Paramecium - tekkieoldteacher
advertisement

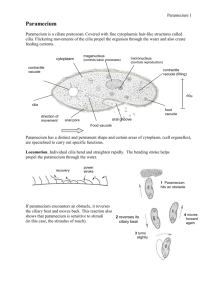
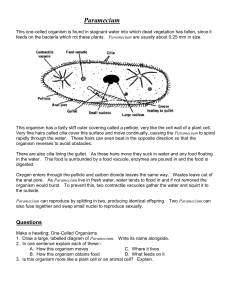
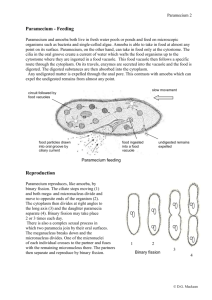
Paramecium By: Elizabeth Kaake Period 7 Bio 1 • • Structure of a paramecium: large ciliate protozoan that lives in stagnant freshwater. • Cilia: minuscule cilia that envelop the paramecium and are used for locomotion. • Contractile vacuole: cavity of the paramecium that is able to contract. • Food vacuole: cavity of the paramecium responsible for digestion. • Micronucleus: one of the less important central organelles of a paramecium. • Oral groove: canal of the paramecium used to ingest nutrients. • Gullet: cavity of the pharynx. • Ectoplasm: vitreous superficial layer of a paramecium. • Endoplasm: central part of a paramecium. • Large nucleus: the most important central organelle of a paramecium. • Canals of contractive vacuole: division of the contractile cavity of a paramecium. • Trochocyst: root of a vibrative cilium of a paramecium. The Definition of Paramecium • any ciliated freshwater protozoan of the genus Paramecium, having an oval body and a long, deep oral groove. • MORE ABOUT THE PARAMECIUM • Paramecia are a group of unicellular ciliate protozoa formerly known as slipper animalcules from their slipper shape. They are commonly studied as a representative of the ciliate group. Paramecia range from about 50 to 350 µm in length, depending on species. Simple cilia cover the body which allow the cell to move with a synchronous motion. There is also a deep oral groove containing inconspicuous compound oral cilia (as found in other peniculids) that is used to draw food inside. They generally feed upon bacteria and other small cells. Osmoregulation is carried out by a pair of contractile vacuoles, which actively expel water absorbed by osmosis from their surroundings. Paramecia are widespread in freshwater environments, and are especially common in scums. Paramecia are attracted by acidic conditions. Certain single-celled eukaryotes, such as Paramecium, are examples for exceptions to the universality of the genetic code. The paramecium is a prolate spheroid, rounded at the front and pointed at the back. The pellicle is a stiff but elastic membrane that gives the paramecium its definite shape. Covering the pellicle are many tiny hairs, called cilia. On the side beginning near the front end and continuing down half way is the oral groove, which collects food until it is swept into the cell mouth. There is an opening near the back end called the anal pore. The contractile vacuole and the radiating canals are also found on the outside of a paramecium. Uses of Paramecium • To eat bad bacteria … AND… • Absorbs a variety of environmental toxins PARAMECIUM PICS (found on Google) Where is PARAMECIUM found?? • PARAMECIUM is usually found in freshwater or water in a pond. – www.ASK.com What do PARAMECIUM eat?? • Paramecium love to eat decayed plant matter, algae and also dead animal mater. As impossible as it may seem, they even eat animals smaller than themselves. – (www.ASK.com) Other Names for PARAMECIUM • Slipper Animalcule, • Lady Slippers……AND…….. • Paramecia Parameciidae. – (www.ASK.com) How does PARAMECIUM move? • Paramecium move sort of like swimming, they propel themselves along by using hair like microtubules as their arms. These "arms" wave around in the water causing motion. (www.ASK.com) What is a PARAMECIUM?? • A paramecium is a small one celled (unicellular) living organism that can move, digest food, and reproduce. They belong to the kingdom of Protista, which is a group (family) of similar living micro-organisms. Microorganism means they are a very small living cell. You might be able to see one as a tiny moving speck if your eyesight is extremely good but for any detail at all you need a microscope to look at and study them. They are about .02 inches long (.5mm). They are also famous for their predator-prey relationship with Didinium. Paramecium are known for their avoidance behavior. If an encounters a negative stimiulus, it is capable of rotating up to 360 degrees to find an escape route. What is the average size of a PARAMECIUM? • 0.25mm long What kingdom does PARAMECIUM belong to? • The Protista kingdom. • http://bio.rutgers.edu /~gb101/lab6_protist s/movies/paramechig h.mov CONCLUSION • Paramecium is important to the world. It eats bad bacteria and yeast. PARAMECIUM IS IMPORTANT • http://bio.rutgers.edu /~gb101/lab6_protist s/movies/parameclow. mov