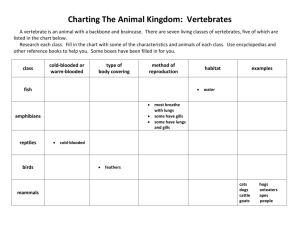
Survey of the Animal Phyla I
advertisement

1. 2. 3. 4. Eukaryotic (cells with a nucleus) Multicellular (organisms are generally large Motile (can move at some point of its life) Heterotrophic (feeds on other organisms) There are 31 Animal Phyla identified by Scientists Major Evolutionary developments occur along the roughly 600 Million years of the Animal Kingdom We will Identify the 10 Largest Phyla of Animals Lack True Tissues Are Filter Feeders Have Choanocytes for Water movement Entirely aquatic 9000 Species Parametazoa- Animals without Tissues Examples include All variety of salt water and fresh water Sponges First Eumetazoans- Animals with tissues All members of this phyla have “Stinging Cells” called nematocysts Have gel-like bodies Salt or fresh water Body form are Polyp (mouth up) or Medusa (mouth down) All have Tentacles with Nematocysts All have Tentacles with Nematocysts Have extra-cellular digestion with a gastrovascular cavity “sac body plan” Have Radial Body Plans 10,000 Species Examples: Hydra, Jellyfish, Man-o-war, Coral, Sea Anemone, Sea Fans First Animals with Bilateral Symmetry All are “Flatworms” with ribbon-like bodies Simplest organisms with specialized organs Single opening into a digestive gut. Can absorb nutrients directly into body Simple Nervous system Many are parasitic living in hosts Free living flatworms live in water 20,000 species Examples include….Planaria, Tapeworms, Flukes, and Marine Flatworms. First organism with an alimentary canal with both mouth and anus Microscopic fresh water organism Has jaws surrounded by cilia to bring in food 2200 Species Non-segmented One way digestive tract Covered by a Thick cuticle First organism with a pseudo-coelom 12,000 species Free living and Parasite species Examples: Pinworms, Ascaris, Hookworms, heartworms, Trichina spiralis (Pork) 110,000 species (Second Largest) Breathe by Gills Mantle secrets a shell in most species Have a true visceral mass with many complex internal organs. Has a muscular “foot” for movement Three main classes of Mollusca ◦ 1. Gastropods-single spiral shell, scraping mouth piece called a “radula” ◦ Examples are snails, slugs, conches ◦ 2. Bivalves-two piece hinged shell, two siphons for filter feeding. ◦ Examples : Clams, Oysters, Scallops, Mussels ◦ 3. Cephalopods-no shell but has a well developed head region, 8 arms/tentacles, mouth part includes a Beak. Eyes very similar to Humans ◦ Examples: Squid, Cuttlefish Octopus, Nautilus Gastropods Bivalves Cephalopods 12,000 Species Internally and externally segmented Well developed nervous system Have a closed circulatory system First organisms with a true body cavity Three Classes: 1. Oligochaeta- terrestrial Earthworms and bloodworms 2. Hirudnia- Parasitic worms like Leeches 3. Polychaeta- marine worms like sandworms, bristleworms, tubeworms and fanworms Largest Animal phyla with over 1.5 million species General Characteristics ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. True body cavity Segmented Jointed Appendages Exoskeleton made of Chitin Must “Molt” to grow 7 Classes of Arthropods Trilobite- Extinct aquatic species Merostomate- Includes only Horseshoe Crabs Crustacians-mostly aquatic, Crabs, Lobster, Shrimp, Barnacles, Pill bugs Insects- largest arthropod class, undergo Metamorphosis, 3 pr. of legs, only group that can fly. Insects- largest arthropod class, undergo Metamorphosis, 3 pr. of legs, only group that can fly. Includes beetles, ants, butterflies, bees, mosquitoes, weevils and grasshoppers Arachnids- 4 pair of legs, have fangs instead of jaws, most produce venom, includes spiders, ticks, scorpions, chiggers Diplopods- four legs per segment, herbivores, includes all Millipedes. Chilopods- two legs per segment, aggressive carnivores, includes all centipedes 10,000 Species Endoskeleton with interlocking plates called ossicles 5 part Radial Body Plan Fundamentally Bilateral Has a Water Vascular system that controls water flow, suction and tube feet. Uses skin gills for respiration Remarkable regenerative abilities. Examples include, sea stars, brittle stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers and sand dollars Animals with a Notocord 42,500 species All chordates have Bilateral Symmetry, notochord, spinal cord and highly developed Head region and brain. Three Sub Phyla 1. Urochordates2. Cephalochordates3. Vertebrates- Vertebrates- Largest Group of Chordates Notocord becomes the Vertebrae during embryo development Largest group of Vertebrates are fish First Vertebrates originated around 500 million years ago. Seven Classes of Vertebrates 1. Agnatha- Primitive jawless Fish. Long tube bodies breathe by gills, Salt Water…. Lampreys 2. Chondrichthytes----Cartilage Fish Has a skeleton made of cartilage, All Salt Water species, gills Includes Sharks, Skates and Sting Rays 3. Osteichthyes—Boney Fish----fresh or salt water, skeleton made of calcium bone. Gill Breathers…. Ex. Include, Bass, Goldfish, Eels, Marlin, Catfish and Tuna 4. Amphibians---Four Legged creatures that can live out of water but need water for reproduction. Lung Breathers as adults, gill breathers as young, Soft Moist skin…. Includes Frogs, Toads, Salamanders and Newts 5. Reptiles Breathe by lungs in all stages. Body covered by scales. Eggs produced on land are tough and leathery. First to have Internal Fertilization. Includes Lizards, Snakes, Turtles, Alligators and relatives. Most include Dinosaurs based on general characteristics All Aves….. Have feathers instead of scales Are warm blooded Have a 4 chambered heart Produce hard shelled eggs Provide much parental involvement in the young Eagles Hawks Partridge Chicken Peacock Sparrow Owl Penguin Ostrich 7. Mammalia--- the Advanced Vertebrates All have hair on the body Warm blooded Have a Four chambered heart Internal fertilization Give live birth Nurse the young with milk External ears 1- Parametazoans to Eumetazoans 2. Radial symmetry to Bilateral Symmetry 3. Acoelomate to Coelomate 4. Gill Breathing to Lung Breathing 5. Protostome to Deuterostome 6. Invertebrates to Vertebrates