1.08 * HDW work with graphs in economics
advertisement

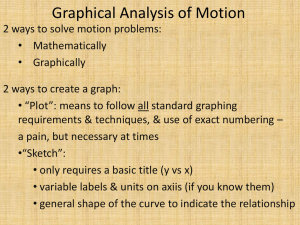
1.08 – HDW work with graphs in economics HW Review • Do Now Normal Line Graphs • Horizontal axis – independent variable • Vertical axis – dependent variable • Read graph from LEFT to RIGHT (like a book!) The Main Graph in Econ • Supply and Demand Curves • Read differently How much would you pay for… • An “A” on the next test? Predicting prices • Who would benefit from being able to predict changes in prices? – Buyers – Sellers – Speculators • Who would benefit from being able to predict changes in quantities sold? – Sellers We will begin by analyzing competitive markets • -- markets in which there are many buyers and many sellers of the same product or service. • The key feature is that no individual’s actions have a noticeable effect on the price at which a good or service is sold. Later in the course we will study other types of market structures such as oligopolies, monopolies and monopolistic competition. The foundation of market analysis: Supply and demand model • -- model of how a competitive market works • This model will help us answer questions such as “How will an increase in gas price effect the price and quantity of SUVs sold?” The demand Schedule • List of prices of a good/service and associated quantities demanded at those prices. • Using the data in the demand schedule, a Demand Curve is a graph that depicts the points in the demand schedule. • What type of relationship do you expect between price and quantity? – INVERSE!!!!! (negative correlation) The law of demand • A higher price of a good, other things being equal, leads people to demand a smaller quantity of the good. A change from one point on this curve to another point on this curve is called a change in quantity demanded. Figure 3-1 The Demand Schedule and the Demand Curve Krugman and Wells: Microeconomics Copyright © 2005 by Worth Publishers • Talking about reading a demand curve • Use economic handbook visuals • Discuss how it is a change in price that drives everything. • Interpret points on the demand curve • A change in price changes “quantity demanded” • Maybe use grebes Issues in Interpreting Graphs • Features in Graph Construction: – Consistent Scale – Area Principle – Truncated Scale – The Effect of Scale (size of increments can affect visual interpretation of data)