PRIVILEGED CLASSES 1 ST Estate
advertisement

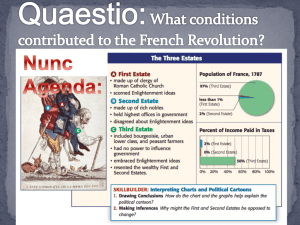
Absolute Monarchy 3 rigid classes: Estates 1st Estate – Clergy 2nd Estate – Nobles 3rd Estate – Commoners PRIVILEGED CLASSES 1ST Estate – Clergy Paid no taxes Wealthy Tithe Land 2nd Estate – Nobility Great wealth and Privileges Exempt from most taxes The Old Regime Underprivileged Classes Paid taxes in money, produce and labor The Third Estate Bourgeoisie (Middle Class) Wealthy, educated, & outspoken Lawyers, bankers, merchants and businessmen Sans Culottes (City Workers) Little education, little money Peasants (Largest Group) Heavy taxes Corvee – forced labor Political Cartoon These 18thc. Political cartoons show a peasant bearing on his and her back a clergyman and a noble. The policies cartoonist is making a bitter comment of the fact that peasants must pay taxes and other dues to support the church, the nobles, and the government, while the clergy and nobles were exempt from most taxes. The triangle represents number of people in each class. Huge Debts had accrued from Previous Rulers: Louis XIV Endless wars Versailles Lavish Spending brought France to the brink of Bankruptcy Louis XV Continued wars Refused to tax the nobility Louis XVI Appointed 2 finance ministers: Turgot and Necker Their solution: Tax the nobility Louis feared the nobles and dismissed Turgot and Necker 1788 France entered bankruptcy Louis called the Estates-General into session (Which had not met since 1614) Estates General – Meeting of Representatives from the 3 Estates 1st Estate 2nd Estate 3rd Estate Despite somewhat proportional representation the voting policy was unfair, with 1 vote per Estate. The Third Estate Demanded the Creation of the National Assembly – Each delegate = 1 vote Locked out of the meeting June 20, 1789 the delegates of the 3rd Estate assembled at an indoor tennis court and stayed until France had a Constitution July 14, 1789 Spurred by rumors– a Paris mob surrounded the Bastille. The Bastille was a prison for debtors and a symbol of the oppression of the Third Estate. Governor of Prison and mayor of Paris were killed and their heads were mounted on pikes and paraded through the city. This event symbolized the beginning of the French Revolution •Peasants started attacking the nobles homes throughout France •Nobles offered to pay taxes in order to end the violence October 5, 1789 Women from neighborhoods around the Bastille, gathered 10,000 people (mostly women) walked to Versailles Goal: to convince King to provide them with bread Louis greeted the women and promised them bread Just before midnight, Louis accepted a prior proposal by the nobles and clergy to the National Assembly What Enlightened ideas to you see? Which thinkers did they come from? End tax exemptions of the privileged classes End payment of feudal dues by the peasants End the tithe End all class distinctions King and his family would be confined to Paris from this point on. Constitution of 1791: Limited Monarchy King remained but… 1. Could not propose laws 2. Only had temporary veto to block legislation What do you see in his face? Why? Separation of Powers 1. Legislative Which 2. Executive Philosophe 3. Judicial Promoted The Legislative Assembly 1. Passed nation’s laws 2. Members had to be property owners and elected by taxpaying citizens Who was being left out? This? Eastern European Powers feared the spread of the Revolution Declaration of Pillnitz Prussia and Austria threatened to use force to protect French Royal Family 1792 The 2 powers entered France August 10 – Paris mob This is how The British viewed the Incident. attacked the Tuileries Palace and Legislative Assembly Took King Captive Forced the Legislative Assembly to suspend the monarchy and draft a constitution to create a French republic Universal Manhood suffrage September 21, 1792 National Assembly declared France a Republic Louis XVI was put on trial for Treason – convicted January 21, 1793 Louis XVI was executed Louis’ execution is considered the beginning of the Radical Phase of the Revolution – the Sans Culottes took over the Revolution. Leaders of 12 member Committee 1. George Danton 2. Jean Paul Marat 3. Maximilien Robespierre Goal: protect Republic from foreign enemies compulsory military service created largest army ever seen in Europe Pushed invading forces (Austria and Prussia) back across the Rhine Turned attention to Domestic Enemies “Drunk with Power” Robespierre instituted the “Reign of Terror” September 1793 – July 1794 Committee arrested people they suspected of treason 20,000 – 40,000 were put to death by guillotine Marie Antoinette, was one victim Nobles and clergy went to guillotine Most victims however were commoners Ended with execution of Robespierre July 1794 After Robespierre – power passed to wealthy middle class National Convention created a new Constitution – The Constitution of 1795 Five Directors – The Directory – acted as the executive authority Incompetent and corrupt the new government could not solve the countries problems. 1799 The popular General Napoleon Bonaparte seized power.