Embryo Development Powerpoint
advertisement

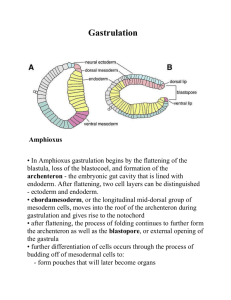
DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY Fertilization to Gastulation ANIMAL DEVELOPMENT Embryology - study of development of the Embryo 5 major stages.. 1. Gametogenesis - gamete production 2. Fertilization - gamete --> zygote 3. Cleavage - Zygote --> Blastula 4. Gastrulation - Blastula --> Gastrula 5. Organogenesis - Organ Formation -i.e. Neurulation- Gastrula --> Neurula FERTILIZATION 1. Sperm attaches the jelly coat of the egg Acrosome cap -contains digestive enzymes that eat away at jelly layer FERTILIZATION 2. Sperm reach vitelline envelope Vitelline layer-species-specific boundary involved in sperm-egg recognition • ensure other species cannot fertilize the egg FERTILIZATION 3. Sperm /egg plasma membrane fuse Sperm nucleus enters the egg Fertilization occurs-sperm nucleus and egg nucleus form a 2N zygote FERTILIZATION Prevention of Polyspermy – entrance of multiple sperm 1.Change of electrical potential of the egg plasma membrane- fast 2.Confusion of sperm- Egg releases all of their Ca ions CLEAVAGE • Cleavage-rapid succession of cell division • doubling with each division each cell smaller than zygote •The produced cells named Blastomeres. During this stage the size of the embryo does not change, the blastomeres become smaller with each division BLASTULA continues divisions to form a ball of 32 cells called the morula. The morula continues divisions to form the hollow blastula with up to several hundred cells. The cavity of the blastula is the blastocoel– fluid filled cavity forms at the center of embryo Vegetal Hemisphere -the lower, yolky portion of the egg; opposite the animal hemisphere. CLEAVAGE OF A FROG Starfish development, unfertilized egg. 16 blastomeres. 2 blastomeres. 32 blastomeres. morula 4 blastomeres. Starfish development, nonmotile blastula. GASTRULATION GASTRULATION (literal meaning - to form a stomach) is a complex series of cell movements Blastula (hollow ball of cells) transformed into the Gastrula (three layered stage) GASTULATION 1. rearranges cells, giving them new neighbors (and thus potentially new signals from other cells and the environment) 2. results in the formation of 3 GERM LAYERS that will form the subsequent embryo: ECTODERM, ENDODERM, and MESODERM GASTRULATION 1. Gastrulation begins- Blastopore formed Blastopore - midway opening on one side of the blastula • Site of cell migration from the surface into the interior • Future site of anus (Deuterostome) or mouth (Protostome) GASTRULATION 2. Cell migrating to form layers • Archenteron – primitive gut formed (endoderm) • The open end of the archenteron is called the blastopore An echinoderm gastrula. A - ectoderm; B - blastocoel; C - archenteron; D - endoderm; E - blastopore. GASTRULATION 3.Gastrulation complete - Gastrula formed: • Endoderm and archenteron -replace the blastocoel • Mesoderm - forms a layer between the ectoderm and endoderm • Ectoderm- forms the outer layer except for a cluster of endodermal cells (yolk plug) • Yolk plug- (endoderm) marks the site of the blastopore and of the future anus DEVELOPMENT OF EGG CELLS 4 stages of embryonic development 1.Cleavage (Mitosis and cytokinesis of thezygote, ) 2.Patterning (organize themselves in layers and masses) 3.Differentiation 4.Grow PROTOSTOME Protostome: animals whose development is characterized by: the mouth is derived from the blastopore Determinate is the form of cleavage in most protostomes. It results in the developmental fate of the cells being set early in the embryo development. Molluscs spiral determinate cleavage Arthropod Rotifers DEUTEROSTOME Deuterostome: animals whose development is characterized by: Echinoderm the mouth is not derived from the blastopore Chordates Indeterminate - when the original cell in a deuterostome embryo divides, the two resulting cells can be separated, and each one can individually develop into a whole organism Hemichordata HUMAN DnaTube.com - Human Development and Stem Cells_WMV V9.wmv DEVELOPMENT AND STEM CELLS Early in development, a group of cells called the inner cell mass (ICM) forms. These cells are able to produce all the tissues of the body. Later in development, during gastrulation, the three germ layers form, and most cells become more restricted in the types of cells that they can produce ORGANOGENESIS Organogenesis is the formation of the organs The layers are germ layers; they have specific fates in the developing embryo: Endoderm: The innermost lining of digestive tract, liver, pancreas, lungs Mesoderm:The middle layer. Goes on to form the blood and muscles, skeleton, gonads, excretory system, circulatory system. Ectoderm :The outermost. Goes on to form the skin and nervous system Human reproduction is an inefficient process: ~ 50% of concepti do not implant (implantation 8-10 dpf, Heart beat at 21 dpf). a further ~30% die and abort after implantation.