exam1_solutions
advertisement
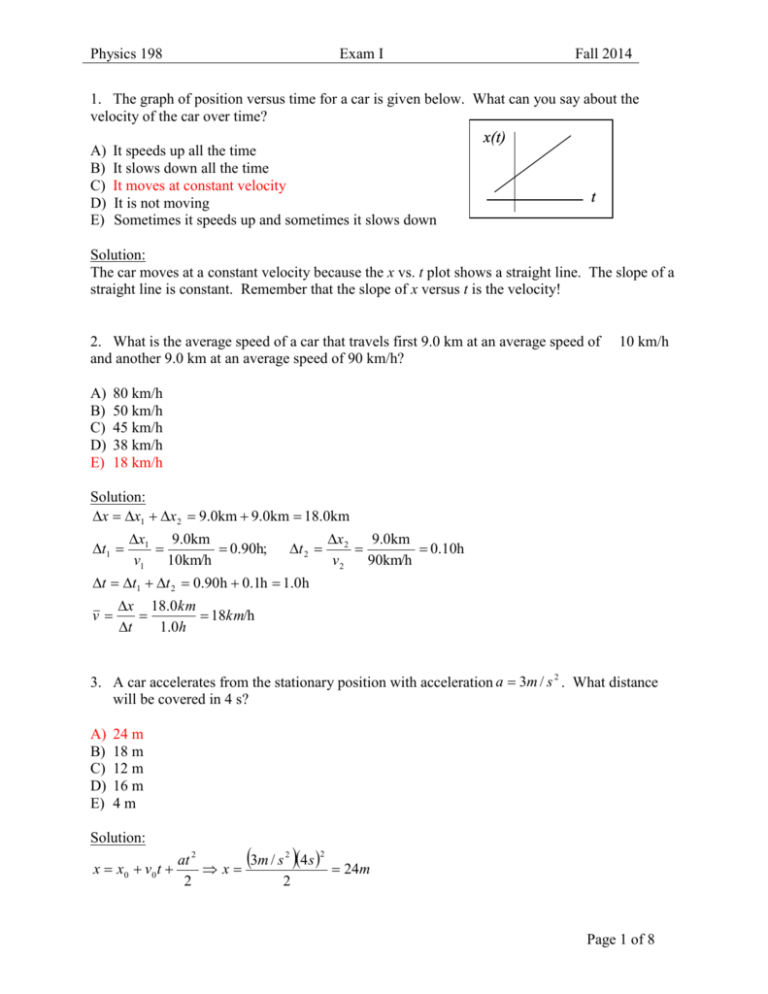
Physics 198 Exam I Fall 2014 1. The graph of position versus time for a car is given below. What can you say about the velocity of the car over time? A) B) C) D) E) It speeds up all the time It slows down all the time It moves at constant velocity It is not moving Sometimes it speeds up and sometimes it slows down x(t) t Solution: The car moves at a constant velocity because the x vs. t plot shows a straight line. The slope of a straight line is constant. Remember that the slope of x versus t is the velocity! 2. What is the average speed of a car that travels first 9.0 km at an average speed of and another 9.0 km at an average speed of 90 km/h? A) B) C) D) E) 10 km/h 80 km/h 50 km/h 45 km/h 38 km/h 18 km/h Solution: x x1 x 2 9.0km 9.0km 18.0km t1 x1 9.0km 0.90h; v1 10km/h t 2 x 2 9.0km 0.10h v2 90km/h t t1 t 2 0.90h 0.1h 1.0h v x 18.0km 18km/h t 1 .0 h 3. A car accelerates from the stationary position with acceleration a 3m / s 2 . What distance will be covered in 4 s? A) B) C) D) E) 24 m 18 m 12 m 16 m 4m Solution: 3m / s 2 4 s at 2 24m x x0 v0 t x 2 2 2 Page 1 of 8 Physics 198 Exam I Fall 2014 4. When throwing a ball straight up, which of the following is true about its velocity v and its acceleration a at the highest point in its path? A) B) C) D) E) both v = 0 and a = 0 v ≠ 0, but a = 0 v = 0, but a ≠ 0 both v ≠ 0 and a ≠ 0 not enough information to answer the question Solution: At the top, clearly v = 0 because the ball has “momentarily stopped” - the velocity of the ball is changing sign (direction). Because velocity is changing the acceleration is definitely not zero! The acceleration is g 9.8m / s 2 . 5. Alice and Bill are at the top of a cliff of height H. Both throw a ball with initial speed v0, Alice straight down and Bill straight up. The speeds of the balls when they hit the ground are vA and vB. If there is no air resistance, which is true? A) v A vB B) C) D) E) vA vA vA vA 2vB 4vB 12 v B 14 v B Solution: Bill’s ball goes up and comes back down to Bill’s level. At that point, it is moving downward with v0, the same as Alice’s ball. Thus, it will hit the ground with the same speed as Alice’s ball. 6. From the same height (and at the same time), one ball is dropped and another ball is fired horizontally. Which ball has the greater velocity at ground level? A) B) C) D) E) The “dropped” ball The “fired” ball Neither – they both have the same velocity on impact It depends on how hard the ball was thrown It depends on the initial height Solution: Both balls have the same vertical velocity when they hit the ground (since they are both acted on by gravity for the same time). However, the “fired” ball also has a horizontal velocity. When you add the two components, the “fired” ball has a larger net velocity when it hits the ground. Page 2 of 8 Physics 198 Exam I Fall 2014 7. A box of mass 2 kg has acceleration 4m/s2. What is the net force applied to the box? A) B) C) D) E) 2N 4N 6m 8N 9.8 N Solution: F ma 2kg 4m / s 2 8N 8. A box with a mass of 10 kg is given an upward acceleration of 2.2 m/s² by a cable. What is the tension in the cable? A) B) C) D) E) 22 N 44 N 98 m 120 N 240 N Solution: Newton’s equation: T mg ma T mg a T 10kg 9.8m / s 2 2.2m / s 2 120 N 9. A hockey puck slides on ice at constant velocity. What is the net force acting on the puck? A) B) C) D) E) More than its weight Equal to its weight Less than its weight but more than zero Depends on the speed of the puck Zero Solution: The puck is moving at a constant velocity, and therefore it is not accelerating. Thus, there must be no net force acting on the puck. Page 3 of 8 Physics 198 Exam I Fall 2014 10. What work should be done by an external force to lift a 2.0 kg block up 3.0 m? A) B) C) D) E) 20 J 30 J 59 J 120 J 180 J Solution: W Fd cos mgh 2.0kg 9.8m / s 2 3.0m 58.8J 59 J 11. An object of unknown mass is projected with an initial speed, v0 = 10 m/s at an unknown angle above the horizontal. If air resistance could be neglected, what would be the speed of the object at height, h = 4.4 m above the starting point? A) B) C) D) E) 3.7 m/s 4.2 m/s 4.9 m/s 6.2 m/s 10 m/s Solution: mv 2 mv02 mgh mg 0 2 2 v v02 2 gh 10m / s 2 2 9.8m / s 2 4.4m 3.7m / s 12. Mass m is attached to a spring with a spring constant k. What happens with the frequency of oscillation if the spring constant k increases by a factor of 4? A) B) C) D) E) Multiplies by a factor of 4 Doubles Halves Multiplies by a factor of ¼ Remains the same Solution: 1 k f 2 m f 4k fk 4k 2 k Page 4 of 8 Physics 198 Exam I Fall 2014 13. A 2.0 kg mass attached to a spring with a spring constant of 200 N/m. What is the frequency of oscillation of the mass? A) 1.6Hz B) C) D) E) 2.4Hz 3.1Hz 6.3Hz 10Hz Solution: f 1 2 k m f 1 2 200 N / m 10 Hz 1.6 Hz 2.0kg 2 14. N-mass vibrator (N masses connected with springs) has: A) B) C) D) E) N longitudinal and N transverse modes of vibration N longitudinal and 2N transverse modes of vibration N longitudinal and 3N transverse modes of vibration 2N longitudinal and N transverse modes of vibration 2N longitudinal and 2N transverse modes of vibration Solution: 15. A sinusoidal wave has a wavelength of 5.00 m and a period of 0.02s. What is the speed of the wave? A) B) C) D) E) 0.10 m/s 5.00m/s 10.0 m/s 250 m/s 340 m/s Solution: v T v 5.00m 0.02s 250m / s Page 5 of 8 Physics 198 Exam I Fall 2014 16. A stretched string has one free end and one fixed end, and is vibrating at its 3rd harmonic frequency. The number of nodes is ___. A) B) C) D) E) 1 2 3 4 5 Solution: Nodes 17. Two speakers S1 and S2 are driven by the same signal generator and are different distances from a microphone P as shown. The minimum frequency for constructive interference to occur at P is __ Hz. (The speed of sound is v = 340 m/s.) A) B) C) D) E) 100 200 300 400 500 Solution: For constructive interference: r2 r1 n n 0,1,2,... f v / f min v 340m / s 200Hz r 2 r1 3.40m 1.70m 18. When both ends of a pipe are open the frequency of the first overtone is 400 Hz. What is the frequency of the first overtone if one end is open and another end is closed (stopped pipe)? The pipe is sufficiently narrow so you can neglect its diameter, i.e. neglect end effects. A) B) C) D) E) 800 Hz 600 Hz 400 Hz 300 Hz 200 Hz Solution: First overtone for the open pipe – second harmonic First overtone for the one end open one end closed pipe – third harmonic nv f nopen m open 3 2 L stopped fn f 2stopped 400 Hz f 2stopped 300Hz fm 2n 22 mv f mstopped 4L Page 6 of 8 Physics 198 Exam I Fall 2014 19. If the linear mass density of a rope is 0.150 g/m and the tension is 6.00 N, what is the speed of waves in the rope? A) B) C) D) E) 100 m/s 120 m/s 200 m/s 220 m/s 240 m/s Solution: 0.150g/m 1.50 10 -4 kg/m v F 6.00N 200m / s 1.50 10 -4 kg/m 20. A 4.00 m long string is connected to a vibrator with frequency 120 Hz. The string is oscillating in its 4 th harmonic. Find the speed of waves in the string. A) B) C) D) E) 100 m/s 120 m/s 200 m/s 220 m/s 240 m/s Solution: 2L 2 4.00m n 4 2.00m n 4 v f 2.00m120Hz 240m / s Page 7 of 8 Physics 198 Exam I Fall 2014 Record Sheet You may fill in this sheet with your choices, detach it and take it with you after the exam for comparison with the posted answers 1 11 2 12 3 13 4 14 5 15 6 16 7 17 8 18 9 19 10 20 Page 8 of 8







