Fingerprint powerpoint
advertisement

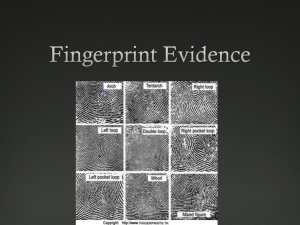
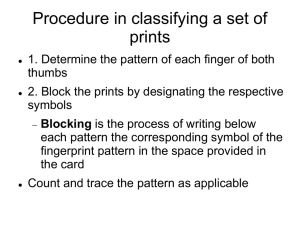
Fingerprints Background Information Each fingerprint is made up of friction ridges, that do not change over time (unless scarring occurs) Fingerprints are formed in the womb Each fingerprint is a deposit of wastes when a person comes in contact with a surface 98 % is water & salts, 1% oils, 1% amino acids Prints at a Crime Scene Divided into 3 types Patent Print Plastic Print Latent Print Patent Print Can be seen with the naked eye Made by a hand that had blood, grease, oil, or any other sticky substance on it Plastic Print Visible to the naked eye Formed when an impression is made in a soft substance such as putty, glue, dust, or butter Latent Print Most common type Cannot be seen without applying powder or chemicals Substances adhere to the amino acids or oils in the fingerprint and make it visible Patterns of Fingerprints 3 basic types of patterns Arch : 5% of population Loop : 65% of population Whorl : 30% of population Basic Fingerprints ARCH LOOP WHORL Plain Arch Left Radial Loop Left Ulnar Loop Plain Whorl Tented Arch Right Radial Loop Right Ulnar Loop Central Loop Whorl Double Loop Whorl Accidental Whorl The Arch Formed when the ridge lines go from one side, rises in the middle, and leaves on the other side (like a wave) Tented arches are more pointed No ridgecount Example of Arch The Loop Ridge lines enters & exits on the same side of the finger Type is determined by the direction the ridges come & leaves If it is from the thumb-side of the finger, it is called a RADIAL LOOP If it is from the little finger side it is called an ULNAR LOOP Examples of Loops The Delta Whorls are subdivided using a ridge characteristic called a DELTA DELTA: Triangle pattern (ridge forks & nearby ridge) Whorls have 2 deltas, loops have 1 delta & arches have 0 deltas The Whorl Ridge Characteristics BIFURCATION (or fork): ridge splits into 2 friction ridges ENCLOSURE: forms an oval ENDING RIDGES: ridges that stop abruptly Ridge Characteristics Continued SHORT RIDGES: begin & end abruptly, traveling a short distance RIDGE DOT: isolated ridge that’s length is approximately its width Examples of Ridge Characteristics Identifying Fingerprints 8-12 points of comparison must be in common to declare the 2 prints a match When a partial print is available, as many characteristics must be matched as possible Characteristics can be matched to the AFIS (Automated Fingerprint Identification System) Example of Positive ID Dusting for FIngerprints NONPOROUS SURFACES WOOD METAL PLASTIC GLASS TILE Chemically Fingerprinting Cyanoacrylate (Superglue), Iodine, Ninhydrin POROUS SURFACES PAPER UNFINISHED WOOD WALLPAPER









![PERSONAL IDENTIFICATION by MMA [Autosaved] [Autosaved] [Autosaved] [Autosaved]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/027020948_1-437ecadf3b2e4350cb31722e4d8851f6-300x300.png)