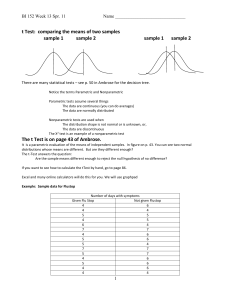
Inferential tests
advertisement

+ Quantitative Analysis: Supporting Concepts EDTEC 690 – Methods of Inquiry Minjuan Wang (based on previous slides) + 2 Agenda Quick review of data Why analysis is necessary – beyond descriptive statistics The Culture data posted on BB Descriptive analysis vs. inferential analysis Review Key Concepts of Descriptive Statistics Inferential analysis concepts Types of tests – parametric and non-parametric What test should I use when? Next steps for your studies We will help you with inferential analysis using SPSS or other + 3 Our Special Guests: Types of Analysis Descriptive statistics Correlation Measuring a relationship between studied variables Inferential statistics Inferences from a studied sample to a population Parametric analyses Nonparametric analyses + 4 What is measurement? Measurement: process of assigning numbers, according to rules defined by the researcher. The numbers are assigned to events or objects, such as responses to items, or to certain observed behaviors Correspondence between event/objective/behavior and number is defined by the researcher + 5 Types of Measurement Scales Nominal Ordinal Involves order of the scores/ratings on some basis (e.g., attitude toward the government) Interval Categorization, no implied order (e.g., sex, eye color) Unit interval is the same across the scale, doesn’t necessarily begin at zero (e.g., time, test score) Ratio Equal unit with a true zero point (e.g., the government expenditures; birth weight in pounds) + 6 Inferential statistics Making inferences from samples to populations Making inferences, then conclusions, from the statistics of a sample – that’s inferential statistics In practical terms, this means testing your hypothesis + 7 Inferential statistics Inferential tests produce a level of significance Significance level or level of significance (α- level) is a probability (for example, 0.05) used in making a decision about the hypothesis (i.e., rejecting the null hypothesis); it is called the alpha level Significance level is set prior to commencing the study In education, typically .05 Compare the P value with a. P is probability of chance + 8 Assumptions of parametric analyses Scale: Dependent variable is measured on an interval scale (or ratio) – not nominal or ordinal Sample: random sampling & normal distribution Normal distribution is required only if sample size is less than 30. More than 30, the sample is large enough to have a normal distribution. Distribution: When two or more populations are being studied, they have homogeneous variance. This means that the populations have about the same dispersion (SD) in their distributions. Mean can differ. When you cannot meet these assumptions (i.e., you have categorical data)… look to non-parametric analyses… + 9 Inferential statistics - parametric t-test (difference between two means) testing the statistical significance of the difference between means from two independent samples, or two sets of scores from the same sample (pre to post) Types: T for 1 (paired samples); and T for 2 (unpaired samples) + Concepts behind Inferential Statistics Drawing conclusions from your data Let’s work on the assumption that we’re measuring knowledge. For EDTEC folks – think Kirkpatrick’s Level II – in other words, mastery of objectives Let’s make our audience diesel technicians who work for dealers of a major auto manufacturer Finally, let’s say we have two treatments: 1. Traditional classroom instruction, with limited exercises 2. Fully hands-on curriculum involving “bugged” trucks and problem solving throughout + 11 Diesel Technician Scores Course objectives-based Test of Mastery (percent mastery) Pretest Mean Posttest Mean Gain (difference in means) Traditional 55.55 94.65 +39.1 Hands-on 53.45 97.76 +44.31 Are there any statistically significant differences? T test will tell. Compare P with a. + 12 Inferential statistics - parametric But what happens when you have more than two independent variables? For example, what if there were three types of classes for the diesel technicians? Analysis of variance (ANOVA) Tests the statistical significance when 2 or more independent variables are present Consider: A study on student learning with the presence of: no music slow music fast music Does Culture Make a Difference in learner perceptions? The survey: Perceptions about being equal with their instructor Chinese, American, Korean students Tests conducted Kruskal-Wallis Analysis of Variance Non-parametric version of ANOVA Results and Interpretation P=0.02 comparing with a=0.05 ??? 13 O. Perceptions about Being Equal with Instructors (the higher the mean, the lower the equality, 1(SA)-5(D)) n Rank Mean su ra m nk American 31 950.0 30.65 Chinese 15 682.5 45.50 1217. 29 5 41.98 Korean Kruskal-Wallis statistic 7.15 p 0.028 14 Parametric versus Nonparametric Parametric – Characteristic is normally distributed in the population; sample was randomly selected; data is interval or ratio Nonparametric Use when you have a specialized population, you’ve not randomly selected, or data is ranked or nominal “Cooking” Analogy steamed versus fried Streamed broccoli versus baked pumpkin pie 15 + Scale: Can be used with ordinal and nominal scale data Sample/Distribution: Inferential statistics - nonparametric Require few if any assumptions about the population under study Nonparametric tests do not emphasize means; they use frequencies and other statistics to investigate significance + Recognize there are many, many statistical tests… And What test should I use? that ED 690 is not intended as a statistics course. Still, you should be conceptually familiar with these statistical tests + 18 Choosing the appropriate test Relationship between variables About means, and parametric assumptions are met Magnitude of Relationship Parametric analyses t-tests Correlation Coefficient Chi-square About frequencies, etc., and parametric assumptions are met Nonparametric analyses ANOVA Chi-square Inferential: Parametric tests T-Test for means T for 1 (pre- post- tests of 1 group) T for 2 (compare the mean of 2 groups) Analysis of Variance ANOVA Compare differences between 2 or more groups Analysis of Covariance 19 Inferential: Non-parametric Nonparametric Techniques for Quantitative Data Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test –Tea for one (Paired Samples T test, Dependent samples T) The Mann-Whitney U Test—for T(ea) for two (Unpaired Samples T Test, Independent Samples T) The Kruskal-Wallis One Way Analysis of Variance—for ANOVA 1 independent variable The Friedman Two-Way Analysis of Variance—for ANOVA 2 or more independent variables 20 + 21 Inferential statistics - nonparametric The Chi-Square (X2) test and distribution Unlike t-distribution, the X2 distribution does not require symmetrical distributions It tests hypotheses about how well a sample distribution fits some theoretical or hypothesized distribution Is there a relationship between eye and hair color? Tails of A Test Two-tailed test (non-directional/both) There is no difference in content acquisition between "discovery learning" and "direct instruction.“ One-tailed test (directional/upper/lower) difference will be in one direction only Students who use "discovery learning" exhibit greater gains in content acquisition than students who use "direct instruction" 22 + 23 Type I and Type II errors What if we observe a difference – but none exists in the population? What if we do not find a difference – but it does exist in the population? These situations are called Type I and II errors These errors cannot be eliminated; they can be minimized, but unfortunately, minimizing one type of error will increase the probability of committing the other error + 24 Type I and Type II errors Conclusion about null hypothesis from statistical test Truth about null hypothesis in population True Accept Null Reject Null Correct Type I error Observe difference when none exists False Type II error Fail to observe difference when one exists Correct Mini-Data Activity (time to embark on it?) Salary Data Culture Data When you are not heavily cognitively overloaded….. 25