LESSON 1: Biomacromolecules
advertisement

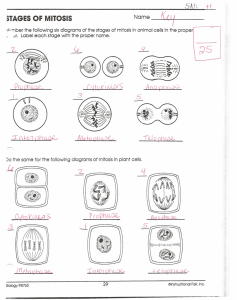
WEEK 5: Cell Replication LEARNING OUTCOMES By the end of this week, you should: Have a knowledge and understanding of the key aspects of mitosis and cytokinesis. Understand that mitosis and cytokinesis form only part of a complete cell cycle. Video clip How Do Cells Multiply? 1. 2. Copy the diagram. Write a short paragraph explaining in your words how you think cells multiply. Key terms Genetic information is contained in the DNA of the cell. DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. Most of the time, DNA is found in long fibres called CHROMATIN. Each long fibre makes up a CHROMOSOME (to get ready for cell division). GENES are small sections of chromosomes that contain the coded information for a specific protein that determines a cell function or characteristic. Why Do Cells Divide? 1) 2) 3) 4) To replace other cells that have worn out or damaged. To allow multi cellular animals to grow. For asexual reproduction. Because they get too big! The Cell Cycle What is Mitosis? 1. 2. Watch the introductory video Watch this animation and see if you can define what is happening Write your own definition of mitosis and be prepared to read it out to the rest of the class Use the following words to help: Nucleus, two, one, cell, chromosomes, identical, genetically, daughter Mitosis Definition Mitosis is the process in which one cell DIVIDES to make two new cells. Each cell has the SAME genetic material as the original cell. It is like “photocopying” the cell - they are IDENTICAL. STUFF TO DO! 1. Write a short description by each stage of mitosis on your sheet. 2. Label each stage with the correct name – use your textbook page 78 5 Cell membrane pinches in (cytokinesis), starting to enclose separated chromatids. 3 Chromosomes line up on the equator attached to the spindle fibres. 2 DNA is replicating and doubling, nucleus is growing. 6 Two identical daughter cells are formed. Mitosis has finished. 1 DNA chromatin condenses and forms into chromosomes. 4 Chromatids are pulled to opposite poles by the spindle fibres. Questions 1. 2. 3. Name three places where you would expect mitosis to occur in a growing plant. Name two places where you expect mitosis to occur in an adult human. When does mitosis occur in bacteria? What is this process called? Write 5 questions in relation to what you have learnt today, make all the answers either true of false then swap with at least one other person and mark theirs. Mitosis Melodies Are you finding the stages of the cell cycle difficult to remember? Perhaps a little melody would help! It’s always easy to remember the words to a song! In group of 4, you will compose a mitosis melody! Be sure to include all of the stages of the cell cycle and all of the major events in each stage. How to get started….. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Choose a well known melody. For example…”Twinkle, Twinkle Little Star” or “Jingle bells” Then, make up words to each verse that describe the stages of mitosis EgThere was a human that had a cell And division was its game-o P-M-A-T-C, P-M-A-T-C, P-M-A-T-C And that’s how it divided! Write out the words to your song (include the melody) For bonus marks...and for fun….perform the song for the class and get everyone to sing along! Evaluation- /15 marks Content- 10 marks Does your song describe the major events of all stages of mitosis? Creativity- 5 marks Is your song creative and fun to sing along to? Bonus- 3 marks (That’s 20% of the total mark!) for performing your melody! Anagrams Race! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. SEAPANAH CLEYC ELLC MESOMOOCH PHATSEELO ROPESHAP HOOLGOOMUS TEEMRORENC TROAMDICH IDOLDIP SAPHERTINE EATHAMPES SITMOSI 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. ANAPHASE CELL CYCLE CHROMOSOMES TELOPHASE PROPHASE HOMOLOGOUS CENTROMERE CHROMATID DIPLOID INTERPHASE METAPHASE MITOSIS