BackBenchersCafe.com CHEMISTRY (HONOURS) Part
advertisement

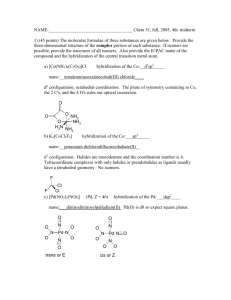
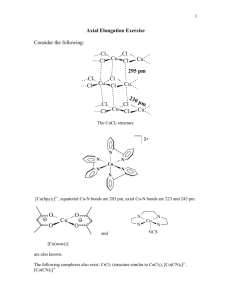
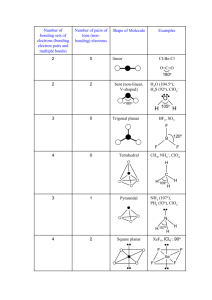
CHEMISTRY (HONOURS) Part-3 PAPER –V 2011 1. (a) Describe the concept of hard and soft acids and base. (b) Whv do you think that phosphines (𝑅3 𝑃) and Phosphineoxides 𝑅3 𝑃𝑂 differ considerably in their base propertis? (c) Which is more stable 𝑃𝑡𝐶𝐼42 or Pt𝐹42 and why? 2. (a) Make drawings of the d-orbital and state which fall in eg and which fall into t2g set in an octahedral field. (b) Prepare a diagram that traces how the d-orbital splitting pattern changes as an octahedral complex is altered via tetragonal distortion that is first weak and then reaches the extreme case where a square four-coordinate complex is obtained. (c) By using orbital spliting diagrams, show which 𝑑 𝑛 elector configurations are capable of giving both low spin and high spin configurations in an octabhedral ligand field. 3. (a) Discuss laporte and spin se lection rules. (b) Discuss spectrochemical series. (c) Draw the combined Orgel diagram for d1 and 𝑑 9 octahedral and tetrahedral complexes. 4. (a)Why do many square planar complexes have two term rate laws for ligand substitution reactions? (b) Discuss trans-effect with suitable examples. 5. (a) Discuss the method of preparation, structure and bonding of Zeise's salt. (b) What are the three broad classes of organometallic compounds? Give an example of each. (c) Gjve two general methods of preparation of metal carbonyls with examples. (d) Which are the only two metals to react directly with CO under conditions suitable for practical syntheses? 6. (a) Write a- short note on nitrogen fixation in biological systems. (b) Discuss the role of C𝑎2+ in biological systems. Write the short .notes on the following: (a) Silicones (b) Russell-Saunders coupling (a) Draw the MO diagram of CO. (b) Draw the stiucture of porphin. (c) Why are tetrahedral complexes usually not low spin? (d) What is the gr ound state term for a d5 ion? 2009 1. (a) Show by means of a diagram how the patterns of d-orbital spliting changes as anoctahedral complex undergoes teragonal distortion and eventually become a square planner complex. (b) What is epectrochemical series and what is its importance? 2. (a) What are organometallic compounds? (b) Describe three important general methods of preparing organometallic compounds. (c) Describe the structure and bonding of the anion [Pt𝐶𝐿3 𝐶𝐿3 CH]- in Zeise's salt. 3. (a)Write the formula of the mononuclear metal carbonyls formed by V, Cr, Fe and Ni. (b)Explain using MO diagram how CO which has neligible doner properties towards simple acceptors such as B𝐹3 can form strong bonds to transition metal atoms. 4. Give short account of substitution reactions in square planar complaxes including transeffect. 5. Write a note on silicones with respect to chemical nature, structure, preparation and industrial applications. (a)Draw the combined Orgel diagram for d1 and 𝑑 9 ions in octahedral and tetrahedral field. (b)Why the tetrahedral complexes of an element give much more intense d-d spectra than its octahedral complexes? (c) Discuss laporte orbital selection rule. 6. (a)Name two non-transition and four transition metals that play important functional roles in biological processes. (b)Write a brief account on the functions of Na and K in biological systems. (c) Give a very brief account of the biological role of La. 7.(a)Discuss the hard and soft acid-base concept. (b)Using the above concept, predict which of the following Adducts should be the more stable adduct and then explain your choice both in terms of -𝜎 and 𝜋– bonding effects : 𝐻3 N:BB𝑅3 or 𝐹3 N:B𝐹3 2008 1. (a) Describe trhe HSAB concept with examples. (b)In terms of HSAB concept which end of SCN ion would you expect to coordinate to 𝐶𝑟 3+ ? to 𝑃𝑡 2+ . (c) Which member of each pair would you except to be more stable (i) 𝑃𝑡𝑐𝑙42− or 𝑃𝐿𝐹42− 3+ (ii) 𝐹𝑒(𝐻2 𝑂)3+ 6 or 𝐹𝑒(𝑃𝐻3 )3 2. (a) Draw an Energy level diagram to show lifting of the degenerace of the 3d orbitals in a tetrahedral ligand field. (b) By using orbital orbital splitting diagrams show which 𝑑 𝑛 electrons configurations in an octahedral ligand field. (c) Calculate spin only magnetic moments for the high spin and low spin octahedral complexes of 𝑑5 transition metal ions. 3. Write short notes on Following: (a) Paramagnetism (b) Ferromagnatism (c)L-S coupling 4. (a) Describe the selection rules for electronic transitions in transitions metelcomplexes. (b) Draw the orgel diagram for 𝑑1 and 𝑑 9 ions in an octahedral field. (c) The absorption spectrum of Ti(𝐻2 𝑂)3+ 6 shows only one band with a peak at −1 20300 𝑐𝑚 . Explain it using the orgel diagram. 5. (a) Define stepwise stability constant and overall stability constant for the formation of a series of complexes. How are they Related. (b) how do the magnitudes of the stepwise stability contants(𝐾𝑒 ) vary withincreasing n? (c) Discuss chelate effect with an example. 6. (a) Give an definition of an organometallic compound. (b) What are the three broad classes of organometallic compounds? Give an example of each. (c) Describe two methods of preparation of Lithium alkyls. (d)Discuss the structure of methyl lithium. 7. (a) What are the functions of hemoglobin and myglobin ? What are the principle similarities in their structure? (b) Write short notes on nitrogen fixation. 8. (a) What are Phospphozenes? (b) Discuss the methods of preparation of phosphozenes. (c) Discuss the structure of phosphozenes.