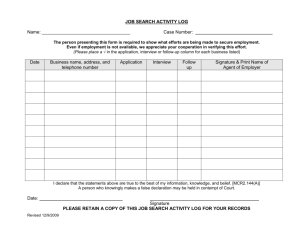
Contempt Presentation Judge McGinley (PPT)
advertisement

CONTEMPT Creed McGinley OBJECTIVES To define and analyze the source of contempt powers. To distinguish between criminal and civil contempt. To identify limitations on our contempt powers. To provide judges with basic background and procedural checklists to deal with contempt situations. CONTEMPT Introduction “ O! It is excellent To have a giant’s strength; but it is tyrannous To use it like a giant.” A Court must possess the authority to protect itself against those who disregard its dignity and authority. CONTEMPT Power is exercised to. . . Maintain order and decorum Punish for disrespect shown to Court or its orders Enforce the Court’s writs orders & Punish acts which obstruct the administration of justice 5 “Walk softly and carry a big stick” Theodore Roosevelt “Walk tall and carry a big stick” -- Buford Pusser 6 “If there is any s-- of a b---- in a person, put a black robe on them and it will come out.” -- Dickie Jerman 7 History & Source of Contempt Powers Statutory Inherent Scott v State, 109 Tenn, 390, 71 S.W. 824 (1902) State v Beeler S.W.3d 511 (2012) Loy v. Loy, Tenn App 450, 222 SW 2d 873 (1949) Statutory Authority & Punishments 1. General - T.C.A. § 29-9-102 – Scope of Power Power to issue attachments or inflict punishments exist in the following cases: • Willful Misbehavior • Willful Disobedience or Resistance • Abuse or Interference with . . . • The Jury • Any other act or omission (declared by law) Statutory Authority & Punishments 2. Domestic - T.C.A. § 36-5-104 Failure to comply w/ child support order – Criminal Sanction 3. Profanity - T.C.A. § 29-9-107 Profanely swears or curses in presence of court (Class C Misdemeanor) 4. Violation of Anti-Nuisance Injunction - T.C.A. § 29-3-111 Any person who enters or uses any building or place while closed under a preliminary or permanent injunction Statutory Authority & Punishments 5. Contempt - T.C.A. § 16-1-103 For the effectual exercise of its powers, court is vested w/ power to punish for contempt (As provided in this Code section). 6. Punishment - T.C.A. § 29-9-103 May be a Fine or Imprisonment or both Circuit, Chancery, & Appellate courts – Fine up to $ 50 & up to 10 days All other courts – Limited to fine of $ 10 7. Damages - T.C.A. § 29-9-105 Performance of forbidden act May be imprisoned until the act is rectified by returning to status quo or by payment of damages. Statutory Authority & Punishments 8. 9. Omission to Perform Act - T.C.A. § 29-9-104 Omission to perform an act which is in person’s power to perform. May be imprisoned until act is performed. Municipal Citation - T.C.A. § 29-9-108 Willful failure to appear in court w/o just cause Fine of up to $ 10 and imprisoned for up to 5 days 10. Violation of Order of Protection - T.C.A. § 36-3-610 Violation of Order – In accordance with the law No difference between general session’s and court of record’s authority provided general session’s judge is a licensed attorney A civil penalty of $ 50 may be assessed Court Rule Tennessee Rules of Criminal Procedure - Rule 42 Criminal Contempt Summary Disposition Disposition upon Notice & Hearing Court Rule Tennessee Rules of Civil Procedure – P. 45.06 – Contempt – P. 65.06 – Enforcement of Restraining Orders & Injunctions Tennessee Rules of Juvenile Procedure – P. 1(b) 14 Terms & Concepts Direct v. Indirect Contempt – Direct Committed in presence of judge & punishable summarily – Indirect Not in presence of judge & only after notice of hearing Criminal v. Civil Contempt (Depends on the purpose for which the power is exercised) – Criminal Primary to preserve Court’s authority & punish for disobedience of its orders – Civil Primary is to provide a remedy or injured suitor & coerce compliance with an order 15 Terms & Concepts Judge Koch describes the difference as: Civil contempt – Intended to benefit the litigant – Imposed to compel compliance (parties in contempt may purge themselves through compliance) Criminal contempt – Intended to punish for an offense against the authority of the court – Imposed as punishment for failure to comply (contemptuous party cannot be freed through eventual compliance) 16 Terms & Concepts Contemnors – – – – – – Attorneys Jurors Witnesses Litigants Domestic “Professional” (repeaters who buck system) 17 Limitations on Powers & Right of Defendants CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS & DUE PROCESS 1. Right to Attorney – Sevier v. Kenneth Turner, 742 F 2d 262 (6th Cir 1984) Mastin v. Fellerhoff, 526 F Supp 969 (SD Ohio 1981) 2. Conflict Free Prosecutor – Wilson v. Wilson, 984 SW 2d 898 (Tenn 1998) Young v US ex rel Vuitton, 481 US 787, 107 S Ct 2124 (1987) 3. Confrontation – Guthrie v Oldham, No 85-118-III (Tenn Crim App. Filed May 9, 1985) 18 Limitations on Powers & Right of Defendants CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS & DUE PROCESS 4. Notice – United States v. United Mine Workers of America, 330 US 258, 297, 67 S Ct 677 (1947) Storey v. Storey, 835 SW 2d 593, 599-600 (Tenn App 1992) 5. Burden of Proof – Criminal Contempt – Beyond a reasonable doubt. State ex rel Anderson v. Daughery, 137 Tenn 126, 191 SW 974 (1916) O’Brien v. State ex rel Bibb, 26 Tenn App 270, 170 SW 2d 931 (1943) Civil Contempt – Clear & convincing evidence. Oriel v. Russell, 278 US 358, 364,49 S Ct 173 (1929) Wright, supra at § 3-16. P 136 19 Limitations on Powers & Right of Defendants CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS & DUE PROCESS 6. Right to Remain Silent – Gompers v. Bucks Stove, 221 US 418,444, 31 S Ct 492 (1991) Kornick v. Kornick, 3 Tenn Civ App 41, 44 (1931) 7. Double Jeopardy – Most courts have previously held that double jeopardy is no bar to conviction for contempt & a criminal conviction for essentially the same act. Maples v. State, 565 SW 2d 202,203 (Tenn 1978) 20 Limitations on Powers & Right of Defendants NO RIGHT TO TRIAL BY JURY Dyke v. Taylor Implement Manufacturing Company 391 US 216, 88 S Ct 1472 (1968) Pass v State 181 Tenn 613, 183 S W 2d 1, (1944) Robinson v. Gaines, 725 SW 2d 992, 695 (Tenn Crim App 1986) CAVEAT – There is also no right to a jury trial in a civil contempt proceeding. Weinstein v. Heinberg, 490 SW 2d 692 (Tenn App 1992) 21 Limitations on Powers & Right of Defendants RIGHT TO UNBIASED JUDGE State v. Swisher, 676 S W 2d 576 (Tenn Crim App1984) Defendant does not disrespect or criticize trial judge – Trial judge not required to disqualify himself. State v. Green, 708 S W 2d 424 (Tenn Crim App 1986) Three contempt charges involved criticism of judge – Judge should have recused himself. 22 Limitations on Powers & Right of Defendants CONTEMPT & AN ERRONEOUS ORDER Principle underlying contempt powers so strong – Even erroneous orders must be obeyed or risk contempt. Walker v. City of Birmingham, 388 US 307, 98 S Ct (1967) State v. Sammons, 656 S W 2d 86d2, 869 (Tenn Crim App 1982) Nucular Fuel v. Local Union, 719 S W 2d 550, 552 (Tenn Crim App 1986) Overnite Transportation Co. v. Teamsters Local Unio No 480 et al, TN Supplement May 16, 2005) 23 Disposition From ABA Standards for Criminal Justice 2d Ed. 1980 STANDARD 6-4.2 Admonition & Warning – No sanction other than censure unless: Character or Acts clearly contemptuous Conduct warranting sanction preceded by a clear warning about impermissibility of conduct and potential sanctions 24 Disposition From ABA Standards for Criminal Justice 2d Ed. 1980 STANDARD 6-4.3 Notice of Intent to Use Contempt Power: Postponement of Adjudication Judge should inform alleged offender of intention to institute proceedings as soon as practicable. Judge should consider advisability of deferring adjudication of contempt until after the trial unless prompt action is imperative. 25 Disposition From ABA Standards for Criminal Justice 2d Ed. 1980 Notice of Charge & Opportunity to be Heard – Before imposing punishment, Offender should be given: STANDARD 6-4.4 – Notice of charges and – An opportunity to adduce evidence or argument relevant to guilt or punishment. 26 Contempt for Violation of Orders REQUIREMENTS ORDERS INCLUDED ALL orders NOT JUST final orders Error or irregularity is not justification for not obeying Need not be entered yet Knowledge of the order Within court’s jurisdiction to make Willful violation of order State v. Green, 783 S W 2d 548 (Tenn 1990) 27 Contempt for Violation of Orders PROBLEM AREAS DEFENSES: Contempt findings required Lack of jurisdiction Orders may not put everyone on notice. B.A.S.I.C v. Kemp, 947 F 2d 11 (1st Cir, 1991) Impossibility Anticipatory Contempt. Keeley v Massey, No 02A01-9307-CH00159 (Tenn App, W S, Feb 28, 1994) Statute of Limitations Commissioner not always personally required to appear. Simerly v. Norris, No 1071 (Tenn Crip App, March 26, 1987) 28 Cases of Special Interest Criticism of Judges Pro se litigant (In contempt) “star chamber, hatchet court, crooked judge, kangaroo trial” McGray v Adcox, 399 SW 2d 753 (Tenn, 1966) Lawyer criticizes judge in press (Not in contempt) No case pending & comment not about a particular case. In re Hicky, 149 Tenn 344, 258 SW 417 (1923) Admin of courts criticized by lawyer (Contempt unsupported) In re Snyder, 472 US 634, 105 S ct 2874 (1985) 29 Cases of Special Interest The Chicken Man Contempt Conviction overturned because defendants dressed like chickens. State v. Hodges, 695 SW 2d 171 (Tenn 1985) Dead Beat Parent Who Won’t Work (Even the lack of employment is no defense to the failure to actively seek & accept employment.) Street Vernacular Witness in trial who referred to assailant as “chicken shit” should not have been held in contempt. Eaton v. City of Tulsa, 415 US 697, 94 S Ct 1228 (1974) Boyd v. Boyd, 8 T A M 1-12 (Tenn App E S 1982) State ex rel Moore v. Owens, 15 T A M 11-17 (Tenn App M S Feb 7, 1990) 30 Cases of Special Interest – Conduct of Lawyer Lawyer constantly interrupts judge and during prosecutor’s argument, assumed a “crucifixion stance” Attorney who refused appointment Lawyer in contempt for disrespect & misconduct 31 Cases of Special Interest – Conduct of Lawyer LATE TO COURT Secretary’s fault - No defense State v. Richard Donnell, 9 TAM 7-38 (Tenn Crim App Dec 20, 1983) Scheduling Conflict - Conviction Reversed No intent for criminal contempt. In re Edward Witt Chandler, 906 F 2d 248 (6th Cir 1990) Business Destroyed by Fire previous night Judge fined $ 25 United States v. Anonymous, 215 F Supp 111 (D.C. Tenn 1963) 32 Cases of Special Interest – Conduct of Lawyer No contact w/ witness by court order. Defense lawyer held in contempt following witness interview. State v. Robert Friedman, no 89-88-III (Ct Crim App March 8, 1990) Two Lawyers fight in hall. No contempt as not in presence of court (room). Fight in courtroom is different. Edwards v. Jameson, 679 S W 2d 195 (Ark 1984) Contra United States v. Patterson, 26 F 509 (6th Cir 1886) Court Order & Willful Violation Attorney violates court order but claims careless not willful. “OOPS” is not a valid defense. In re Zimmerman, No 85-331-III (Ct of Crim App Aug 7, 1986) 33 Cases of Special Interest Attorney Fees & Contempt Jury in Contempt Advice of Counsel as a Defense Sheriff’s Mistreatment of Pretrial Detainee Perjury Intoxication in Court 34 Cases of Special Interest Contempt – Awarding of Damages T-Shirt Deposition Misconduct 35 Direct Criminal Contempt ELEMENTS Checklist (Rule 42(a)) Conduct occurs in the presence of the judge? Actor knows or should the actor know that conduct is impermissible? Actor knows the consequences of continuing? Conduct is willful or intentional? 36 Direct Criminal Contempt ELEMENTS Checklist (Rule 42(a)) Is the conduct: Obstructive? Disruptive? Interruptive? Derogatory Are immediate actions necessary to maintain order & decorum or to preserve the authority of the judge? 37 Direct Criminal Contempt DISPOSITION Checklist (Rule 42(a)) Take a recess! Make findings on the record for each of the elements of direct criminal contempt. Give the actor an opportunity to respond to the findings. Make a finding of guilt. Give the actor an opportunity for allocution. 38 Direct Criminal Contempt DISPOSITION Checklist (Rule 42(a)) Summarily impose penalties: Statutory fine (< $50) Sentence (< 10 days) Other restrictive sanctions Order of Contempt shall: Recite the facts, Be signed by judge, and Entered into the record. 39 Indirect Criminal Contempt ELEMENTS Checklist (Rule 42(b)) Conduct occurs outside the presence of the judge? Actor knows or should the actor know that conduct is impermissible? Actor knows the consequences of continuing? Conduct is willful or intentional? 40 Indirect Criminal Contempt ELEMENTS Checklist (Rule 42(b)) Is the conduct: Obstructive? Disruptive? Interruptive? Derogatory Are immediate actions necessary to maintain order & decorum or to preserve the authority of the judge? 41 Indirect Criminal Contempt DISPOSITION Checklist (Rule 42(b)) Take a recess! Give notice of time & place of hearing allowing reasonable time for preparation of defense AND state the essential facts constituting criminal contempt charged. (May be oral in open court or by charging instrument.) If charge involves disrespect to or criticism of judge, recusal mandatory. 42 Indirect Criminal Contempt DISPOSITION Checklist (Rule 42(b)) Make finding of guilt beyond a reasonable doubt. Upon finding of guilt by court, order to be entered fixing punishment: Fine (< $50) Jail Sentence (< 10 days) 43 Direct Contempt - Civil ELEMENTS Checklist Conduct occurs in the presence of the judge? Actor knows or should the actor know that conduct is prohibited or directed by the order of the court? Actor knows the consequences of continuing? Conduct is willful or intentional? Is punishment necessary to compel compliance w/ order? 44 Direct Contempt - Civil DISPOSITION Checklist Take a recess! Make findings on the record of each element. Make a finding of guilt. Give actor final opportunity to comply & to purge the contempt. Summarily impose any reasonable fine and/or sentence which TERMINATES upon compliance w/ the order. 45 Indirect Contempt - Civil ELEMENTS Checklist Conduct occurs outside the presence of the judge? Actor knows or should the actor know that conduct is prohibited or directed by the order of the court? Actor knows the consequences of continuing? Conduct is willful or intentional? Is punishment necessary to compel compliance w/ order? 46 Indirect Contempt - Civil DISPOSITION Checklist Upon notice of violation of court’s order, notice the actor to appear and to show cause why he/she should not be held in contempt. After hearing, make findings on the record of each element. Make a finding of guilt. Grant actor a reasonable time to purge the contempt. Upon a failure to purge, impose any reasonable fine and/or sentence which TERMINATES upon compliance w/ the order. 47 Where to Get More Information General Reference Materials on Contempt Raybin, Criminal Practice and Procedure § 24. 14-15 (1985) Pivnick, Tennessee Circuit Court Practice § 3-16 (1991) Burch, Trial Handbook For Tennessee Lawyers § 49-54 (1980) Wright, Federal Practice and Procedure (Criminal) § 701713 (2nd Ed.1982) Feldman, Criminal Offenses and Defenses in Tennessee, p. 122-133 (1988) Garrett, Tennessee Divorce, Alimony and Child Custody § 16-2-4 (1995 Ed) When a ship misses the harbor, it is rarely the fault of the HARBOR!! 49