FCE Linkers - WordPress.com
advertisement

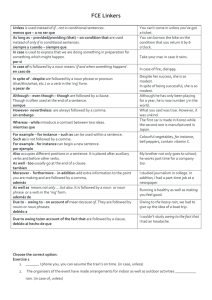
FCE Linkers Conditionals Conditional clauses can begin with: Unless As long as – provided/providing (that) – on condition that In case – in case of When & How Unless Unless is used instead of if...not in conditional sentences of all types: I wouldn't eat that food if I wasn't really hungry. = I wouldn't eat that food unless I was really hungry I wouldn't have phoned him if you hadn't suggested it. = I wouldn't have phoned him unless you'd suggested it. When & How As long as – provided/providing (that) – on condition that As long as – provided/providing (that) – on condition that are used instead of only if in conditional sentences: You will get the job only if you prepare for the interview. = You will get the job as long as you prepare for the interview. When & How In case – in case of We use in case to express that we are doing something in preparation for something which might happen: In case I forget later, here are the keys to the garage. (I might forget to give you the garage keys) We use in case of + noun to mean ‘if and when something happens’: In case of fire, leave the building as quickly as possible. (If there is a fire) Exercise 1 1. _______ I phone you, you can assume the train’s on time. (in case, unless) 2. The organisers of the event have made arrangements for indoor as well as outdoor activities ___________ rain. (in case of, unless) 3. You can play in the living room _____________ you don’t make a mess. (as long as, unless) 4. We’ll have to cancel the show__________ we sell more tickets at the last minute. (as long as, unless) 5. Let’s take our swimming costumes _________ there’s a pool at the hotel. (in case, unless) Exercise 1 1. Unless I phone you, you can assume the train’s on time. 2. The organisers of the event have made arrangements for indoor as well as outdoor activities in case of rain. 3. You can play in the living room as long as you don’t make a mess. 4. We’ll have to cancel the show unless we sell more tickets at the last minute. 5. Let’s take our swimming costumes in case there’s a pool at the hotel. Contrast Linkers When we want to introduce contrast in English, we use the following words: In spite of/Despite (the fact that) Although/Even though/Though However/Nevertheless Whereas When & How In spite of/Despite Followed by a noun phrase or pronoun (that/this/what, etc.) or a verb in the ‘ing’ form Despite their money, they can’t buy happiness. (noun phrase) Despite what I said last night, I still love you. (pronoun) In spite of having so much money, they can’t buy happiness. (verb in the ‘ing’ form) When & How Although/Even though/Though Followed by a clause/complete sentence with subject + verb Although she sang beautifully, she didn’t win the contest. I am going out tonight, even though I am tired. When & How Though Though is often used at the end of a sentence. The house isn’t very nice. I like the garden though. Compare although & in spite of/despite Although the traffic was bad, I arrived on time. In spite of the traffic, I arrived on time. I couldn’t sleep although I was very tired. I couldn’t sleep despite being very tired. Exercise 2 1. ________ it was raining, I didn’t use my umbrella. (although, despite) 2. I’d like to talk to you _______ I know you’re busy. (although, in spite of) 3. _______ her efforts, she failed the exam. (despite, although) 4. _______we were having difficulties, we felt optimistic. (although, in spite of) 5. We didn’t win the game ______ all our hard work. (although, in spite of) Exercise 2 1. Although it was raining, I didn’t use my umbrella. 2. I’d like to talk to you although I know you’re busy. 3. Despite her efforts, she failed the exam. 4. Although we were having difficulties, we felt optimistic. 5. We didn’t win the game in spite of all our hard work. When & How However/Nevertheless We can express a contrast by using the adverbs however/nevertheless with two sentences. They are always followed by a comma. She was feeling very ill. However, she went to school. You need some help with your homework. Nevertheless, no one can help you and you have to do it yourself. When & How Whereas/While Introduce a contrast between two ideas. The original movie was quite interesting, whereas the remake was really boring. Whereas you have lots of time to do your homework, I have very little time indeed. Exercise 3 1. _______ Andrew was warned of the risks, he decided to travel alone to South America. (although, whereas) 2. Maria did not get a promotion ________ her qualifications. (however, despite) 3. Zambia is a land-locked country, _________ Kenya has a coastline. (however, whereas) 4. The city has a 50 kph limit. ____________, people are often caught speeding. (however, whereas) 5. He is quiet and shy, ______ his sister is lively and talkative. (although, whereas) Exercise 3 1. Although Andrew was warned of the risks, he decided to travel alone to South America. 2. Maria did not get a promotion despite her qualifications. 3. Zambia is a land-locked country, whereas Kenya has a coastline. 4. The city has a 50 kph limit. However, people are often caught speeding. 5. He is quiet and shy, whereas his sister is lively and talkative. Examples For example – for instance Such as When & How For example – for instance – such as Each phrase can be used within a sentence: I can play quite a few musical instruments, for example, the flute, the guitar, and the piano. Colourful vegetables, for instance, bell peppers, contain vitamin C. She has many good qualities, such as intelligence and wit. Note: such as is not followed by a comma When & How For example – for instance – such as If the words after such as are necessary and essential to the meaning of the sentence – don’t use commas. Wild flowers such as mountain pansies and thyme are rapidly disappearing. If you take out such as mountain pansies and thyme the meaning will change – it could mean all wild flowers are disappearing - which is not true. When & How For example – for instance – such as For example and for instance can begin a new sentence when the phrase is followed by a complete idea or sentence: My father loves going to restaurants which serve exotic foods. For instance, last week he went to a restaurant which serves deep-fried rattlesnake. Adding a point Also As well - too Moreover, furthermore, in addition As well as When & How Also - as well – too Also occupies different positions in a sentence. It is placed after auxiliary verbs and before other verbs. Some tablet computers can also be used to make phone calls. I am not about to buy this house. It is small. Also, it needs a lot of repairs. She contacted him in the office but he didn’t answer the phone. His mobile phone was silent also. When & How Also - as well – too As well and too usually go at the end of a clause. She not only sings; she plays the piano as well. My brother not only goes to school; he works part time for a company too. When & How In addition - moreover – furthermore Moreover, furthermore and in addition add extra information to the point you are making and are followed by a comma: I studied journalism in college. In addition, I had a part-time job at a newspaper. We often use “moreover” and “furthermore” when we talk about our opinions: The politician is too old to be our president. Moreover, he is not trustworthy. When & How As well as As well as means not only ….but also. It is followed by a noun or noun phrase or a verb in the ‘ing’ form: She is not only beautiful, but also clever. = She is clever as well as beautiful. (noun) Running is healthy as well as making you feel good. (verb in the ‘ing’ form) Results & reasons Due to – owing to – on account of When & How Due to – owing to – on account of Due to, owing to and on account of mean because of. They are followed by nouns or noun phrases: The man was detained due to his suspicious behaviour. Owing to the heavy rain, we had to give up the idea of a boat trip. When & How Due to/ owing to/on account of the fact that Due to owing to/on account of the fact that are followed by a clause. I couldn’t study owing to the fact that I had an headache. Exercise 4 1. __________ staff shortages, there was no restaurant car on the train. (owing to, due to the fact that) 2. When they go to Austria, they like walking ________ skiing.(also, as well as) 3. Marketing plans give us an idea of the potential market. __________, they tell us about the competition. (moreover, owing to) 4. Vegetables __________ spinach contain calcium. (for instance, such as) 5. _____________ offering a 15% discount on the furniture, Smith’s Furniture delivered it free to our house.. (in addition, as well as) Exercise 4 1. Owing to staff shortages, there was no restaurant car on the train 2. When they go to Austria, they like walking as well as skiing. 3. Marketing plans give us an idea of the potential market. Moreover, they tell us about the competition. 4. Vegetables such as spinach contain calcium. 5. As well as offering a 15% discount on the furniture, Smith’s Furniture delivered it free to our house.. The End