12 Unit 3 Study Guide, anatomy, SC
advertisement
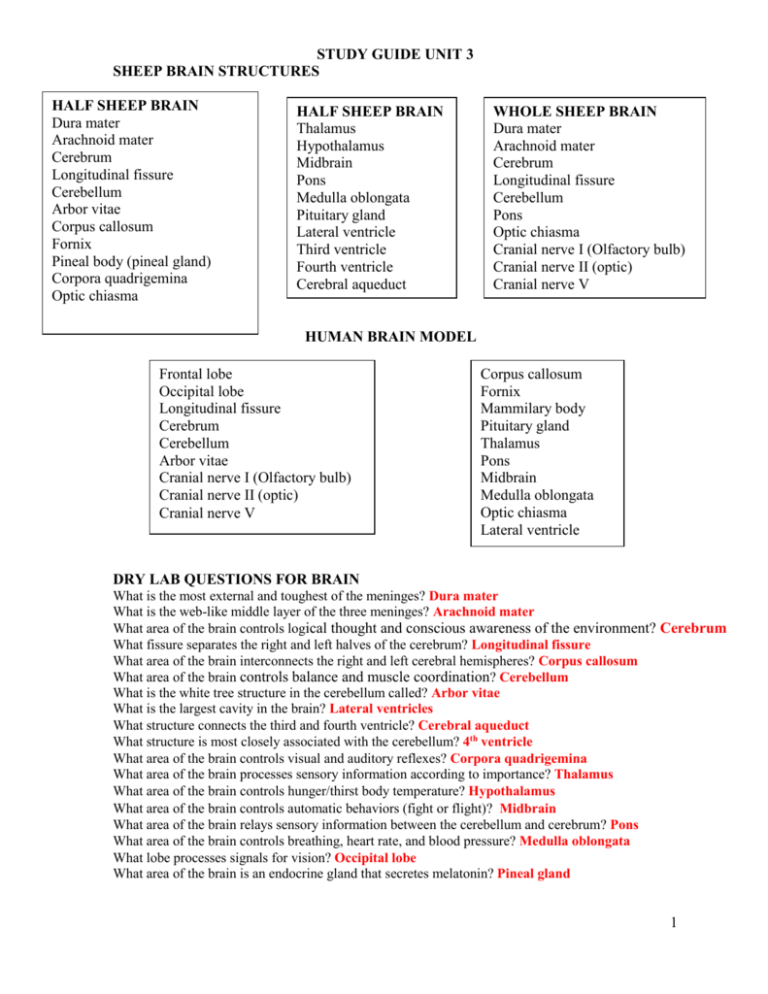
STUDY GUIDE UNIT 3 SHEEP BRAIN STRUCTURES HALF SHEEP BRAIN Dura mater Arachnoid mater Cerebrum Longitudinal fissure Cerebellum Arbor vitae Corpus callosum Fornix Pineal body (pineal gland) Corpora quadrigemina Optic chiasma HALF SHEEP BRAIN Thalamus Hypothalamus Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Pituitary gland Lateral ventricle Third ventricle Fourth ventricle Cerebral aqueduct Pineal gland WHOLE SHEEP BRAIN Dura mater Arachnoid mater Cerebrum Longitudinal fissure Cerebellum Pons Optic chiasma Cranial nerve I (Olfactory bulb) Cranial nerve II (optic) Cranial nerve V HUMAN BRAIN MODEL Frontal lobe Occipital lobe Longitudinal fissure Cerebrum Cerebellum Arbor vitae Cranial nerve I (Olfactory bulb) Cranial nerve II (optic) Cranial nerve V Corpus callosum Fornix Mammilary body Pituitary gland Thalamus Pons Midbrain Medulla oblongata Optic chiasma Lateral ventricle DRY LAB QUESTIONS FOR BRAIN What is the most external and toughest of the meninges? Dura mater What is the web-like middle layer of the three meninges? Arachnoid mater What area of the brain controls logical thought and conscious awareness of the environment? Cerebrum What fissure separates the right and left halves of the cerebrum? Longitudinal fissure What area of the brain interconnects the right and left cerebral hemispheres? Corpus callosum What area of the brain controls balance and muscle coordination? Cerebellum What is the white tree structure in the cerebellum called? Arbor vitae What is the largest cavity in the brain? Lateral ventricles What structure connects the third and fourth ventricle? Cerebral aqueduct What structure is most closely associated with the cerebellum? 4th ventricle What area of the brain controls visual and auditory reflexes? Corpora quadrigemina What area of the brain processes sensory information according to importance? Thalamus What area of the brain controls hunger/thirst body temperature? Hypothalamus What area of the brain controls automatic behaviors (fight or flight)? Midbrain What area of the brain relays sensory information between the cerebellum and cerebrum? Pons What area of the brain controls breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure? Medulla oblongata What lobe processes signals for vision? Occipital lobe What area of the brain is an endocrine gland that secretes melatonin? Pineal gland 1 SPINAL CORD MODEL AND PHOTO White matter (contains myelinated nerve axons) Grey matter (contains nerve cell bodies) Ventral horn Dorsal horn Ventral root (ramus) Dorsal root (ramus) Dorsal root ganglion Anterior median fissure Posterior median sulcus Central canal Dura mater (model only) Sympathetic trunk ganglion (model only) NERVE HISTOLOGY (WE WILL GO OVER THIS IN UNIT 4) Neuron PERIPHERAL NERVES (Extra credit) Axillary, radial, musculocutaneus, ulnar, median, Sciatic, femoral, Common fibular, superficial fibular, deep fibular, tibial STRUCTURES TO KNOW ON THE SHEEP HEART TISSUE LAYERS OF THE HEART A. myocardium B. endocardium C. visceral pericardium STRUCTURES 1. Apex 2. Interventricular septum (IV septum) 3. Left ventricle 4. Right ventricle 5. Right atrium 6. Left atrium 7. Papillary muscles 8. Chordae tendinae 9. Tricuspid valve 10. Mitral valve (bicuspid valve) 11. Trabeculae carni 12. Aortic semilunar valve 2 STRUCTURES ON THE PLASTIC AND PLASTER HUMAN HEART MODELS TISSUE LAYERS OF THE HEART A. myocardium B. endocardium C. visceral pericardium PLASTIC HEART VESSELS PLASTIC HEART STRUCTURES A. pulmonary trunk B. pulmonary veins (there are four) C. pulmonary arteries D. right coronary artery E. left coronary artery F. Circumflex artery G. Coronary sinus H. posterior interventricular artery I. anterior interventricular artery J. Right Brachiocephalic K. Right subclavian L. Right common carotid M. Left common carotid N. Left subclavian O. aorta P. superior vena cava Q. inferior vena cava 1. Apex 2. Interventricular septum (IV septum) 3. Left ventricle 4. Right ventricle 5. Right atrium 6. Left atrium 7. Atrial septum 8. Chordae tendinae 9. Trabeculae carni 10. Mitral valve (bicuspid valve) 11. Tricuspid valve 12. Pulmonary semilunar valve 13. Aortic semilunar valve 14. Auricle PLASTER HEART PLASTIC HEART PLASTER HEART STRUCTURES Right atrium Apex Auricle Pulmonary trunk Pulmonary semilunar valve Aortic semilunar valve Coronary sinus Note: These are the only structures you need to know on the plaster heart. 3 EYE MODELS PLASTIC EYE Sclera Cornea Pupil Lens Iris Retina Choroid layer Optic disc Ora serrata Cilliary body PLASTIC EYE Posterior cavity (do not call this the posterior chamber) Anterior cavity (do not call this the anterior chamber) Fovea centralis (area of the retina where light focuses) PLASTER EYE Lens Posterior cavity Ora serrata Cilliary body COW EYE Cornea Sclera Lens Retina Choroid layer . EAR MODEL External acoustic meatus (Auditory canal) Pinna Tympanum (tympanic membrane) Eustachian tube (function is to equalize pressure on both sides of the tympanic membrane) Semi-circular canal (function is for balance) Cochlea (function is for hearing) Vestibulocochlear nerve BLOOD CELLS (MICROSCOPE) Neutrophil Lymphocyte Monocyte BLOOD VESSELS (EXTRA CREDIT PHOTOS) Artery Vein Arteriole Venuole Capillary DRY LAB QUESTIONS Which fetal heart CHAMBER is where blood is most highly oxygenated? Right atrium Which fetal VESSEL is where blood is most highly oxygenated? Umbilical vein Which fetal vessel carries oxygenated blood from the placenta? Umbilical vein What is the hole between the fetal atria? Foramen ovale What is the foramen ovale called in adults? Fossa ovalis What is the connection between the pulmonary artery and the aorta? Ductus arteriosus What is the name for the venous vessel leading to the liver? Hepatic portal vein (not hepatic vein!) A portal system is a ________ system within the ________system Capillary/venous What does the term “common” mean in the circulatory system? That a vessel will branch into two other vessels with the same name. 4 VEINS IN THE CAT AND HUMAN MODELS NOTE: There are three types of jugular veins and three types of iliac veins in the cat. Do not just write “jugular” or “iliac” on the test! NOTE: There are three types of carotid arteries and three types of iliac arteries. Do not just write “carotid” or “iliac” on the test! NOTE: There are three types of aorta: aortic arch, thoracic aorta, and abdominal aorta. Do not just write “aorta” on the test! VEINS TO KNOW ON THE CAT SUPERIOR VENA CAVA INFERIOR VENA CAVA BRACHIOCEPHALIC SUBCLAVIAN AXILLARY BRACHIAL EXTERNAL JUGULAR INTERNAL JUGULAR TRANSVERSE JUGULAR MAXILLARY FACIAL SUPRASCAPULAR SUBSCAPULAR VERTEBRAL INTERNAL THORACIC (mammary) AZYGOUS SUPRARENAL RENAL GONADAL LUMBAR EXTERNAL ILIAC INTERNAL ILIAC MEDIAN SACRAL FEMORAL DEEP FEMORAL GREAT SAPHENOUS POPLITEAL ARTERIES TO KNOW ON THE CAT BRACHIOCEPHALIC SUBCLAVIAN AXILLARY BRACHIAL COMMON CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID MAXILLARY FACIAL INTERNAL THORACIC (mammary) SUPRASCAPULAR SUBSCAPULAR VERTEBRAL THORACIC AORTA POSTERIOR INTERCOSTALS ABDOMINAL AORTA CELIAC TRUNK SUPERIOR MESENTERIC INFERIOR MESENTERIC SUPRARENAL RENAL GONADAL LUMBAR EXTERNAL ILIAC INTERNAL ILIAC MEDIAN SACRAL FEMORAL DEEP FEMORAL SAPHENOUS POPLITEAL 5 FLAT MAN VESSELS Aortic Arch Brachiocephalic Vein Subclavian A/V Axillary A/V Brachial A/V Common Carotid External Jugular Vein Abdominal Aorta Hepatic Artery Splenic Artery Superior Mesenteric Inferior Mesenteric Renal A/V Common Iliac Artery External Iliac Artery Internal Iliac Artery Femoral Artery Femoral Vein Saphenous Artery Greater Saphenous Vein Popliteal Artery Posterior Tibial artery Dorsalis pedis (artery) Radial artery SKULL MODEL ARTERIES Common Carotid External Carotid Internal Carotid Maxillary Facial Vertebral Circle Of Willis TORSO AND ½-SIZE MAN MODELS Aortic Arch Brachiocephalic Vein Subclavian Vein Common Carotid External Jugular Vein Posterior Intercostal A/V Abdominal Aorta Celiac Trunk Superior Mesenteric Inferior Mesenteric Suprarenal Vein Renal Artery Renal Vein Common Iliac Artery Common Iliac Vein External Iliac Artery Internal Iliac Artery Internal Iliac Vein Femoral A/V Median sacral artery HEPATIC PORTAL VEIN (Don’t ID, just know this is the major vein leading into the liver REPRODUCTIVE MODEL ARTERIES Abdominal aorta Gonadal artery Internal iliac artery External iliac artery Inferior mesenteric artery 6 THESE ARE THE HUMAN MODELS YOU NEED TO KNOW VESSELS ON FLAT MAN (look at both types) TORSO-1 SKULL TORSO-2 7 REPRODUCTIVE MODEL HALF-SIZE MAN MODEL 8




