AP Psychology: Statistics - What you need to know for the AP Psych
advertisement

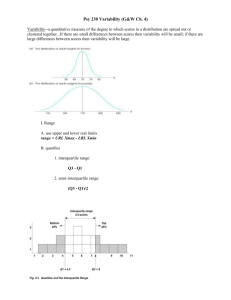
AP Psychology: Statistics - What you need to know for the AP Psych , the AP Exam Population: Psychology researches the behavior of a population ( example: teens ) Sampling: You can’t research the entire population so you study a sample ( example: 1,000 teens ). Sample is selected for study that is representative of a larger population. Sampling is done randomly - better represents the population. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS: ( look at the word ) – describes a set of data and are used to organize and summarize data. You DESCRIBE the behavior of the sample with DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS. INFERENTIAL STATISTICS You INFER / JUDGE/ EVALUATE whether the behavior of the sample is representative of the population using INFERENTIAL STATISTICS. Helps psychologists draw conclusions about the general population. DESCRIPTIVE STATISICS Central Tendency: Attempt to find out the typical or average score, or the center of distribution scores. - Mean: Average of all scores ( Example: Scores: 2, 4, 6, 8. Mean: 5 ) Joe got a 70% on his test. Is this a good score? Central Tendency tells you. The mean is 30%. 70 on the test is awesome. If the mean is 90%, then a 70 is bad. - Median: The score that falls EXACTLY in the center of a distribution of scores Example: Scores 86, 88, 92, 95, 99 Median is 92 - Mode: The most frequent score. Example: 70, 74, 80, 81, 81, 81, 80. Mode is 81. A distribution can be bi-modal, having two modes. Measures of Variability ( also known as the spread of dispersion ) - Range – the difference between the highest and lowest scores High score of 10, and a low score of 2 = Range of 8 Measures of Variability ( also known as the spread or dispersion of scores ) Variability or variance – how much the scores vary from the mean (average) Standard of Deviation is the square root of the variance – Like variance, calculates the average distance of any score from the mean (average) The higher the variance and standard deviation, the more spread out the deviation. - How to calculate standard deviation? Square Root of Variance If variance is 100 then Standard Deviation (SD) is 10 If variance is 16 then SD is 4 How to calculate variance? Square Root of SD If SD is 8 then Variance is 64. Correlation Coefficients – a number that demonstrates degree of relationship between 2 variables o + means a positive correlation, variables are in the same direction. As studying increases, grades increase. o – means negative correlation, variables are in the opposite direction. As TV watching increases, grades go down. Numbers -1 -.75 -.50 -.25 0 +.25 +.50 +.75 +1 +1 or -1 means 100% correlation or cause and effect. 0 means no correlation …. Wearing a purple shirt to school and grades go up. Most scores fall in between INFERENTIAL STATISTICS MEMORIZE!!!!!!!!!!!!! DO NOT CALCULATE!!!!!!!!!!!!! After descriptive statistics completed for a study, inferential statistics are used to interpret the data and draw conclusions. After an experiment, the researcher needs to ask “Is the observed difference between the two groups large enough to support the hypothesis? Statistical significance – when statistical calculations indicate that research results are NOT due to chance; when the probability that the observed findings are very low that they are due to chance ( less than 5 chances in 100, .05 level of significance. The normal curve is a predetermined IDEAL upon which data is measured. Memorize – no need to calculate. If the sample is 95% accurate to the normal curve then the data is statistically significant. 99% is better. 68% is 1 SD from mean, 95% is 2SD from mean, 99% is 3 SD from the mean - This is on the normal curve.