Economic issues of the day: Inflation

Inflation: a sustained rise in the general level of prices of goods and service over a period of time.
Erodes the purchasing power of consumers.
Calculation using a price index.
• CPI
• PPI
CPI: measures changes in consumer prices.
Headline rate of inflation.
CPIX: CPI - interest rates on mortgage bonds.
PPI: consists of a ‘basket’ of local, exported and imported goods.
• No ‘average household’
• Selection of goods/services not always representative of entire population.
• Weighting may not be accurate
• Random sampling may not represent population as a whole.
Demand-pull inflation: total demand for goods and services exceeds total supply.
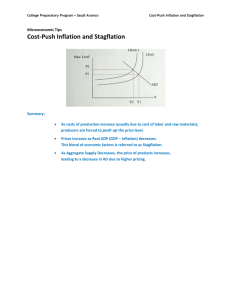
Cost-push inflation: due to increases in the costs of factors of production, such wages & raw materials.
Stagflation: persistent high inflation, a slowing economic growth rate and high unemployment.
Difficult for economic policy because:
• to lower inflation (↑ IR’s) → higher unemployment
• increasing employment → higher inflation
Hyperinflation: extravagant and unrestrained general price increases in excess of 50% per month.
650 million googol per cent
6,5 × 10 108 per cent or 65 followed by 107 zeros
government creates money to pay for its expenses causes further acceleration in prices.
currency loses its real value very quickly people quickly spend whatever they receive as the value decreases prices increase dramatically
Cause by factors that ↑ C, I, G (X-M)
Moneterists: ↑ in money supply main cause
Keynsians: Inability of increase output to meet the increased demand
Caused by increase in…
• Imported raw materials and capital equipment
(weak rand)
• price of oil
• Increased labour costs (wage increases > productivity increases
• Rise in interest rates
• Increase in taxes
Negative impact on economic growth.
Discourages savings & investments
Real value of money and savings decreases
5% interest - 8% inflation rate = real rate of interest of –3%.
Balance of payments
Prices of exported goods increase & imported goods decrease
Loss of export competitiveness → unemployment.
Redistribution of income in a country
Low-income groups more affected
• No assets that to rise faster than inflation
• poor wage bargaining power
Causes further inflation
Higher wage demands cause producers to increase their prices to maintain their profits…
Volatility of inflation not good for investment
Higher than EU & USA therefore SA’s prices rise faster than trading partners ↓ competitiveness.
Dealing with demand-pull inflation
Restrictive fiscal policy
↑ taxes
↓ gov spending
Restrictive monetary policy
↑ interest rates
Dealing with cost-push inflation
• compulsory measures to contain wage and price increases.
• polices aimed at increasing productivity
– tax rebates/subsidies for workplace education & technology.
Adopted in 2000
Inflation target set MPC (Gill and Pravin)
3% - 6%
SARB committed to achieve this
Policy instrument = repo rate
MPC meets every 3 months – public information
Accountable to parliament