 24 • The minimum installation program is designed to conserve disk space on your system. • The typical installation installs all the components of IIS included in the minimum installation. In addition, it installs the rest of the optional IIS components. Included in the typical installation is the FTP service, the Internet Service Manager (HTML), and help on server administration, content management, and content development. • The custom installation allows you to choose which IIS components you want on the computer, apart from the components that are required and selected by default. • Let’s choose the Custom installation, which allows you to select any combination of components in addition to the IIS component that is required to run the IIS server. By Tom Truong 25 By Tom Truong 26 By Tom Truong 27 By Tom Truong 28 By Tom Truong 29 By Tom Truong 30 By Tom Truong 31 By Tom Truong 32 By Tom Truong 33 By Tom Truong 34 By Tom Truong 35 By Tom Truong 36 By Tom Truong 37 By Tom Truong 38 By Tom Truong 39 By Tom Truong 40 By Tom Truong 41 •If you are using IIS on an intranet, you can copy the unattend.txt file from the Option Pack CD to a folder on the local computer (The unattend.txt file is located on the CD in the CPU_Type/inetsrv/directory, where CPU_Type is the processor on the computer where IIS will be installed.) This file allows you to perform unattended installations from that folder. This is useful for performing installations without having to remain at the computer and step through the installation options. • To start the unattended setup, you either place the CD in the CD drive, or make a network connection to the CD drive containing the Option Pack CD. You then copy unattend.txt to your local hard disk and make any necessary changes to install the appropriate components. • At a command prompt, you change to the folder on the CD containing setup.exe, then enter the following path: setup/u:<full path to Unattend.txt>. For example, if the file located in the temp directory on the C drive, you type: setup/u:c:\temp\unattend.exe By Tom Truong 42 TROUBLESHOOTING TCP/IP By Ben Lee 43 Presentation Objectives Identify some of the problems which may arise in a network that uses TCP/IP as its communication protocol Explain the utilities that are available for troubleshooting TCP/IP By Ben Lee 44 TCP/IP Problems Configuration of the local computer Connecting to other hosts on the network Routing problems Naming resolution errors Source and destination hosts are trying to communicate using different protocols By Ben Lee 45 Tools that come with Windows NT Microsoft SNMP Service Event Viewer Performance Moniter Registry Editor Network Monitor, Agent, and Tools By Ben Lee 46 Utilities used for troubleshooting TCP/IP IPConfig Ping Hostname Nbtstat ARP Tracert Nslookup Netstat Route By Ben Lee 47 IPConfg Display current TCP/IP network configuration values, and update or release TCP/IP network configuration values. Display IP address, subnet mask, and WINS and DNS configuration. By Ben Lee 48 By Ben Lee 49 IPConfg By Ben Lee 50 IPConfg By Ben Lee 51 Ping Verify whether TCP/IP is configured correctly and that a remote TCP/IP system is available. Ensure that a host computer you are trying to reach is actually operating. Used with a host that is operating to see how long it takes to get a response back. By Ben Lee 52 •Ping sends an ICMP echo request to a target host name or IP address. By Ben Lee 53 •If there is an error message using your own IP address, view the configuration to check and correct it. By Ben Lee 54 Nbtstat Useful tool for solving NetBios name resolution problems Switch to display the names that were registered locally on the system By Ben Lee 55 Nbtstat By Ben Lee 56 -a Lists the remote computer's name table given its host name. -A Lists the remote computer's name table given its IP address specified in dotted decimal notation. -c Lists the contents of the NetBIOS name cache, with the IP address of each name. -n Lists local NetBIOS names. In this listing, "Registered" indicates that the name has been registered on this network node, either by b-node broadcast or by a WINS server. By Ben Lee 57 -R Reloads the LMHOSTS file after purging all names from the NetBIOS name cache. -r Lists name resolution statistics for Windows networking. On a computer configured to use WINS, this option returns the number of names resolved and registered broadcast or WINS. -S Displays both workstation and server sessions, listing the remote hosts by IP address only. -s Displays both workstation and server sessions. It attempts to convert the remote host IP address to a name using the HOSTS file. By Ben Lee 58 Nbtstat When adding more than 25 dialout devices under Windows NT 4.0 RAS, the NBTSTAT command will return the following message: – Unable to access NBT driver; Unknown Error This problem is because NBTSTAT is not reading the entire contents of a registry key. By Ben Lee 59 ARP ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is a protocol for mapping an Internet Protocol address (IP Address) to a physical machine address that is recognized in the local network. The most common level of IP in use today, an address is 32 bits long. By Ben Lee 60 How ARP Works When an incoming packet destined for a host machine on a particular local area network arrives at a gateway, the gateway asks the ARP program to find a physical host or MAC address that matches the IP address. By Ben Lee 61 Route The route table controls any routing decisions made by the hosts on a network You can display the route table using the Route Print command. By Ben Lee 62 Route By Ben Lee 63 Tracert Examine the route between two nodes on a network Determines the route by sending the first echo packet with a TTL of 1 and incrementing the TTL by 1 on each subsequent transmission until the target responds or the maximum TTL is reached. By Ben Lee 64 Tracert By Ben Lee 65 Netstat Displays protocol statistics and current TCP/IP network connections. Syntax : netstat [-a] [-e][n][s] [-p protocol] [-r] [interval] By Ben Lee 66 Netstat By Ben Lee 67 By Ben Lee 68 By Ben Lee 69 Nslookup Lets an Internet server administrator or user enter a host name and find out the corresponding Internet Address. It will also do reverse name lookup and find the host name for an IP address you specify. By Ben Lee 70 Nslookup For example, if you entered "whatis.com", you would receive as a response our IP address, which happens to be : 199.45.146.176 Or if you entered "199.45.146.176", it would return "whatis.com". By Ben Lee 71 Internet Information Server Web Applications Group 4 By Javier Ek 72 Introduction Internet Information Server can be used for interactive applications and scripts for your website. IIS can be used for CGI Scripts and ISAPI Applications. Using IIS with ASP pages on a server. By Javier Ek 73 Methods CGI(Common Gateway Interface) ISAPI(Internet Server Application Program Interface) ASP(Active Server Page) Applications SSI(Server Side Includes) By Javier Ek 74 CGI By Javier Ek 75 CGI What is CGI? By Javier Ek 76 CGI By Javier Ek 77 CGI CGI script conforms to CGI standards. Scripts or programs can be written in any language for applications to be executed on a system. These languages can be C++, PERL, Visual Basic, and NT Batch Files. Programs such as VB and C++ need to be compiled in order to work. Scripts do not need to be compiled and are much more portable. By Javier Ek 78 CGI – Security Issues There are several security issues in regards to CGI. Intruders and hackers can manipulate CGI script to access sensitive information such as passwords and registry files. They can also use CGI script to run system commands. This risk can be reduced by having experts write the scripts and keeping them in one single directory with only an administrator access. By Javier Ek 79 CGI - Requirements To write CGI Scripts a working knowledge of HTML and HTTP protocol is needed. By Javier Ek 80 ISAPI What is ISAPI(Internet Server Application Program Interface)? By Javier Ek 81 ISAPI Applications that use ISAPI have executable code that reside in NT DLL(Dynamic Link Library). There two areas of development are applications and filters. ISAPI applications are known as Internet Server Applications(ISAs) By Javier Ek 82 ISAPI – How It Works By Javier Ek 83 ISAPI and CGI By Javier Ek 84 Active Server Pages(ASPs) Active Server Pages are a scripting environment that overcome the limitations of CGI. With ASP you can combine HTML, scripts, and text on web pages. The built-in Active X components can be used to perform dynamic tasks, such as connecting to a database or performing calculations. By Javier Ek 85 ASP ASP eliminates the need to learn a full programming language or compile programs separately. Any scripting language that follows the ActiveX scriting standard such as Vbscript or Javascript. To use other languages such as PERL, Python, or REXX you need a separate scripting engine from a third party developer. By Javier Ek 86 ASP Properties By Javier Ek 87 ASP Security ASP offers the most security of the three methods. By Javier Ek 88 ASP Advantages ASP applications are easy to modify and develop. An ASP file is simply a text file that can contain HTML tags and embedded script commands. ASP uses ActiveX Control which are essential to dynamic web pages. By Javier Ek 89 Summary Internet Information Server can be extended to use CGI, ISAPI, and ASP for web applications. CGI is the most common but ISAPI, and ASP are also used. ASP offers several advantages over CGI in terms of security, capabilities, and browser compatibility. Internet Service Manager can be used to specify a starting point directory and to configure your application. By Javier Ek 90 References http://www.pcmagazine.com http://www.pcworld.com CBT Courses – IIS http://www.whatis.com http://www.microsoft.com Internet Information Server END OF PRESENTATION Group 4 Javier Ek Jimmy Phung Tom Truong Benjamin Lee